Mixed media art combines various materials such as paint, paper, fabric, and found objects to create unique, textured compositions that push traditional boundaries. This versatile approach encourages experimentation and allows artists to express complex ideas through layered storytelling and visual depth. Discover how mixed media can transform your creative projects by exploring the techniques and inspirations detailed in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
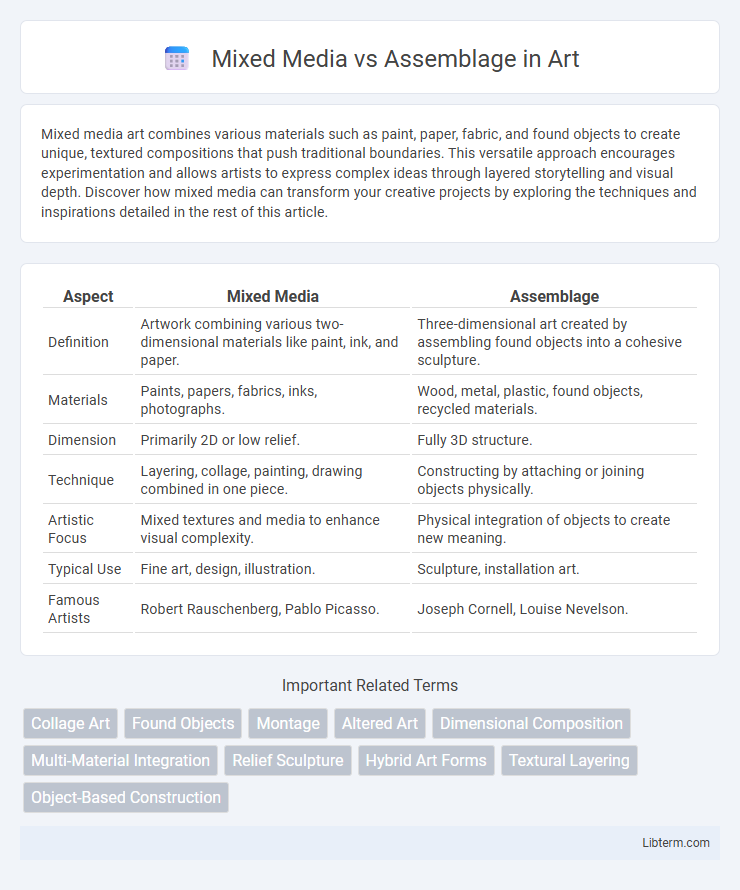
| Aspect | Mixed Media | Assemblage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Artwork combining various two-dimensional materials like paint, ink, and paper. | Three-dimensional art created by assembling found objects into a cohesive sculpture. |
| Materials | Paints, papers, fabrics, inks, photographs. | Wood, metal, plastic, found objects, recycled materials. |
| Dimension | Primarily 2D or low relief. | Fully 3D structure. |
| Technique | Layering, collage, painting, drawing combined in one piece. | Constructing by attaching or joining objects physically. |
| Artistic Focus | Mixed textures and media to enhance visual complexity. | Physical integration of objects to create new meaning. |
| Typical Use | Fine art, design, illustration. | Sculpture, installation art. |
| Famous Artists | Robert Rauschenberg, Pablo Picasso. | Joseph Cornell, Louise Nevelson. |
Introduction to Mixed Media and Assemblage
Mixed media art combines various materials such as paint, paper, fabric, and found objects to create layered, textured compositions that emphasize visual diversity and tactile interest. Assemblage is a specific form of mixed media focused on three-dimensional art constructed from pre-existing objects, often repurposed or discarded items, arranged to convey new meanings or narratives. Both techniques explore unconventional materials, but assemblage prioritizes sculptural form and spatial relationships while mixed media emphasizes two-dimensional or collage approaches.
Defining Mixed Media Art
Mixed media art combines various artistic materials and techniques within a single work, integrating mediums such as paint, ink, collage, and digital elements to create layered visual effects. This approach emphasizes the interplay of different textures and forms, allowing artists to experiment beyond traditional boundaries. Assemblage, a subset of mixed media, specifically involves constructing three-dimensional compositions from found or tangible objects, distinguishing itself through physical depth and sculptural qualities.
What Sets Assemblage Apart?
Assemblage distinguishes itself from mixed media by its three-dimensional construction, combining found objects and materials into sculptural artworks rather than just layering diverse mediums on a flat surface. This technique emphasizes tactile interaction and spatial relationships, often incorporating everyday items to create immersive, tangible compositions. Unlike mixed media, which primarily blends paints, papers, and inks, assemblage transforms disparate objects into a cohesive, physical form, pushing boundaries between sculpture and collage.
Historical Origins of Both Techniques
Mixed media emerged in the early 20th century, popularized by artists such as Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque, who integrated various materials like paper, fabric, and paint to challenge traditional boundaries of painting and sculpture. Assemblage originated slightly later, in the 1950s, with artists like Joseph Cornell and Louise Nevelson creating three-dimensional compositions by assembling found objects and everyday materials. Both techniques reflect shifts in artistic practice towards experimentation and the incorporation of unconventional elements to expand artistic expression.
Techniques and Materials Used
Mixed media art incorporates various materials such as paint, ink, paper, fabric, and found objects combined on a single surface, allowing for layering and diverse textures. Assemblage specifically involves creating three-dimensional compositions by assembling everyday objects and scrap materials, often glued, nailed, or wired together to form a sculptural piece. Techniques in mixed media emphasize collage and surface manipulation, while assemblage techniques focus on construction, spatial arrangement, and the physical interaction of objects.
Key Differences in Artistic Approach
Mixed media involves combining various artistic materials such as paint, ink, and collage elements on a single surface to create layered visual effects. Assemblage, by contrast, is a three-dimensional art form that constructs sculptures from found objects and disparate materials, emphasizing physical depth and spatial relationships. The key difference lies in mixed media's two-dimensional integration of diverse mediums versus assemblage's sculptural synthesis of tangible components.
Influential Artists in Mixed Media and Assemblage
Influential artists in mixed media include Robert Rauschenberg, whose combines integrated painting and sculpture to challenge traditional boundaries, and Louise Nevelson, renowned for her monochromatic wooden assemblages. In assemblage, Joseph Cornell's intricate shadow boxes craft poetic narratives through found objects, while Edward Kienholz's environmental installations confront social issues with raw, immersive elements. Both art forms emphasize the transformative use of materials, with mixed media blending diverse mediums and assemblage assembling three-dimensional objects into cohesive artworks.
Visual Impact and Aesthetic Outcomes
Mixed media combines various materials such as paint, paper, fabric, and found objects to create layered textures and vibrant color contrasts, resulting in dynamic visual impact and diverse aesthetic outcomes. Assemblage primarily involves three-dimensional construction from found objects and sculptural elements, emphasizing depth, shadow, and physicality for a tactile and immersive viewer experience. Both approaches challenge traditional boundaries of art, but mixed media emphasizes surface complexity while assemblage showcases spatial composition and material juxtaposition.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Artwork
Mixed media involves combining various artistic materials such as paint, ink, and collage elements on a two-dimensional surface, emphasizing texture and layered effects. Assemblage utilizes three-dimensional, often found objects, arranged in a sculptural form to create a tactile, spatial composition. Selecting between mixed media and assemblage depends on your artwork's desired depth, interaction with space, and the tactile experience you want to convey to viewers.
Conclusion: Deciding Between Mixed Media and Assemblage
Choosing between mixed media and assemblage depends on the intended artistic expression and material interaction. Mixed media offers versatility through combining various two-dimensional and three-dimensional materials, fostering experimentation with textures and visual depth. Assemblage emphasizes three-dimensional composition by uniting found objects into cohesive sculptural art, prioritizing tactile experience and spatial relationships.
Mixed Media Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com