Polymer glaze offers a durable, glossy finish that enhances the appearance and protection of various surfaces. This versatile coating resists scratches, chemicals, and weathering, making it ideal for automotive, furniture, and industrial applications. Discover how polymer glaze can transform your projects by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
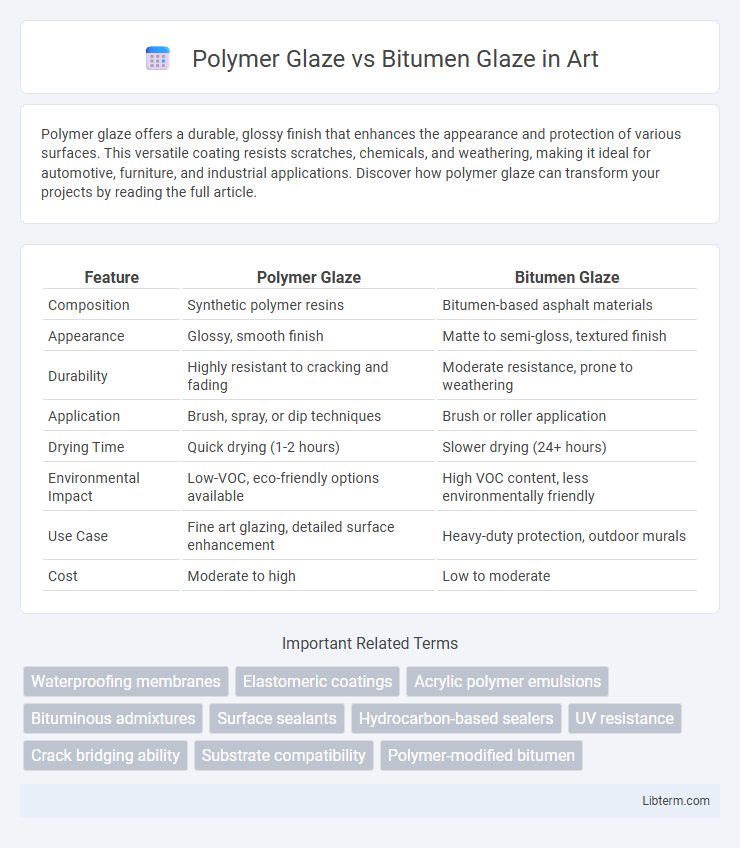
| Feature | Polymer Glaze | Bitumen Glaze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Synthetic polymer resins | Bitumen-based asphalt materials |
| Appearance | Glossy, smooth finish | Matte to semi-gloss, textured finish |
| Durability | Highly resistant to cracking and fading | Moderate resistance, prone to weathering |
| Application | Brush, spray, or dip techniques | Brush or roller application |
| Drying Time | Quick drying (1-2 hours) | Slower drying (24+ hours) |
| Environmental Impact | Low-VOC, eco-friendly options available | High VOC content, less environmentally friendly |
| Use Case | Fine art glazing, detailed surface enhancement | Heavy-duty protection, outdoor murals |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Polymer Glaze and Bitumen Glaze
Polymer glaze consists of synthetic polymers designed to provide a durable, weather-resistant coating with enhanced flexibility and UV protection, making it ideal for surfaces requiring long-term resilience. Bitumen glaze is derived from natural or refined asphalt, offering excellent waterproofing and adhesion properties primarily used in roofing and construction applications. Both coatings serve protective functions, but polymer glaze typically outperforms bitumen in elasticity and environmental resistance.
Composition and Chemical Properties
Polymer glaze consists primarily of synthetic polymers such as acrylics or urethanes, offering superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and UV stability. Bitumen glaze is composed mainly of bituminous materials derived from crude oil, characterized by excellent waterproofing, high adhesion to substrates, and resistance to moisture but limited UV resistance. The chemical properties of polymer glaze provide enhanced durability and elasticity compared to the more rigid, hydrocarbon-based bitumen glaze, making polymers more suitable for applications requiring long-term exposure to harsh environmental conditions.
Application Areas and Usage
Polymer glaze is primarily used in automotive refinishing and industrial coating applications due to its superior UV resistance, flexibility, and chemical durability, making it ideal for exterior surfaces exposed to harsh weather conditions. Bitumen glaze finds extensive use in waterproofing, roofing, and road construction, as it provides excellent adhesion to porous materials and strong moisture barrier properties. While polymer glaze excels in protective finishes for plastics and metals, bitumen glaze is preferred for infrastructure projects requiring robust waterproof seals and corrosion protection.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Polymer glaze offers superior durability due to its enhanced flexibility and resistance to UV radiation, making it ideal for long-term exposure without cracking or peeling. Bitumen glaze provides excellent waterproofing and adhesion properties but tends to degrade faster under harsh weather conditions, leading to potential brittleness and reduced lifespan. The performance of polymer glaze generally surpasses bitumen glaze in maintaining structural integrity and aesthetic appeal over time, especially in environments with fluctuating temperatures and moisture levels.
Weather Resistance and Longevity
Polymer glaze offers superior weather resistance due to its flexible, UV-resistant properties that prevent cracking and fading over time, making it ideal for areas with harsh sunlight and temperature fluctuations. Bitumen glaze, while effective at providing waterproofing, tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to UV rays and extreme weather, leading to brittleness and reduced durability. Consequently, polymer glaze typically ensures longer longevity and sustained protection on surfaces compared to bitumen glaze.
Installation Process and Techniques
Polymer glaze involves a precise application of synthetic resins that require clean, dry surfaces and controlled curing conditions, ensuring strong adhesion and flexibility. Bitumen glaze installation relies on heating bitumen to a liquid state before spreading it evenly, demanding careful temperature management to avoid degradation and ensure waterproof sealing. Both techniques necessitate skilled labor, but polymer glaze offers faster curing times and easier handling compared to the heat-dependent, labor-intensive bitumen application.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polymer glaze offers superior environmental benefits compared to bitumen glaze due to its lower volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and enhanced biodegradability, minimizing air and soil pollution. Bitumen glaze, derived from petroleum products, poses sustainability challenges with high carbon footprints and limited recyclability, contributing significantly to non-renewable resource depletion. Choosing polymer glaze supports sustainable construction by promoting eco-friendly materials and reducing harmful environmental impacts associated with traditional bitumen-based glazing solutions.
Cost Analysis and Economic Benefits
Polymer glaze typically incurs higher initial costs compared to bitumen glaze due to advanced material composition and application techniques. Despite the upfront investment, polymer glaze offers superior durability and longer lifespan, reducing maintenance and replacement expenses over time. Bitumen glaze presents a cost-effective option for budget-sensitive projects but may require more frequent repairs, impacting long-term economic benefits.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifespan
Polymer glaze offers superior durability and requires minimal maintenance due to its resistance to cracking, fading, and UV damage, extending its lifespan up to 20 years. Bitumen glaze demands more frequent inspections and maintenance to prevent degradation from weather exposure, typically lasting around 10 to 15 years. Choosing polymer glaze reduces long-term upkeep costs and enhances surface protection compared to bitumen glaze.
Choosing the Right Glaze for Your Project
Polymer glaze offers superior flexibility and UV resistance, making it ideal for outdoor or high-traffic areas, while bitumen glaze excels in waterproofing and adhesion on roofing materials. Selecting the right glaze depends on project requirements such as durability, environmental exposure, and substrate compatibility. Understanding these key differences ensures optimal protection and longevity for construction or renovation projects.
Polymer Glaze Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com