Restoring damaged files or systems requires a precise approach to ensure data integrity and prevent further loss. Utilizing specialized software tools and following step-by-step recovery procedures can significantly improve restoration success rates. Discover effective restoration techniques and tips in the rest of this article to protect your valuable data.
Table of Comparison
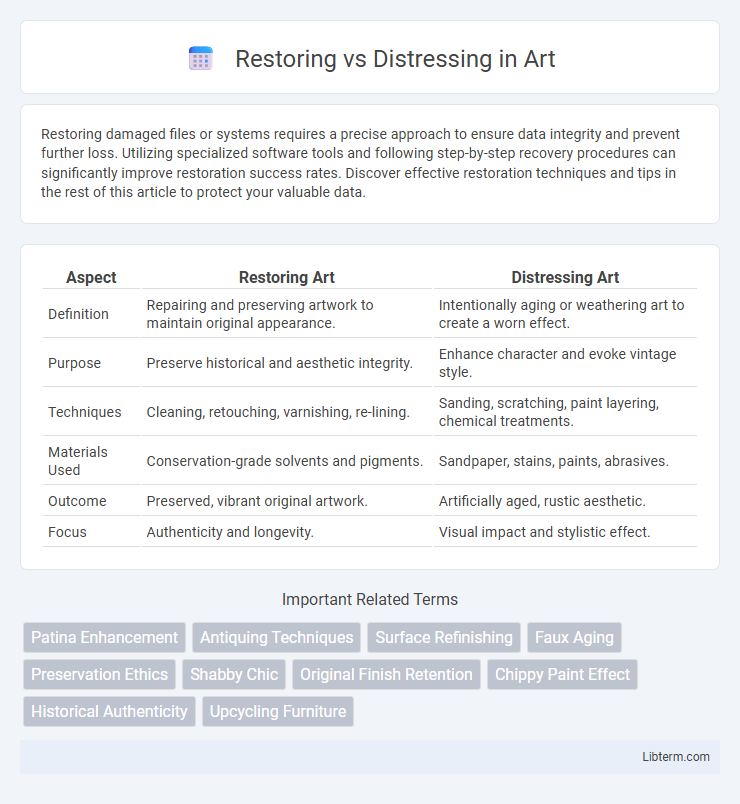
| Aspect | Restoring Art | Distressing Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repairing and preserving artwork to maintain original appearance. | Intentionally aging or weathering art to create a worn effect. |
| Purpose | Preserve historical and aesthetic integrity. | Enhance character and evoke vintage style. |
| Techniques | Cleaning, retouching, varnishing, re-lining. | Sanding, scratching, paint layering, chemical treatments. |
| Materials Used | Conservation-grade solvents and pigments. | Sandpaper, stains, paints, abrasives. |
| Outcome | Preserved, vibrant original artwork. | Artificially aged, rustic aesthetic. |
| Focus | Authenticity and longevity. | Visual impact and stylistic effect. |
Understanding Restoration: Bringing Furniture Back to Life
Restoration involves meticulously repairing and refinishing furniture to preserve its original appearance and structural integrity, often using techniques like sanding, staining, and varnishing. This process enhances the piece's historical value and extends its lifespan by addressing wear, cracks, or damage while maintaining authenticity. Unlike distressing, which artificially ages furniture for aesthetic purposes, restoration prioritizes quality craftsmanship and genuine preservation.
What Is Distressing? Creating the Aged Look
Distressing is a popular technique in furniture design that intentionally creates an aged, worn appearance by simulating natural wear and tear through sanding, scraping, or applying paint unevenly. This method enhances character by revealing underlying layers or wood texture, giving pieces a vintage or antique aesthetic. Unlike restoring, which aims to return furniture to its original condition, distressing adds modern charm by embracing imperfections and signs of aging.
Key Differences: Restoring vs Distressing Techniques
Restoring techniques focus on repairing or rejuvenating surfaces by preserving original textures and materials, often involving gentle cleaning, polishing, or minor touch-ups to enhance durability and appearance. Distressing techniques intentionally age or weather surfaces to create a worn, vintage look through methods like sanding, staining, or applying patinas that simulate damage or wear. The key difference lies in restoring aiming to maintain integrity and freshness, while distressing emphasizes aesthetic alteration to evoke character and history.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Piece
Restoring preserves the original condition and integrity of furniture by repairing damage and maintaining authentic finishes, ideal for valuable antiques. Distressing intentionally ages or damages surfaces to create a worn, vintage look, suitable for new pieces needing character. Selecting the right approach depends on the piece's value, desired aesthetic, and historical significance, ensuring the final result aligns with your design goals and preservation priorities.
Tools & Materials Needed for Restoration
Restoring furniture requires tools such as sandpaper, wood fillers, clamps, and quality brushes, along with materials like wood stain, varnish, and sealants to preserve and enhance the original wood. Distressing techniques often use wire brushes, hammers, chains, and chisels to create intentional wear and texture, complemented by paint, wax, and antiquing glazes to achieve an aged look. Choosing the right combination of tools and materials is crucial for either preserving the piece's integrity during restoration or achieving authentic distressing effects.
Essential Steps for Effective Distressing
Effective distressing involves carefully sanding, scraping, or applying chemicals to achieve a weathered look while preserving the structural integrity of the wood. Restoring focuses on repairing and refinishing surfaces to bring them back to their original condition, often requiring cleaning, filling cracks, and sealing. Essential steps for effective distressing include selecting appropriate tools, testing techniques on a sample, and sealing the finished piece to protect the aged appearance.
Pros and Cons: Restoration vs Distressing
Restoring furniture preserves original materials and craftsmanship, enhancing its value and historical integrity, while often requiring specialized skills and higher costs. Distressing creates an aged, vintage look through techniques like sanding and staining but may reduce the item's longevity and resale value. Choosing between restoring and distressing depends on desired aesthetics, functional use, and the importance of maintaining authenticity versus embracing a worn, customized appearance.
Best Wood Finishes for Each Method
Restoring wood focuses on preserving natural beauty using finishes like tung oil, shellac, or natural wax, which penetrate and nourish the wood without stripping its character. Distressing benefits from matte or satin finishes such as milk paint or matte polyurethane that enhance texture and imperfections while protecting the surface. Choosing finishes with low VOC content and appropriate durability ensures longevity tailored to either restoring smoothness or embracing aged aesthetics.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Both Processes
Common mistakes in restoring involve using harsh chemicals or abrasive tools that damage the original material, while in distressing, overdoing the wear can lead to unnatural or inconsistent finishes. Ignoring proper surface preparation often results in poor adhesion or uneven textures during both processes. Failing to research the specific material's properties and using incompatible methods can compromise durability and aesthetic quality in restoration and distressing projects.
Maintenance Tips After Restoring or Distressing
Maintenance tips after restoring or distressing wood furniture include regular dusting with a soft cloth to prevent dirt buildup and using a high-quality furniture wax or oil to nourish and protect the surface. Avoid exposing the wood to direct sunlight and humidity fluctuations, as these elements can cause warping or fading. For distressed finishes, gently clean with mild soap and water to preserve the aged look without removing the paint or finish layers.
Restoring Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com