Drawing enhances creativity and improves fine motor skills by allowing you to express ideas visually. It serves as both a relaxing hobby and a powerful tool for communication across various fields. Explore the rest of the article to discover expert tips and techniques that can elevate your drawing skills.
Table of Comparison
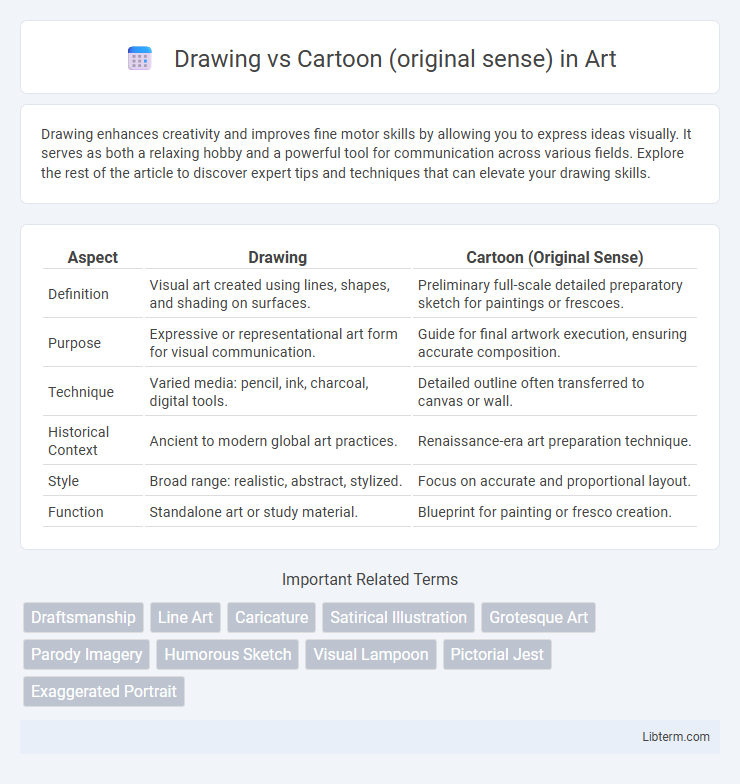
| Aspect | Drawing | Cartoon (Original Sense) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Visual art created using lines, shapes, and shading on surfaces. | Preliminary full-scale detailed preparatory sketch for paintings or frescoes. |
| Purpose | Expressive or representational art form for visual communication. | Guide for final artwork execution, ensuring accurate composition. |
| Technique | Varied media: pencil, ink, charcoal, digital tools. | Detailed outline often transferred to canvas or wall. |
| Historical Context | Ancient to modern global art practices. | Renaissance-era art preparation technique. |
| Style | Broad range: realistic, abstract, stylized. | Focus on accurate and proportional layout. |
| Function | Standalone art or study material. | Blueprint for painting or fresco creation. |
Understanding Drawing: Definitions and Context
Drawing is the art of creating images by making marks on a surface, typically paper, using tools like pencils, pens, or charcoal; it serves as a foundational skill for various visual arts including cartoons. Unlike cartoons, which are simplified, exaggerated, and often humorous illustrations designed to entertain or convey satirical messages, drawings encompass a broad range of styles and purposes, from realistic sketches to abstract representations. Understanding drawing requires recognizing its role as both a technical practice and a means of visual expression that conveys texture, form, and depth beyond the narrative or comedic intent found in cartoons.
The Original Sense of Cartoons: Historical Background
The original sense of cartoons dates back to the Renaissance period, where they referred to full-scale preparatory drawings used by artists to transfer designs onto frescoes or tapestries. These cartoons served as detailed, life-sized sketches that guided painters in executing their intricate works. Over time, the term evolved to denote humorous or satirical illustrations in newspapers and magazines, diverging from its initial artistic purpose.
Key Differences Between Drawings and Cartoons
Drawings are visual representations created using various techniques such as sketching, shading, and line work to depict realistic or abstract subjects with detailed precision. Cartoons, in the original sense, emphasize simplified and exaggerated features, often incorporating humor or satire to convey messages or stories. The key differences lie in purpose and style: drawings prioritize aesthetic detail and form, while cartoons use stylization and narrative to engage viewers emotionally or comically.
Techniques Used in Drawing vs. Cartoons
Drawing techniques often involve precise line work, shading, and textural details using pencils, charcoal, or ink to create realistic or stylized images. Cartoons utilize simplified shapes, exaggerated expressions, and bold outlines, frequently employing digital tools or traditional ink to emphasize humor or storytelling. Both methods rely on foundational skills in composition and perspective but differ in their approach to detail and abstraction.
Symbolism and Purpose in Drawings and Cartoons
Drawings primarily employ symbolism to convey nuanced meanings or emotions through detailed, often realistic representations aiming to evoke contemplation or interpretation. Cartoons use exaggerated features and simplified forms as symbolic tools to deliver humor, satire, or social commentary with immediacy and clarity. The purpose of drawings is to explore artistic expression and capture complex ideas, while cartoons focus on engaging audiences quickly through visually accessible storytelling.
Evolution of Cartoon Art Through History
The evolution of cartoon art traces back to early drawings used for humor and satire in ancient civilizations, progressively transforming during the Renaissance with the integration of exaggerated features and storytelling elements. In the 19th century, cartoons evolved into political and editorial commentary in newspapers, while the 20th century introduced animated cartoons, pioneering new visual techniques and character development. Contemporary cartoon art combines traditional drawing methods with digital technologies, expanding its cultural impact and artistic expression globally.
Artistic Expressions: Realism vs. Exaggeration
Drawing encompasses a wide range of artistic expressions characterized by realism, where artists strive to accurately depict subjects with precise details, shading, and proportions. Cartooning, in its original sense, emphasizes exaggeration through stylized features, bold lines, and simplified forms to convey humor, emotion, or storytelling. This contrast highlights how drawing prioritizes lifelike representation while cartoons focus on imaginative and exaggerated visual communication.
Cultural Impact of Drawings and Cartoons
Drawings and cartoons have profoundly shaped cultural narratives by reflecting societal values, humor, and political commentary. Drawings often serve as detailed artistic expressions influencing fine arts and education, while cartoons distill complex ideas into accessible visual satire and storytelling that resonate widely across generations. Both mediums drive cultural discourse, with cartoons playing a pivotal role in mass media and social critique.
Notable Examples of Classic Drawings and Cartoons
Leonardo da Vinci's "Vitruvian Man" and Albrecht Durer's "Praying Hands" stand as iconic examples of classic drawings, showcasing meticulous detail and anatomical precision. In contrast, early cartoons like Winsor McCay's "Gertie the Dinosaur" and George Herriman's "Krazy Kat" highlight exaggerated features and humor, emphasizing narrative and character over realism. These works collectively illustrate the fundamental distinctions between drawing as fine art and cartoons as visual storytelling.
Choosing Between Drawing and Cartooning: Which Suits Your Style?
Drawing emphasizes realistic representation and detailed technique, ideal for artists seeking precision and depth in their work. Cartooning prioritizes exaggerated features and simplified forms, appealing to those who want to convey humor, emotion, or storytelling with bold, expressive lines. Choosing between drawing and cartooning depends on whether you prefer meticulous realism or vibrant, stylized communication.
Drawing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com