Abstract Expressionism revolutionized modern art by emphasizing spontaneous, automatic, or subconscious creation through bold brushstrokes and vibrant colors. This movement prioritized emotional intensity and individual expression over traditional forms and realism. Discover how Abstract Expressionism shaped contemporary art and what it means for Your appreciation of creative freedom in the following article.
Table of Comparison
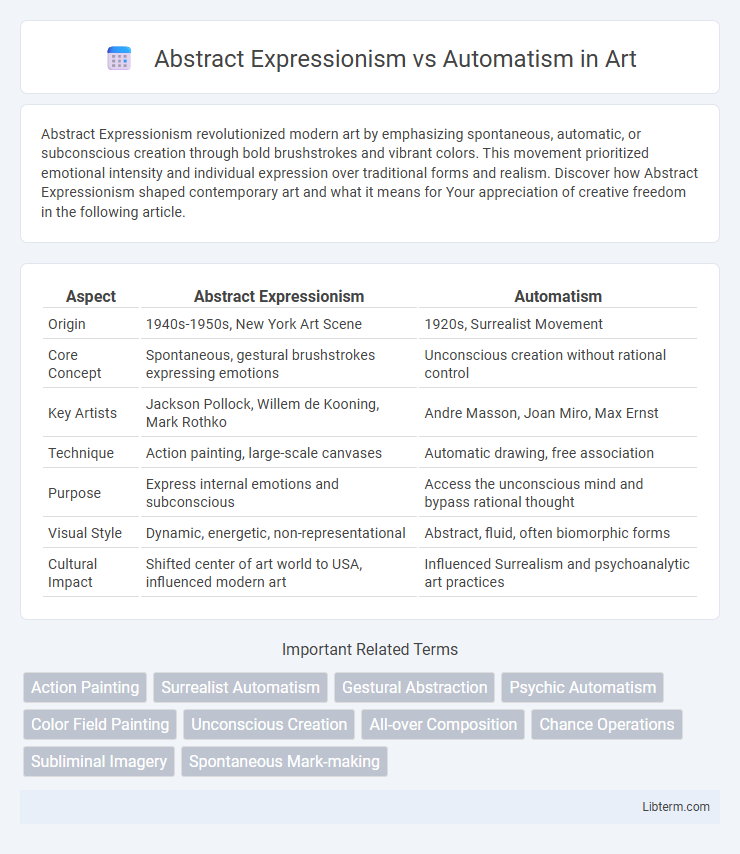
| Aspect | Abstract Expressionism | Automatism |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | 1940s-1950s, New York Art Scene | 1920s, Surrealist Movement |
| Core Concept | Spontaneous, gestural brushstrokes expressing emotions | Unconscious creation without rational control |
| Key Artists | Jackson Pollock, Willem de Kooning, Mark Rothko | Andre Masson, Joan Miro, Max Ernst |
| Technique | Action painting, large-scale canvases | Automatic drawing, free association |
| Purpose | Express internal emotions and subconscious | Access the unconscious mind and bypass rational thought |
| Visual Style | Dynamic, energetic, non-representational | Abstract, fluid, often biomorphic forms |
| Cultural Impact | Shifted center of art world to USA, influenced modern art | Influenced Surrealism and psychoanalytic art practices |
Introduction to Abstract Expressionism and Automatism
Abstract Expressionism emerged in the 1940s as a bold movement characterized by spontaneous, gestural brushstrokes and a focus on conveying emotional intensity through large-scale canvases. Automatism, rooted in Surrealist practices, involves creating art by tapping into the subconscious mind without rational control, encouraging unplanned and instinctive marks. Both methodologies prioritize the expression of inner experience but differ in execution, with Abstract Expressionism often emphasizing dynamic physicality and Automatism emphasizing subconscious impulses.
Historical Origins and Influences
Abstract Expressionism emerged in the 1940s in New York, heavily influenced by Surrealism, particularly its emphasis on subconscious creativity and psychological exploration. Automatism, pioneered by Surrealists like Andre Breton and Joan Miro in the 1920s, involved spontaneous, unplanned creation to tap into the unconscious mind. While Abstract Expressionism integrated automatist techniques, it expanded towards conveying intense emotion and individual expression through large-scale, gestural brushstrokes.
Key Philosophies and Ideologies
Abstract Expressionism emphasizes spontaneous, emotional expression and the subconscious mind, prioritizing individual creativity and the physical act of painting as a form of personal liberation. Automatism, rooted in Surrealism, focuses on accessing the unconscious through automatic, unplanned gestures without rational control, aiming to reveal hidden thoughts and desires. Both philosophies explore the unconscious but differ in their approach: Abstract Expressionism channels emotional intensity, while Automatism seeks pure psychic automatism as a pathway to deeper truths.
Prominent Artists and Their Contributions
Abstract Expressionism features prominent artists like Jackson Pollock, whose drip paintings revolutionized the art world with dynamic movement and emotional intensity. Automatism, a technique rooted in Surrealism, was chiefly practiced by Andre Masson, who used spontaneous drawing to access the unconscious mind and inspire creativity. Both movements significantly influenced modern art by emphasizing intuitive processes but diverged in their approaches: Abstract Expressionism embraced large-scale, gestural abstraction while Automatism prioritized subconscious imagery and free association.
Techniques and Processes Compared
Abstract Expressionism employs vigorous brushstrokes, large-scale canvases, and spontaneous, gestural application of paint to convey emotional intensity and individual expression. Automatism relies on subconscious creation through automatic drawing or painting, emphasizing uninhibited, free-flowing lines and shapes produced without conscious control to access the artist's inner psyche. Both techniques prioritize spontaneity, but Abstract Expressionism harnesses dynamic physical gestures, whereas Automatism seeks to bypass rational thought via subconscious impulses.
The Role of Spontaneity in Both Movements
Abstract Expressionism and Automatism both embrace spontaneity as a core element, with Abstract Expressionism emphasizing dynamic, gestural brushstrokes that capture the artist's immediate emotions and subconscious impulses. Automatism relies on automatic, unplanned actions such as spontaneous drawing or writing, aimed at bypassing conscious control to access the unconscious mind directly. The role of spontaneity in both movements challenges traditional artistic discipline by prioritizing instinct and raw expression over meticulously planned composition.
Emotional Expression vs. Subconscious Creation
Abstract Expressionism centers on intense emotional expression, channeling the artist's inner feelings through dynamic brushstrokes and vivid colors to evoke visceral responses. Automatism emphasizes subconscious creation, allowing spontaneous, unplanned gestures to bypass rational control and reveal hidden thoughts or emotions from the psyche. Both movements explore depth of human experience but differ in reliance on conscious emotional intent versus unconscious psychic emergence.
Impact on Contemporary Art
Abstract Expressionism revolutionized contemporary art by emphasizing spontaneous, expressive brushwork and large-scale canvases that conveyed intense emotions and personal freedom. Automatism, rooted in Surrealist practices, influenced contemporary art by encouraging subconscious creativity and unmediated expression through techniques like automatic drawing and writing. Both movements significantly shaped modern artistic exploration, fostering innovative approaches to abstraction and psychological depth in visual art.
Global Reach and Cultural Variations
Abstract Expressionism, originating in post-World War II New York, expanded globally with influential centers in Europe, Latin America, and Asia, adapting to regional cultural narratives and political climates. Automatism, rooted in Surrealist practices, found varied expressions across continents, reflecting indigenous spiritual traditions and subconscious explorations unique to cultures in Africa, South America, and Oceania. These movements illustrate dynamic cross-cultural dialogues, blending universal psychological motifs with localized artistic vocabularies that shaped global modern art development.
Legacy and Lasting Influence
Abstract Expressionism revolutionized modern art by emphasizing spontaneous, emotional expression and pioneering techniques such as gestural brushstrokes and large-scale canvases, profoundly influencing post-war artistic movements worldwide. Automatism, rooted in Surrealism, advanced the exploration of the subconscious through automatic drawing and writing, laying foundational practices for contemporary art therapy and experimental creativity. Both movements left lasting legacies by challenging traditional art forms and expanding the boundaries of artistic freedom and psychological depth in visual art.
Abstract Expressionism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com