Casting plays a critical role in shaping the foundation and durability of metal structures by ensuring the precise formation and strength of components. Proper casting techniques influence the quality, performance, and cost-efficiency of manufactured parts in industries like automotive, aerospace, and construction. Discover how mastering casting processes can enhance your projects by exploring the detailed insights in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
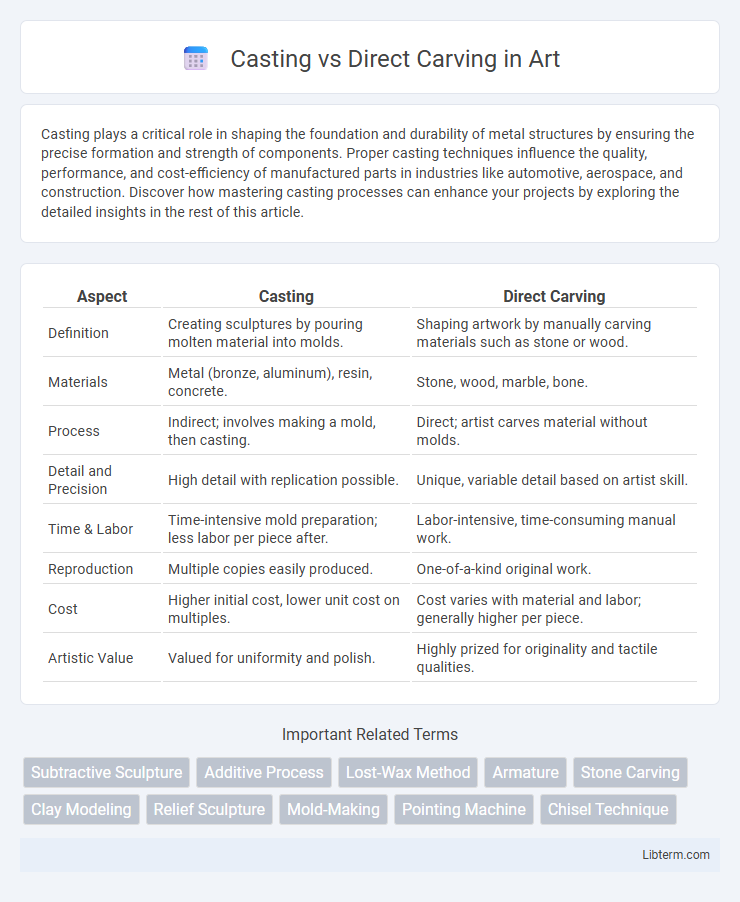
| Aspect | Casting | Direct Carving |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creating sculptures by pouring molten material into molds. | Shaping artwork by manually carving materials such as stone or wood. |
| Materials | Metal (bronze, aluminum), resin, concrete. | Stone, wood, marble, bone. |
| Process | Indirect; involves making a mold, then casting. | Direct; artist carves material without molds. |
| Detail and Precision | High detail with replication possible. | Unique, variable detail based on artist skill. |
| Time & Labor | Time-intensive mold preparation; less labor per piece after. | Labor-intensive, time-consuming manual work. |
| Reproduction | Multiple copies easily produced. | One-of-a-kind original work. |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, lower unit cost on multiples. | Cost varies with material and labor; generally higher per piece. |
| Artistic Value | Valued for uniformity and polish. | Highly prized for originality and tactile qualities. |
Introduction to Casting and Direct Carving
Casting involves creating sculptures by pouring molten material such as metal or plaster into a mold, allowing for precise reproduction of intricate details and complex shapes. Direct carving, also known as sculpting in the round, entails removing material directly from a solid block like stone or wood, emphasizing the artist's skill in shaping the form without intermediate steps. Both techniques serve different artistic goals, with casting enabling mass production and detailed replication, while direct carving highlights originality and tactile engagement with the medium.
Historical Background of Sculptural Techniques
Casting, dating back to ancient civilizations like Mesopotamia and Egypt, revolutionized sculptural techniques by enabling the mass production of bronze and metal artworks through molds. Direct carving, favored during the Renaissance and by modernist sculptors such as Constantin Brancusi, emphasizes the artist's intimate interaction with stone or wood, shaping material without preliminary models. These contrasting methods reflect cultural shifts in artistic values, from replicability and durability in casting to authenticity and originality in direct carving.
Defining Casting: Process and Principles
Casting is a manufacturing process where molten material, typically metal or plastic, is poured into a mold to solidify and form a specific shape, allowing for complex and detailed designs. The principles of casting involve melting the base material, controlling the mold temperature, and ensuring proper cooling to prevent defects like porosity or warping. This method is ideal for producing multiple identical parts efficiently and with high precision.
Understanding Direct Carving: Methods and Materials
Direct carving involves sculpting materials such as stone, wood, or ivory without preliminary models, relying on the artist's intuition and skill to shape the final form. Key methods include subtractive techniques using chisels, mallets, and rasps, allowing precise control over texture and detail. Common materials favored for direct carving are marble, limestone, and hardwoods like oak and mahogany, chosen for their durability and workability in achieving intricate artistic expressions.
Key Differences Between Casting and Direct Carving
Casting involves creating sculptures by pouring molten material such as metal or plaster into molds, enabling mass production and precise replication of intricate details. Direct carving requires the artist to sculpt materials like wood or stone manually, emphasizing originality and the natural texture of the medium. Key differences include casting's reliance on molds and indirect fabrication, while direct carving is a hands-on, subtractive process focusing on unique, singular artworks.
Artistic Intent: Expression Through Technique
Casting allows artists to reproduce intricate details and complex forms by pouring molten materials into molds, offering precision and consistency that support refined artistic expression. Direct carving requires direct interaction with the material, enabling artists to convey spontaneity and personal touch, emphasizing the uniqueness of each piece. Both techniques shape artistic intent distinctly, with casting favoring replication and precision, while carving highlights immediacy and tactile engagement.
Materials Commonly Used in Casting vs Direct Carving
Casting commonly utilizes metals such as bronze, aluminum, and iron, as well as resins and plaster for creating detailed and durable sculptures. Direct carving typically involves materials like marble, limestone, wood, and alabaster, which are chosen for their ability to be shaped and refined by hand tools. The material selection significantly impacts the artistic process and final texture of the sculpture, with casting favoring fluid materials and direct carving depending on solid, workable substances.
Advantages and Challenges of Each Approach
Casting offers advantages like the ability to produce complex shapes with fine detail and consistent replication, making it ideal for mass production and intricate designs. Challenges include the need for molds, higher initial setup costs, and potential defects such as porosity or shrinkage during cooling. Direct carving provides unique, one-of-a-kind artworks with a tactile and expressive quality, but it is labor-intensive, time-consuming, and limited by the material's physical constraints and the artist's skill.
Notable Artists and Iconic Works
Casting techniques were employed by artists like Auguste Rodin, whose sculpture "The Thinker" exemplifies the precision and detail attainable through mold-making and bronze casting. In contrast, direct carving was favored by Brancusi, notable for "Bird in Space," emphasizing the artist's intimate interaction with the material for a more tactile and organic form. Both methods have shaped modern sculpture, with casting enabling replication and mass production, while direct carving highlights individual craftsmanship and material authenticity.
Choosing the Right Technique: Factors to Consider
Choosing between casting and direct carving depends on factors such as desired detail, material durability, and production volume. Casting allows for precise replication and is ideal for complex designs and mass production, while direct carving offers a unique, tactile approach suited for one-of-a-kind pieces with emphasis on material texture. Consider budget, time constraints, and artistic intent to select the technique that best aligns with the project's goals.
Casting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com