Subordination enhances sentence clarity by linking dependent clauses to main clauses, creating a clear hierarchy of ideas. Mastering this grammatical structure allows you to express complex thoughts with precision and flow. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical tips for using subordination effectively in your writing.
Table of Comparison
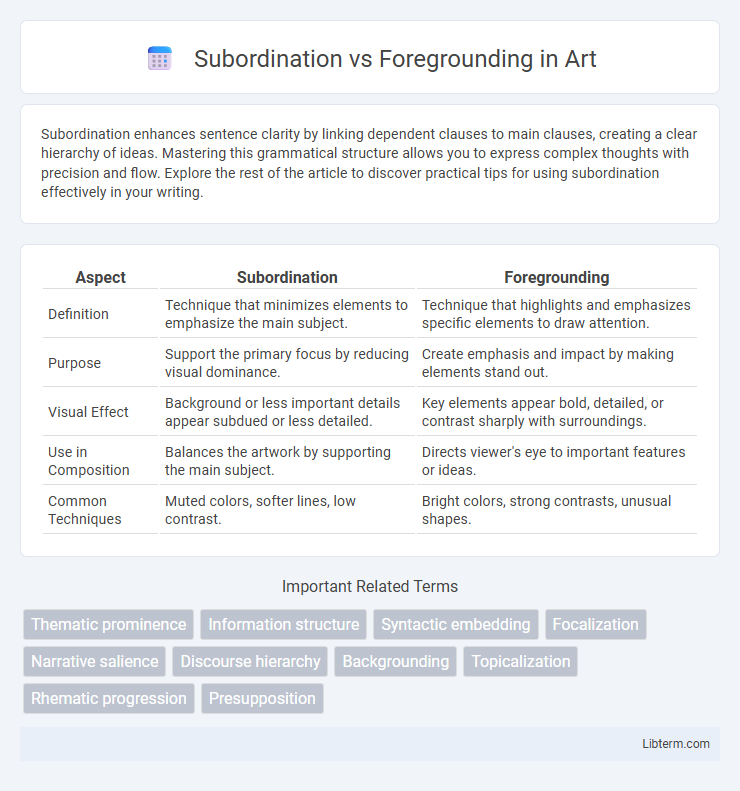
| Aspect | Subordination | Foregrounding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technique that minimizes elements to emphasize the main subject. | Technique that highlights and emphasizes specific elements to draw attention. |
| Purpose | Support the primary focus by reducing visual dominance. | Create emphasis and impact by making elements stand out. |
| Visual Effect | Background or less important details appear subdued or less detailed. | Key elements appear bold, detailed, or contrast sharply with surroundings. |
| Use in Composition | Balances the artwork by supporting the main subject. | Directs viewer's eye to important features or ideas. |
| Common Techniques | Muted colors, softer lines, low contrast. | Bright colors, strong contrasts, unusual shapes. |
Understanding Subordination in Writing
Understanding subordination in writing enhances sentence complexity by linking a dependent clause to an independent clause, creating clear hierarchical relationships between ideas. This technique allows writers to emphasize main information while providing additional context or details, improving clarity and coherence. Effective use of subordination reduces sentence ambiguity and guides readers through the logical flow of arguments or narratives.
Defining Foregrounding and Its Purpose
Foregrounding involves emphasizing specific linguistic elements within a text to highlight their significance and create a distinct stylistic effect. It disrupts ordinary linguistic patterns to draw the reader's attention, often through deviation or parallelism, enhancing thematic depth and emotional impact. This technique contrasts with subordination, which organizes ideas hierarchically to establish relationships between clauses and information.
The Key Differences Between Subordination and Foregrounding
Subordination involves placing less important information in dependent clauses to support the main clause, enhancing sentence clarity and hierarchy. Foregrounding emphasizes specific elements, often through stylistic choices such as repetition or unusual syntax, to capture the reader's attention and create a strong impact. The key difference lies in subordination's function to organize information hierarchy, while foregrounding aims to highlight and make certain elements stand out for rhetorical effect.
How Subordination Shapes Narrative Structure
Subordination in narrative structure organizes information by prioritizing main ideas while embedding supplementary details in dependent clauses, which guides readers through complex storylines with clarity. This hierarchical arrangement emphasizes causality and temporal sequences, enhancing coherence and control over the narrative flow. Foregrounding, in contrast, disrupts this hierarchy by highlighting specific elements for stylistic or thematic impact, but subordination remains essential for maintaining the underlying framework of the plot.
Foregrounding: Drawing Attention to Key Elements
Foregrounding emphasizes key elements within a text by making them stand out through linguistic features such as repetition, deviation, or prominence in sentence structure. It enhances reader engagement by highlighting important themes, emotions, or stylistic devices, ensuring that crucial information captures attention effectively. This technique contrasts with subordination, which organizes elements hierarchically but may not directly intensify focus on specific components.
Applications of Subordination in Academic Writing
Subordination in academic writing is essential for clarifying relationships between ideas by embedding dependent clauses within main clauses, which enhances the specificity and coherence of arguments. It allows writers to present complex information systematically, such as explaining causes, conditions, or contrasts, which improves the clarity and flow of research papers. Utilizing subordination effectively aids in emphasizing critical points while maintaining a logical progression, vital for persuasive and analytical academic texts.
Techniques for Achieving Foregrounding
Techniques for achieving foregrounding include deviation from linguistic norms, such as unusual syntax, phonological patterns, or semantic shifts, which draw readers' attention to specific text elements. Parallelism and repetition also enhance foregrounding by emphasizing key ideas or themes through structural or lexical recurrence. The strategic use of foregrounding contrasts with subordination, where subordinate clauses serve to background information, thereby highlighting the main clause for thematic focus.
Effects of Subordination on Reader Perception
Subordination in writing structures information hierarchically, guiding readers to prioritize the main ideas while treating secondary details as supportive, which clarifies the text's logical flow. This technique subtly influences reader perception by emphasizing the importance of certain concepts and shaping the overall message's tone and focus. By controlling the relationship between clauses, subordination can create nuanced meanings and enhance the reader's understanding of complex arguments.
Foregrounding in Literary Analysis
Foregrounding in literary analysis refers to the technique of making certain elements in a text stand out to enhance meaning, often through deviation from linguistic norms, such as unusual syntax, diction, or imagery. This technique draws the reader's attention to significant themes, emotions, or motifs by prioritizing these features over the background elements, contrasting with subordination where the main clause holds primary importance. Foregrounding amplifies the aesthetic experience and interpretive depth by emphasizing stylistic choices that disrupt the expected flow of language.
Choosing Between Subordination and Foregrounding in Your Writing
Choosing between subordination and foregrounding in your writing depends on the emphasis you want to create. Subordination allows you to de-emphasize less important information by embedding it within complex sentences, guiding readers through a hierarchy of ideas. Foregrounding, through techniques such as repetition, unusual syntax, or vivid imagery, highlights key elements to capture attention and enhance thematic impact.
Subordination Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com