Scumbling is a painting technique involving the application of a thin, opaque layer of paint over a dry underlayer to create a textured, softened effect. This method enhances depth and visual interest in artwork while allowing subtle colors or textures beneath to show through. Discover how mastering scumbling can transform your artistic creations by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
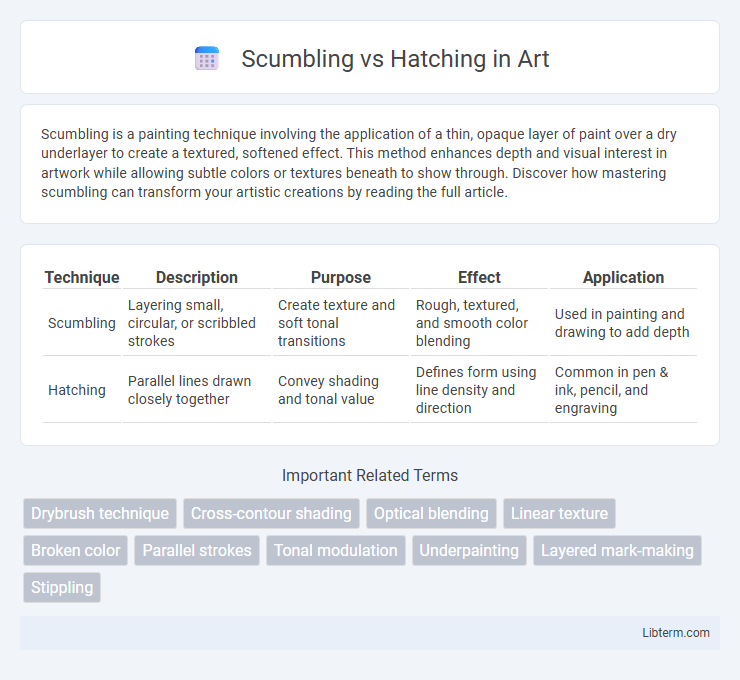
| Technique | Description | Purpose | Effect | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scumbling | Layering small, circular, or scribbled strokes | Create texture and soft tonal transitions | Rough, textured, and smooth color blending | Used in painting and drawing to add depth |
| Hatching | Parallel lines drawn closely together | Convey shading and tonal value | Defines form using line density and direction | Common in pen & ink, pencil, and engraving |
Understanding Scumbling: Definition and Techniques
Scumbling is a painting technique characterized by applying a thin, semi-transparent layer of paint with a dry brush to create texture and subtle color variations. This method enhances depth and atmosphere by allowing underlying layers to show through, often producing a soft, hazy effect. Unlike hatching, which uses parallel lines to build texture and shading, scumbling relies on circular, scrubbing motions to achieve its distinctive visual softness.
What is Hatching? An Overview of the Method
Hatching is a drawing technique that uses closely spaced parallel lines to create tonal or shading effects, enhancing depth and texture in artworks. This method allows artists to control light, shadow, and form by varying the density, length, and direction of lines, making it essential for detailed sketches and realistic renderings. Unlike scumbling, which relies on circular, scribbled marks, hatching provides a more structured and directional approach to building value and dimension.
Key Differences Between Scumbling and Hatching
Scumbling creates texture using small, circular, overlapping strokes to build up tone and depth, while hatching employs parallel lines to indicate shading and form. Scumbling produces a softer, more textured effect, ideal for blending and transitions, whereas hatching emphasizes direction and structure through linear marks. The key difference lies in scumbling's random, layered application versus hatching's organized, repetitive line patterns.
Materials and Tools Needed for Scumbling vs Hatching
Scumbling requires a soft pencil or pastel to create a textured, layered effect using circular, scribbled strokes, often on rough or textured paper to enhance the technique's depth. Hatching relies on fine, linear strokes made with sharp graphite pencils, pens, or ink, and smooth paper surfaces are preferred to allow precise, controlled lines. Both techniques may benefit from blending tools such as tortillons for hatching or fingers for scumbling to achieve desired tonal variations.
The Role of Texture in Scumbling and Hatching
Scumbling creates rich, textured surfaces by applying broken, overlapping layers of paint or pencil strokes that build depth and softness, ideal for atmospheric effects. Hatching uses closely spaced parallel lines to produce texture and tonal variation, giving a more linear and controlled structure to shadows and forms. Both techniques manipulate texture strategically to enhance dimensionality and visual interest in drawings and paintings.
When to Use Scumbling vs Hatching in Art
Scumbling is ideal for creating soft, textured layers and subtle tonal variations, often used in landscapes and atmospheric effects to build depth without harsh lines. Hatching excels in defining form and structure, providing clear directional strokes that convey volume and contour, making it suitable for detailed sketches and figure drawings. Artists choose scumbling when aiming for a loose, blended appearance, while hatching is preferred for precise shading and emphasizing light and shadow contrasts.
Step-by-Step Guide: Scumbling Technique
The scumbling technique involves applying small, circular, and overlapping strokes with a dry brush or pencil to create texture and depth. Begin by lightly layering pigments in a random, circular motion, gradually building intensity to achieve the desired tone and texture. This method contrasts with hatching, which uses parallel or crosshatched lines for shading.
Step-by-Step Guide: Hatching Technique
Hatching technique involves drawing closely spaced parallel or crossed lines to build texture, tone, and shading gradually. Begin by selecting a pencil hardness suitable for your desired darkness, then lightly sketch parallel lines in the direction of the object's form or light source. Increase line density and cross lines at varying angles to intensify shadows and create depth, avoiding harsh or overly uniform strokes for a natural effect.
Common Mistakes in Scumbling and Hatching
Common mistakes in scumbling include applying uneven pressure, which leads to inconsistent texture and unintended patchiness, while hatching errors often stem from irregular line spacing and poor directional control, resulting in a lack of depth and tonal variation. In scumbling, over-layering without allowing underlying colors to show through can create a muddy appearance, whereas in hatching, neglecting to follow the form contours diminishes the effectiveness of shading. Mastery of both techniques requires attention to stroke density, angle, and pressure to achieve smooth transitions and realistic textures.
Comparing Results: Visual Impact of Both Techniques
Scumbling creates soft, textured layers of color that produce a more diffused and atmospheric effect, while hatching uses precise, parallel lines to build form and shading with structured detail. The visual impact of scumbling often appears more organic and blended, offering subtle transitions and depth, whereas hatching emphasizes contour and contrast, resulting in sharper definition and a sense of movement. Artists choose scumbling for mood and softness, and hatching for clarity and linear intensity in their artwork.
Scumbling Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com