Cross-hatching is a drawing technique that uses intersecting sets of parallel lines to create shading, texture, and depth in artwork. This method allows artists to build tonal variation and intricate details without relying on solid fills, making it ideal for sketches and detailed illustrations. Explore the rest of the article to discover tips and techniques for mastering cross-hatching in your own drawings.
Table of Comparison
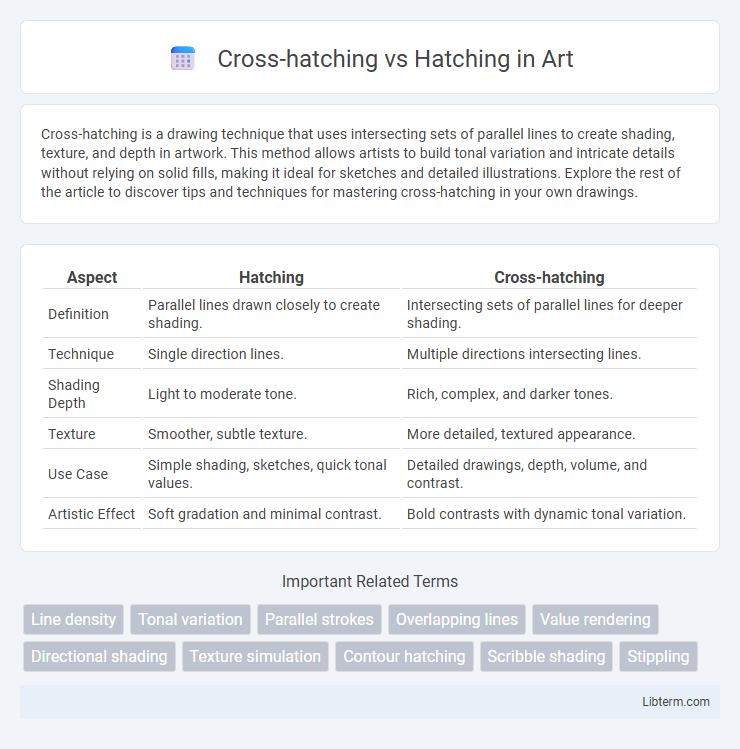
| Aspect | Hatching | Cross-hatching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Parallel lines drawn closely to create shading. | Intersecting sets of parallel lines for deeper shading. |
| Technique | Single direction lines. | Multiple directions intersecting lines. |
| Shading Depth | Light to moderate tone. | Rich, complex, and darker tones. |
| Texture | Smoother, subtle texture. | More detailed, textured appearance. |
| Use Case | Simple shading, sketches, quick tonal values. | Detailed drawings, depth, volume, and contrast. |
| Artistic Effect | Soft gradation and minimal contrast. | Bold contrasts with dynamic tonal variation. |
Introduction to Hatching and Cross-Hatching
Hatching employs closely spaced parallel lines to create shading and texture, enhancing the dimensionality of drawings. Cross-hatching builds on this technique by layering intersecting sets of lines, increasing tonal depth and contrast. Both methods are fundamental in art for depicting light, shadow, and form with precision.
Defining Hatching: Basics and Techniques
Hatching, a fundamental drawing technique, involves creating tonal or shading effects with closely spaced parallel lines that vary in length, thickness, and density to suggest texture and shadow. It serves as the basis for more complex methods like cross-hatching, which layers intersecting sets of parallel lines to enhance depth and intensity. Mastering hatching techniques, including variations in line direction and pressure, is essential for artists to effectively convey form and dimension in monochromatic sketches.
Understanding Cross-Hatching: How It Differs
Cross-hatching involves layering intersecting lines at varying angles to create shading and texture, whereas hatching uses parallel lines in a single direction. The density and overlap of cross-hatched lines enhance tonal depth more effectively than the uniform strokes of hatching. This technique allows artists to achieve richer gradients and three-dimensional effects in drawings.
Historical Origins and Artistic Evolution
Cross-hatching and hatching both originated during the Renaissance period as fundamental drawing techniques to create texture and depth through line work. Hatching uses parallel lines to suggest light and shadow, while cross-hatching involves layering intersecting sets of lines for denser shading and richer tonal variation. Historical artworks by masters like Albrecht Durer and Leonardo da Vinci showcase the evolution of these techniques, highlighting their significance in the development of realistic and expressive illustrations.
Visual Impact: Texture, Depth, and Shading
Cross-hatching enhances visual impact by layering intersecting lines to create rich texture, increased depth, and nuanced shading, producing a more dynamic and three-dimensional appearance. In contrast, hatching uses parallel lines that vary in density and thickness to suggest light and shadow, offering a simpler yet effective way to convey form and texture. The interplay of line direction and spacing in cross-hatching generates complex tonal variations, while hatching relies on uniform strokes for a more minimalist visual effect.
Popular Tools and Materials Used
Popular tools for hatching and cross-hatching include fine-tipped pens, graphite pencils, and technical drawing pens, which allow precise line work essential for texture and shading. Artists often prefer high-quality sketchbooks with smooth paper surfaces to enhance ink flow and prevent smudging during cross-hatching techniques. Digital tablets equipped with pressure-sensitive styluses also provide versatile options for intricate hatching effects in modern digital art workflows.
Step-by-Step Guide: Hatching vs Cross-Hatching
Hatching involves drawing parallel lines in one direction to create shading and depth, while cross-hatching overlays a second set of parallel lines at an angle, increasing tonal complexity. Start with light, evenly spaced lines for hatching, then build up texture and darkness by layering angled lines for cross-hatching. Mastery of these techniques enhances control over light, shadow, and texture in sketches and detailed drawings.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Common mistakes in cross-hatching include inconsistent line spacing and overly heavy strokes that reduce texture clarity, while hatching errors often involve parallel lines that lack direction and variation. Avoid these pitfalls by maintaining uniform, controlled pressure and varying line angles in cross-hatching to build depth and tone effectively. Practice steady hand movement and assess light sources carefully to ensure hatching lines enhance contours without creating unintended shadows.
Choosing the Best Technique for Your Artwork
Cross-hatching involves layering sets of parallel lines at varying angles to create depth and texture, making it ideal for detailed shading in complex artworks. Hatching uses single-direction parallel lines, offering a simpler, more subtle effect suitable for lighter shading and cleaner designs. Selecting between cross-hatching and hatching depends on the desired intensity and texture in your artwork, with cross-hatching providing richer tonal variations and hatching delivering minimalistic shading.
Conclusion: When to Use Hatching or Cross-Hatching
Hatching is ideal for creating subtle shading and texture effects with parallel lines, suitable for lighter tonal areas and fine details. Cross-hatching offers greater depth and intensity by layering intersecting lines, making it perfect for shadows and complex textures. Choose hatching for simplicity and light shading, and cross-hatching when stronger contrast and dimensionality are needed.
Cross-hatching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com