Tenebrism is a dramatic painting style characterized by stark contrasts between light and dark, emphasizing intense shadows to create a sense of volume and depth. This technique, popularized during the Baroque period, highlights illuminated subjects against dark backgrounds, evoking strong emotional responses. Discover how tenebrism can transform your understanding of art by exploring its origins and notable examples in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
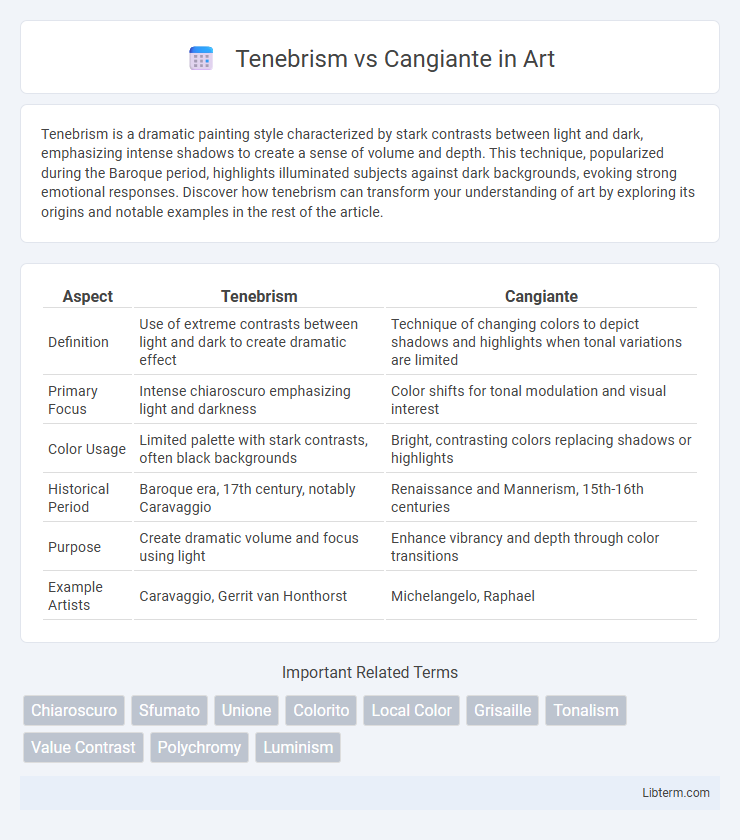
| Aspect | Tenebrism | Cangiante |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of extreme contrasts between light and dark to create dramatic effect | Technique of changing colors to depict shadows and highlights when tonal variations are limited |
| Primary Focus | Intense chiaroscuro emphasizing light and darkness | Color shifts for tonal modulation and visual interest |
| Color Usage | Limited palette with stark contrasts, often black backgrounds | Bright, contrasting colors replacing shadows or highlights |
| Historical Period | Baroque era, 17th century, notably Caravaggio | Renaissance and Mannerism, 15th-16th centuries |
| Purpose | Create dramatic volume and focus using light | Enhance vibrancy and depth through color transitions |
| Example Artists | Caravaggio, Gerrit van Honthorst | Michelangelo, Raphael |
Introduction to Tenebrism and Cangiante
Tenebrism is a painting technique characterized by dramatic contrasts between light and dark, emphasizing intense shadows to create a sense of volume and depth, popularized by artists such as Caravaggio during the Baroque period. Cangiante, on the other hand, is a Renaissance painting method that involves changing to a different hue when the original color's tonal range cannot be adjusted to depict light and shadow effectively, often used by Michelangelo to enhance vibrancy and form. These techniques showcase distinct approaches to rendering light and color, with Tenebrism focusing on chiaroscuro effects and Cangiante emphasizing bold, chromatic shifts.
Historical Origins of Tenebrism
Tenebrism originated in the early 17th century, emerging prominently through the works of Italian Baroque painter Caravaggio, who employed dramatic contrasts between light and dark to heighten emotional intensity and realism. This technique, rooted in Renaissance chiaroscuro, evolved to emphasize stark shadows and illuminated subjects, creating a theatrical visual impact that influenced Baroque and subsequent art movements. Cangiante, by contrast, is a Renaissance technique characterized by shifting color hues to depict light and shadow when tonal variations were limited, marking distinct functional and historical differences between the two styles.
The Emergence of Cangiante Technique
The emergence of the cangiante technique marked a pivotal evolution in Renaissance painting, emphasizing vibrant color shifts to model form rather than relying solely on light and shadow, as seen in tenebrism. While tenebrism utilizes intense chiaroscuro to create dramatic contrasts and depth, cangiante introduces bold, complementary color changes to depict volume and highlight, often shifting from warm to cool hues. This innovative approach allowed artists like Michelangelo and Raphael to achieve more expressive and dynamic compositions, expanding the visual language beyond the monochromatic intensity of tenebrism.
Key Artists of Tenebrism
Tenebrism is characterized by dramatic contrasts of light and dark, prominently used by artists such as Caravaggio, whose intense chiaroscuro emphasizes emotional depth and realism. Key figures include Georges de La Tour and Artemisia Gentileschi, who employed sharp lighting contrasts to highlight narrative intensity and psychological complexity in their works. In contrast, Cangiante, favored by Renaissance painters like Michelangelo and Leonardo da Vinci, focuses on shifting color tones to depict light and shadow rather than tonal variations.
Renowned Cangiante Practitioners
Renowned cangiante practitioners include Michelangelo and Titian, who masterfully employed this technique to create vibrant color transitions in their Renaissance paintings. Unlike tenebrism, which emphasizes stark chiaroscuro contrasts and dramatic light-dark effects, cangiante focuses on color shifts to represent light and shadow when tonal variations are limited. This method enriched the visual depth and emotional expressiveness of artworks during the Italian Renaissance, distinguishing it from the tenebrism style popularized by Caravaggio.
Core Characteristics of Tenebrism
Tenebrism is characterized by stark contrasts between intense light and deep shadow, emphasizing dramatic illumination on key subjects to create a sense of volume and emotional intensity. This technique uses sharp chiaroscuro to isolate figures from dark backgrounds, enhancing a three-dimensional effect and directing viewer attention. Unlike Cangiante, which changes colors to depict light and shadow, Tenebrism relies primarily on tonal contrasts to achieve its powerful visual impact.
Distinctive Features of Cangiante
Cangiante is a Renaissance painting technique characterized by the use of contrasting colors to depict changes in light and shadow, especially when the original hue cannot be darkened sufficiently. Unlike Tenebrism, which relies on stark chiaroscuro and intense contrasts of light and dark with a limited palette, Cangiante emphasizes vibrant color shifts to create volume and depth. This method utilizes tonal variations and hue contrasts to simulate form, making it distinctive for its expressive use of bright, often complementary colors rather than solely tonal gradations.
Comparative Analysis: Tenebrism vs Cangiante
Tenebrism emphasizes dramatic chiaroscuro with intense contrasts between light and dark, creating depth and emotional intensity, while cangiante relies on vibrant color shifts to model form and enhance visual interest without using traditional shading. Tenebrism primarily utilizes a limited palette dominated by dark tones and bright highlights, whereas cangiante embraces bold, often contrasting hues to depict shadows and highlights, enriching the coloristic complexity. In techniques, tenebrism manipulates lighting to evoke realism and drama, while cangiante exploits color variation as a structural and expressive tool in Renaissance and Baroque painting.
Influence on Art Movements and Styles
Tenebrism, characterized by dramatic contrasts of light and shadow, deeply influenced Baroque art by intensifying emotional expression and realism in works by Caravaggio and his followers, inspiring chiaroscuro techniques in later Romanticism and Realism. Cangiante, with its vibrant color shifts and bold use of contrasting hues, played a pivotal role in Mannerism by enhancing dynamic compositions and emotional intensity, subsequently informing the vivid palettes of Fauvism and Expressionism. Both techniques contributed uniquely to the evolution of Western art, shaping the visual language and stylistic approaches of multiple art movements.
Lasting Impact on Contemporary Art
Tenebrism's dramatic use of intense chiaroscuro profoundly influences contemporary artists exploring contrast and emotional depth, evident in modern figurative and narrative painting. Cangiante's vibrant color shifts continue to inspire contemporary painters and digital artists seeking dynamic tonal transitions and bold palettes. Both techniques shape contemporary art's approach to light, shadow, and color, enriching visual storytelling and expressive potential.
Tenebrism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com