Gel offers a versatile and effective solution for skincare, hair styling, and medical applications, providing easy application and long-lasting results. Its unique formulation allows for targeted benefits such as hydration, hold, or topical healing, making it essential in your daily routine. Explore the rest of the article to discover the different types of gels and how they can enhance your self-care regimen.
Table of Comparison
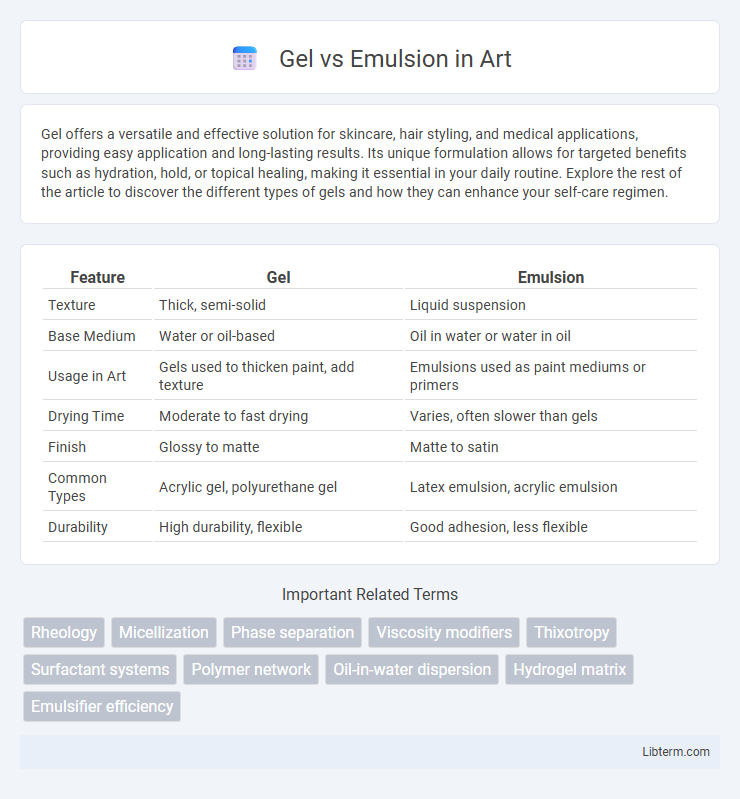
| Feature | Gel | Emulsion |
|---|---|---|
| Texture | Thick, semi-solid | Liquid suspension |
| Base Medium | Water or oil-based | Oil in water or water in oil |
| Usage in Art | Gels used to thicken paint, add texture | Emulsions used as paint mediums or primers |
| Drying Time | Moderate to fast drying | Varies, often slower than gels |
| Finish | Glossy to matte | Matte to satin |
| Common Types | Acrylic gel, polyurethane gel | Latex emulsion, acrylic emulsion |
| Durability | High durability, flexible | Good adhesion, less flexible |
Understanding Gels: Definition and Characteristics
Gels are semi-solid substances consisting of a three-dimensional polymer network that traps liquid, providing a firm but flexible texture ideal for skincare applications. Their high viscosity and stability create a cooling, non-greasy sensation, distinguishing them from emulsions, which are typically mixtures of oil and water phases with a creamier consistency. Gels' water-based formulation enhances rapid absorption and is suitable for oily or sensitive skin types, making them a preferred choice for delivering active ingredients efficiently.
What is an Emulsion? Key Properties Explained
An emulsion is a fine dispersion of two immiscible liquids, typically oil and water, where one liquid is dispersed as small droplets within the other, stabilized by emulsifying agents. Key properties of emulsions include droplet size, viscosity, stability against separation, and the hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) of the emulsifier used. These characteristics determine the texture, appearance, and shelf life of cosmetic and pharmaceutical products formulated as emulsions.
Gel vs Emulsion: Core Differences
Gels consist of a network of solid particles suspended in a liquid, offering a thick, transparent, and non-greasy texture ideal for quick absorption and cooling effects. Emulsions are a mixture of two immiscible liquids, typically oil and water, stabilized by emulsifiers, providing a creamy, moisturizing texture suitable for hydrating and protecting the skin. The core difference lies in their composition and texture: gels are water-based and lightweight, while emulsions combine oil and water phases, resulting in a richer, more emollient product.
Common Ingredients in Gels and Emulsions
Common ingredients in gels typically include a high concentration of water, gelling agents like carbomers or xanthan gum, and solvents such as alcohol or propylene glycol for enhanced penetration. Emulsions consist primarily of oil and water phases stabilized by emulsifiers like lecithin, polysorbates, or stearates, often combined with humectants like glycerin and occlusive agents such as petrolatum or dimethicone. Both formulations may also contain preservatives, fragrances, and active ingredients tailored to their specific delivery mechanisms and skin benefits.
Texture and Sensory Experience: Gel vs Emulsion
Gels offer a lightweight, cooling texture that absorbs quickly into the skin, providing a refreshing and non-greasy sensory experience ideal for oily or combination skin types. Emulsions feature a creamy, silky consistency that feels richer and more moisturizing, delivering a smoother, more hydrated sensation suited for dry or sensitive skin. The tactile difference between gel and emulsion influences user preference, with gels emphasizing lightness and emulsions prioritizing nourishment and softness.
Skin Compatibility and Suitability
Gels typically offer higher skin compatibility for oily and acne-prone skin due to their lightweight, non-comedogenic formulation that absorbs quickly without clogging pores. Emulsions, combining oil and water phases, provide balanced hydration, making them suitable for dry and sensitive skin by maintaining the skin's moisture barrier and preventing irritation. Both formulations require careful ingredient selection to optimize skin compatibility based on individual skin types and conditions.
Application and Absorption Rates
Gels typically have a lighter, water-based consistency that allows for faster absorption into the skin, making them ideal for quick application and non-greasy finishes often preferred in oily or acne-prone skin. Emulsions, combining oil and water phases, provide a balanced hydration suitable for dry or sensitive skin, with a slower absorption rate that offers prolonged moisturizing effects. Application of gels suits conditions requiring rapid drug delivery or refreshment, while emulsions are favored for sustained nourishment and barrier protection.
Best Uses: When to Choose Gel or Emulsion
Gels are best used for oily or acne-prone skin as they provide lightweight, fast-absorbing hydration without clogging pores. Emulsions suit dry or sensitive skin types, offering richer moisture and a protective barrier without heaviness. Choose gels for daytime or hot climates to maintain a matte finish, while emulsions work well for nighttime or colder conditions to deeply nourish the skin.
Pros and Cons: Gel compared to Emulsion
Gel formulations offer rapid absorption and a lightweight feel, making them ideal for oily or acne-prone skin, but they can sometimes cause dryness or irritation. Emulsions provide superior moisturizing benefits and a smoother texture suitable for dry or sensitive skin, although they may feel heavier and take longer to absorb. Choosing between gel and emulsion depends on skin type and desired hydration level, balancing fast penetration with lasting moisture.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Skin
Choosing between gel and emulsion depends on your skin type and hydration needs; gels are ideal for oily and acne-prone skin due to their lightweight, fast-absorbing texture, while emulsions suit dry or sensitive skin as they provide balanced moisture without heaviness. Both deliver hydration but vary in consistency and absorption rates, influencing their effectiveness based on individual skin conditions. Understanding your skin's needs ensures the right product enhances moisture retention and promotes overall skin health.
Gel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com