Collograph and lithograph are two distinct printmaking techniques, each offering unique textures and artistic effects. Collograph involves creating a textured plate using various materials, which is then inked and pressed onto paper, while lithograph relies on a flat stone or metal plate where images are drawn with a greasy substance. Explore the differences and benefits of both methods to enhance your understanding and appreciation of printmaking in the full article.
Table of Comparison
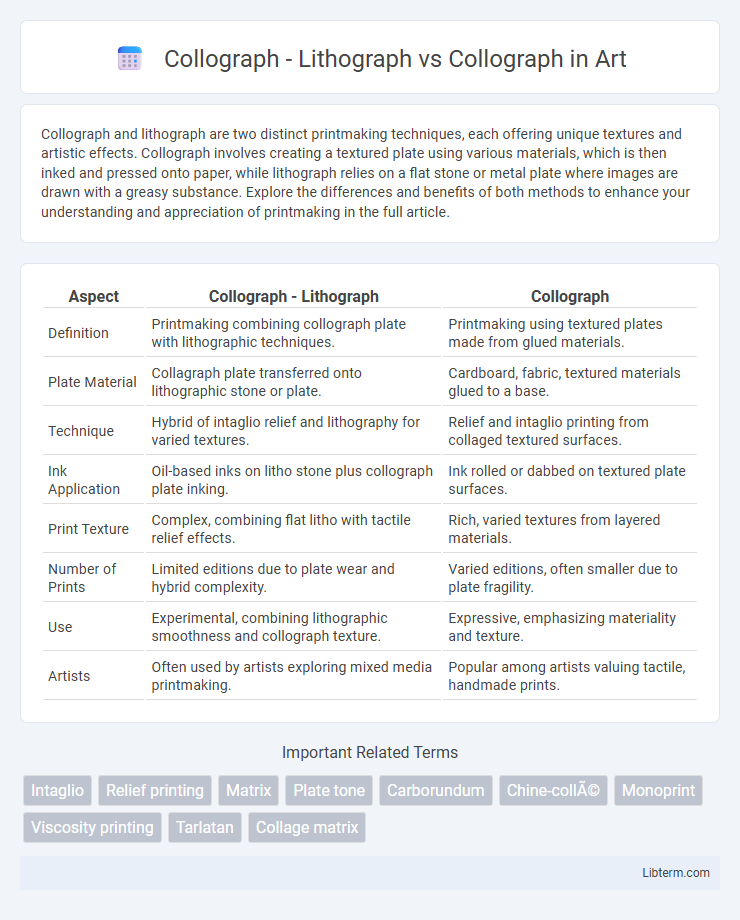
| Aspect | Collograph - Lithograph | Collograph |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Printmaking combining collograph plate with lithographic techniques. | Printmaking using textured plates made from glued materials. |
| Plate Material | Collagraph plate transferred onto lithographic stone or plate. | Cardboard, fabric, textured materials glued to a base. |
| Technique | Hybrid of intaglio relief and lithography for varied textures. | Relief and intaglio printing from collaged textured surfaces. |
| Ink Application | Oil-based inks on litho stone plus collograph plate inking. | Ink rolled or dabbed on textured plate surfaces. |
| Print Texture | Complex, combining flat litho with tactile relief effects. | Rich, varied textures from layered materials. |
| Number of Prints | Limited editions due to plate wear and hybrid complexity. | Varied editions, often smaller due to plate fragility. |
| Use | Experimental, combining lithographic smoothness and collograph texture. | Expressive, emphasizing materiality and texture. |
| Artists | Often used by artists exploring mixed media printmaking. | Popular among artists valuing tactile, handmade prints. |
Introduction to Printmaking Techniques
Collograph and lithograph are distinct printmaking techniques that offer unique textures and visual effects in art. Collograph involves creating a textured plate by gluing materials onto a surface, which is then inked and pressed onto paper to produce rich, tactile prints. Lithograph relies on the principle of oil and water repulsion, using a flat stone or metal plate to create inked images through a chemical process, resulting in smooth, detailed prints.
Understanding Collograph: Definition and Process
Collograph is a printmaking technique that involves creating a textured plate by collaging various materials onto a substrate, which is then inked and pressed onto paper. Unlike lithography, which relies on the chemical repulsion of oil and water on a flat stone or metal plate, collograph emphasizes the physical buildup of texture and relief for print variation. The process includes assembling materials such as fabric, cardboard, or textured paper, sealing the plate with varnish, applying ink with brushes or rollers, and printing with a press or by hand.
What is Lithography? An Overview
Lithography is a printing process that relies on the immiscibility of oil and water to transfer images from a flat stone or metal plate to paper. Unlike collograph, which builds texture through collage materials on a plate, lithography uses chemical techniques to create image areas that attract ink and repel water. This method enables high-quality, detailed prints ideal for reproducing fine lines and subtle gradations.
Key Differences Between Collograph and Lithograph
Collograph involves creating a textured printing plate using various materials glued to a surface, producing prints with rich surface texture and tactile depth, while lithograph relies on the chemical repulsion of oil and water on a flat stone or metal plate for image transfer, resulting in smooth tonal gradations. Key differences include the relief nature of collograph plates compared to the planographic surface of lithographs, and the materials used--collograph uses collage elements whereas lithography depends on greasy drawing materials. Collograph is more experimental and textural, whereas lithograph is traditionally valued for its precision and subtle shading capabilities.
Materials Used in Collograph vs Lithograph
Materials used in collograph printing include cardboard, fabric, textured papers, and various adhesives that create raised surfaces for inking. Lithograph printing relies on smooth, flat limestone or aluminum plates treated chemically to separate oil and water regions for image transfer. The porous and flexible materials in collograph allow for diverse textures, whereas lithograph's specialized plates enable precise replication of detailed drawings.
Artistic Effects: Textures and Visual Qualities
Collograph prints offer rich, tactile textures created by building up materials on a plate, resulting in pronounced relief and dynamic visual depth that emphasize an organic, handcrafted quality. Lithographs produce smooth, flat surfaces through a chemical process on limestone or metal plates, facilitating fine details and subtle tonal variations, ideal for delicate shading and precise line work. The contrasting artistic effects position collographs as bold, textured artworks, while lithographs excel in refined, detailed imagery with a polished finish.
Step-by-Step: Collograph Printing Process
The collograph printing process involves creating a textured plate by adhering various materials such as fabric, cardboard, or textured paper onto a rigid backing, which is then sealed and inked before pressing onto paper to produce unique prints. In contrast to lithographs, which rely on chemical repulsion between oil and water on a flat stone or metal plate, collographs emphasize tactile surface variations and relief elements for image formation. Step-by-step, collograph printing includes preparing the plate base, building up texture, sealing the surface, applying ink with rollers or brushes, wiping away excess ink from non-textured areas, and finally pressing the plate onto paper using a printing press or hand burnishing.
Step-by-Step: Lithographic Printing Process
The lithographic printing process involves preparing a smooth stone or metal plate coated with a greasy substance that repels water but attracts ink, enabling image transfer. The plate undergoes chemical treatment to fix the design, followed by dampening with water and inking, where ink adheres only to the greasy image areas. Pressing the plate against paper completes the transfer, highlighting lithography's use of immiscible oil and water based on chemical repulsion for high-quality reproductions.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Method
Collograph printmaking offers a textured, tactile quality through layered materials on a plate, providing rich depth and versatility but may suffer from less precision compared to lithography. Lithograph relies on the chemical repulsion of oil and water on a flat stone or metal plate, allowing for detailed, smooth gradations and sharp lines, though it requires specialized materials and can be time-consuming. The collograph's advantage lies in its accessible, mixed-media approach suitable for experimental textures, while lithography excels in fine detail and reproducible consistency but demands more technical skill and equipment.
Choosing the Right Technique: Collograph or Lithograph
Choosing between collograph and lithograph depends on desired texture and detail; collograph offers rich, tactile surfaces through collage elements, while lithograph excels in fine lines and smooth shading using a stone or metal plate. Collograph suits expressive, relief-based prints with varied materials, whereas lithograph is ideal for precise, consistent images with a range of tones. Consider project goals, material availability, and print run size to determine the most suitable technique.
Collograph - Lithograph Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com