Shellac is a natural resin secreted by the lac bug, commonly used as a wood finish and food glaze due to its glossy, protective properties. Its eco-friendly and non-toxic nature makes it a popular choice for sealing, varnishing, and coating various surfaces while enhancing durability and aesthetic appeal. Explore the rest of this article to discover the diverse applications and benefits of shellac for your projects.
Table of Comparison
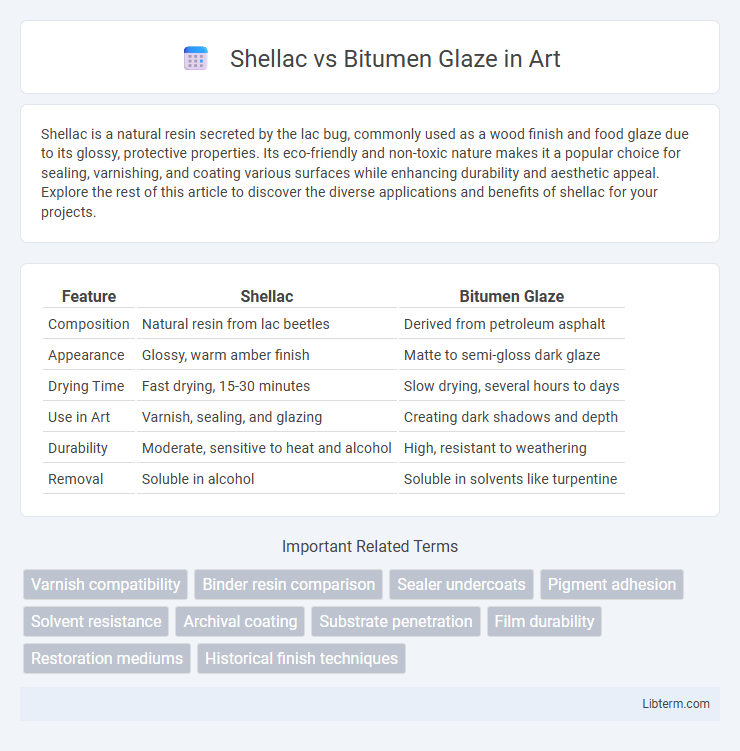
| Feature | Shellac | Bitumen Glaze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Natural resin from lac beetles | Derived from petroleum asphalt |
| Appearance | Glossy, warm amber finish | Matte to semi-gloss dark glaze |
| Drying Time | Fast drying, 15-30 minutes | Slow drying, several hours to days |
| Use in Art | Varnish, sealing, and glazing | Creating dark shadows and depth |
| Durability | Moderate, sensitive to heat and alcohol | High, resistant to weathering |
| Removal | Soluble in alcohol | Soluble in solvents like turpentine |
Introduction to Shellac and Bitumen Glaze
Shellac is a natural resin secreted by the lac bug, widely used as a wood finish due to its high gloss and quick drying properties, enhancing surface durability and aesthetic appeal. Bitumen glaze, derived from petroleum, serves as a protective coating with excellent waterproofing and corrosion-resistant qualities, commonly applied in industrial and roofing contexts. Both materials offer distinct advantages in sealing and protecting surfaces, with shellac favored for interior wood finishes and bitumen glaze preferred for heavy-duty waterproofing applications.
Composition and Chemical Properties
Shellac is a natural resin secreted by the lac bug, primarily composed of aleuritic acid and shellolic acid, making it a durable, alcohol-soluble film-former with excellent adhesion and moisture resistance. Bitumen glaze consists of asphaltic compounds derived from petroleum, characterized by its high viscosity, hydrophobicity, and thermoplastic properties, providing superior waterproofing and UV resistance. The chemical stability of shellac reduces under alkaline conditions, while bitumen exhibits strong chemical inertness, maintaining performance under extreme temperatures and harsh environmental exposure.
Application Techniques Compared
Shellac requires precise brushing techniques for an even, smooth finish and must be applied in thin, multiple coats to avoid streaks and bubbles, typically using natural bristle brushes or pads. Bitumen glaze is applied with a trowel or brush and is valued for its thicker, more durable coverage, often used to waterproof and protect surfaces with fewer layers needed. Shellac dries rapidly, necessitating quick, skillful application, while bitumen glaze cures more slowly, allowing time for texture adjustment and thickness control.
Aesthetic Effects and Finishes
Shellac provides a warm, amber finish that enhances wood grain with a smooth, glossy sheen, making it ideal for fine furniture and decorative projects. Bitumen glaze offers a deep, rich appearance with a matte to semi-gloss finish, often used to create an antique or rustic effect on surfaces. Both materials deliver distinct aesthetic effects; shellac highlights natural textures, while bitumen glaze adds depth and aged character.
Durability and Longevity
Shellac offers moderate durability with a smooth, glossy finish but is prone to damage from heat and moisture, reducing its longevity in high-traffic or outdoor environments. Bitumen glaze provides superior durability and excellent resistance to water, chemicals, and extreme weather, making it ideal for long-lasting protective coatings on metal and concrete surfaces. The longevity of bitumen glaze typically surpasses shellac by several years, especially in harsh conditions where moisture and wear are prevalent.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Shellac is a natural resin derived from lac bugs, making it biodegradable and non-toxic, which reduces environmental harm and health risks during application. Bitumen glaze, made from petroleum derivatives, poses greater environmental hazards due to its non-biodegradable nature and toxic emissions when heated or applied. Shellac offers safer indoor air quality and minimal ecological footprint compared to the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released by bitumen glazes.
Cost and Availability
Shellac is generally more expensive than bitumen glaze due to its natural resin content and complex production process, often priced between $10 to $20 per quart, whereas bitumen glaze is more affordable, typically costing $5 to $10 per gallon. Shellac is widely available in hardware stores and specialty paint shops, favored for its quick drying time and glossy finish, but bitumen glaze is commonly found in industrial suppliers and used for waterproofing and protective coatings. Bitumen's availability in larger volumes makes it cost-effective for extensive applications, while shellac suits smaller, decorative projects requiring fine detail.
Common Uses in Art and Industry
Shellac is commonly used in fine art for wood finishing and as a protective coating due to its glossy appearance and quick drying time, making it ideal for furniture restoration and musical instruments. Bitumen glaze is frequently applied in industrial contexts such as waterproofing, corrosion protection, and as a base for road construction because of its strong adhesive properties and durability. Both materials serve protective and aesthetic functions, with shellac favored for delicate surfaces and bitumen preferred for heavy-duty applications.
Maintenance and Removal
Shellac provides easier maintenance due to its quick drying time and water-resistant properties, allowing for simple cleaning with mild soap and water. Bitumen glaze, being oil-based and thicker, requires solvents like turpentine or mineral spirits for effective removal, making its maintenance more labor-intensive. Regular upkeep of shellac surfaces involves minimal abrasion, while bitumen glazed surfaces may need periodic reapplication and careful removal to avoid surface damage.
Choosing Between Shellac and Bitumen Glaze
Choosing between shellac and bitumen glaze depends on the desired finish and application environment. Shellac provides a smooth, glossy surface ideal for indoor wood projects, offering excellent adhesion and fast drying times. Bitumen glaze, known for its water resistance and durability, is better suited for outdoor use and protection against harsh weather conditions.
Shellac Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com