Structural drawing provides detailed visual guidelines essential for the construction of buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure, ensuring safety and stability. These drawings specify materials, dimensions, and assembly instructions that guide engineers, architects, and contractors through the construction process. Explore the rest of this article to understand how structural drawings can optimize your project's accuracy and compliance.
Table of Comparison
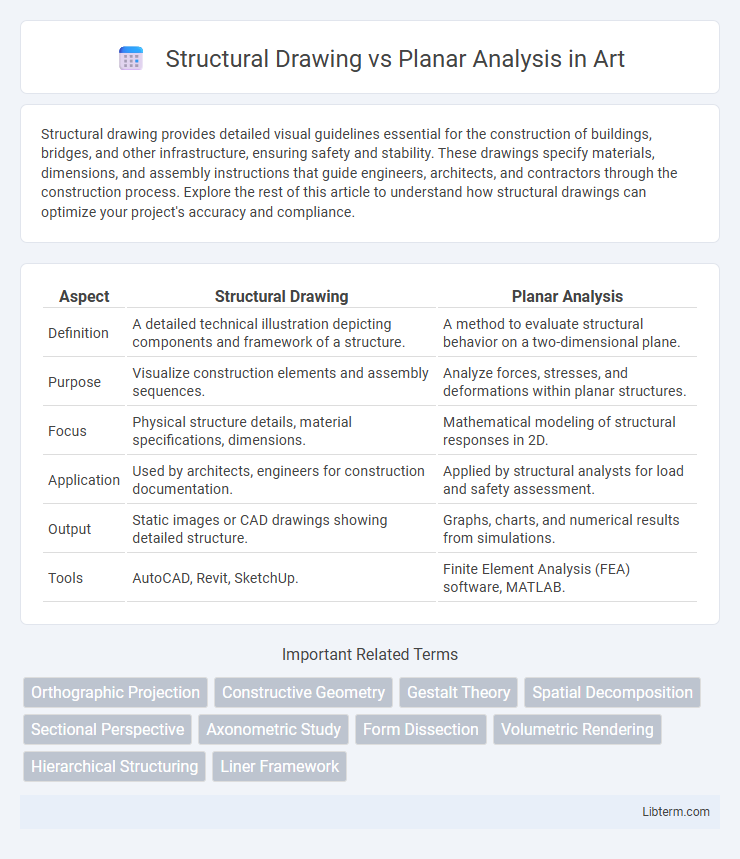
| Aspect | Structural Drawing | Planar Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A detailed technical illustration depicting components and framework of a structure. | A method to evaluate structural behavior on a two-dimensional plane. |
| Purpose | Visualize construction elements and assembly sequences. | Analyze forces, stresses, and deformations within planar structures. |
| Focus | Physical structure details, material specifications, dimensions. | Mathematical modeling of structural responses in 2D. |
| Application | Used by architects, engineers for construction documentation. | Applied by structural analysts for load and safety assessment. |
| Output | Static images or CAD drawings showing detailed structure. | Graphs, charts, and numerical results from simulations. |
| Tools | AutoCAD, Revit, SketchUp. | Finite Element Analysis (FEA) software, MATLAB. |
Introduction: Understanding Structural Drawing and Planar Analysis
Structural drawing visually represents the components and framework of a building or infrastructure, detailing beams, columns, and load paths essential for construction accuracy. Planar analysis, by contrast, is a computational technique that evaluates the structural behavior of two-dimensional planes, such as walls or slabs, under various load conditions to ensure safety and stability. Understanding the differences highlights the complementary roles of detailed design documentation and engineering simulations in structural engineering.
Definitions: What is a Structural Drawing?
A structural drawing is a detailed architectural diagram that illustrates the framework and support systems of a building, including beams, columns, and foundations. It serves as a blueprint for engineers and construction professionals to ensure the structural integrity and safety of the design. These drawings are essential for visualizing load-bearing components and verifying compliance with building codes and standards.
Definitions: What is Planar Analysis?
Planar analysis is a structural engineering method that evaluates the behavior of flat, two-dimensional frameworks under applied loads, focusing on forces, moments, and deformations within a single plane. It simplifies complex three-dimensional structures into planar models to facilitate accurate analysis of stress distribution and stability. This approach contrasts with structural drawing, which visually represents the design but does not inherently analyze the mechanical performance of the structure.
Key Differences Between Structural Drawing and Planar Analysis
Structural drawing provides a detailed graphical representation of building elements, showing dimensions, materials, and construction methods, while planar analysis is a computational evaluation technique used to assess the structural behavior of components within a flat plane under various loads. Structural drawing emphasizes the physical and architectural layout necessary for construction execution, whereas planar analysis focuses on understanding stress distribution, deformation, and stability of planar structural elements. The key differences lie in structural drawing's role in documentation and construction guidance versus planar analysis's application in engineering validation and design optimization.
Purpose and Applications in Engineering
Structural drawing serves as a detailed graphical representation of building components, illustrating dimensions, materials, and assembly instructions essential for construction and fabrication. Planar analysis evaluates two-dimensional structural elements under various loads, determining stress distribution and deformation to ensure stability and safety in engineering designs. While structural drawings guide the physical realization of structures, planar analysis provides critical data for optimizing design efficiency and verifying compliance with engineering standards.
Essential Elements of Structural Drawings
Structural drawings include detailed essential elements such as dimensions, material specifications, load-bearing components, reinforcement details, and connection methods that ensure accurate representation of a building's framework. These drawings serve as a comprehensive guide for construction, highlighting beams, columns, slabs, and foundation layouts critical for structural integrity. Planar analysis focuses more on evaluating the behavior of structural elements in two dimensions, but lacks the detailed construction elements crucial in structural drawings.
Components and Techniques of Planar Analysis
Planar analysis involves examining structural components such as beams, slabs, and frames within a two-dimensional plane to assess forces, moments, and deformation accurately. Techniques used include finite element modeling for stress distribution, matrix stiffness methods for component interaction, and load path analysis to ensure structural integrity under various conditions. These methods enable precise evaluation of planar elements, contrasting with structural drawing's role in visually representing the design and connectivity of these components.
Accuracy and Detailing: Structural Drawing vs Planar Analysis
Structural drawing offers detailed, scaled representations of building components, ensuring precise visualization of load-bearing elements and connections critical for construction accuracy. Planar analysis focuses on evaluating stress, strain, and deformation within specific planes of a structure, providing essential data for structural integrity assessments but lacks the comprehensive detailing found in structural drawings. Combining both enhances design validation by integrating exact geometric detailing with analytical depth for accurate engineering decisions.
Integration in Construction and Design Projects
Structural drawing serves as a detailed blueprint representing the framework of a building, while planar analysis focuses on evaluating force distribution and stability within two-dimensional sections. Integration of structural drawings with planar analysis enhances accuracy in load calculations and optimizes design efficiency, ensuring safer and more cost-effective construction projects. Effective collaboration between architects and structural engineers during this integration streamlines project workflows and minimizes errors during execution.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Structural drawing provides detailed visualization of an object's components, essential for precise construction and fabrication. Planar analysis simplifies complex structures into two-dimensional planes to assess stress, strain, and load distribution efficiently. Selecting the right approach depends on project requirements: use structural drawing for exact design specifications and planar analysis for rapid evaluation of structural integrity under various conditions.
Structural Drawing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com