Highlighting key information enhances comprehension and retention by drawing attention to critical concepts and details. Effective highlighting techniques include using bold text, color contrasts, or underlining to differentiate important points without overwhelming the reader. Discover practical tips and strategies for perfecting your highlighting in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
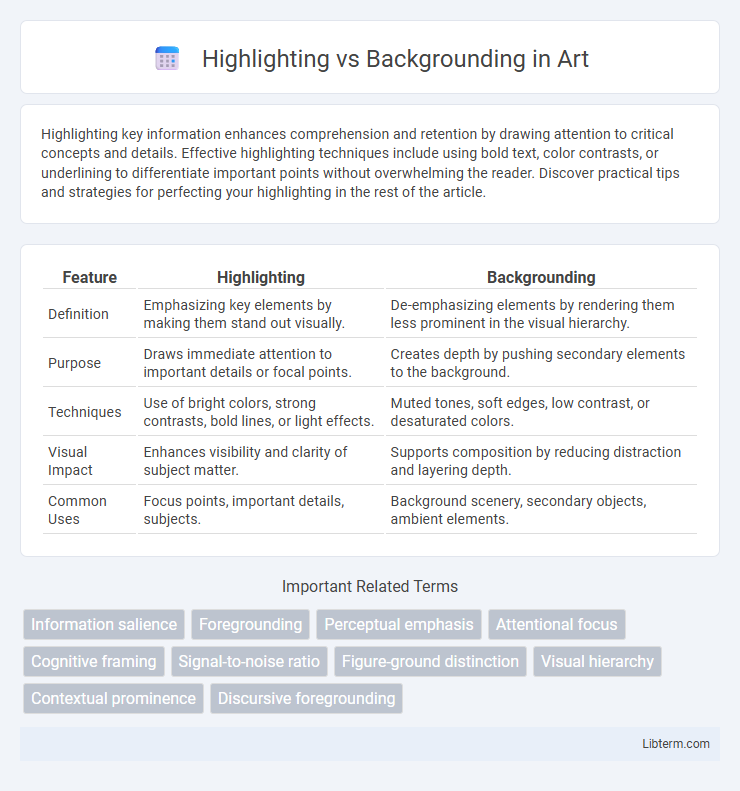
| Feature | Highlighting | Backgrounding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emphasizing key elements by making them stand out visually. | De-emphasizing elements by rendering them less prominent in the visual hierarchy. |
| Purpose | Draws immediate attention to important details or focal points. | Creates depth by pushing secondary elements to the background. |
| Techniques | Use of bright colors, strong contrasts, bold lines, or light effects. | Muted tones, soft edges, low contrast, or desaturated colors. |
| Visual Impact | Enhances visibility and clarity of subject matter. | Supports composition by reducing distraction and layering depth. |
| Common Uses | Focus points, important details, subjects. | Background scenery, secondary objects, ambient elements. |
Understanding Highlighting and Backgrounding
Understanding highlighting involves emphasizing key elements or information to draw attention and improve recall, often used in text annotation and visual design. Backgrounding refers to de-emphasizing or minimizing less critical details to prevent cognitive overload and maintain focus on primary content. Effective use of highlighting and backgrounding enhances information processing and comprehension in educational and professional contexts.
Key Differences Between Highlighting and Backgrounding
Highlighting emphasizes specific elements within a text by making them visually distinct, often using brighter colors or bold fonts, to draw immediate attention to key information. Backgrounding involves altering the backdrop, usually with softer colors or shading, to provide context and enhance readability without overshadowing the primary content. The key difference lies in highlighting's role to spotlight important details versus backgrounding's function to support overall comprehension by creating a subtle contrast.
The Purpose of Highlighting in Content Creation
Highlighting in content creation serves to draw readers' attention to key information, enhancing comprehension and retention of important concepts. It improves the user experience by making content more scannable, allowing audiences to quickly identify critical points or actions. Effective highlighting uses typography, color, or formatting to differentiate essential elements from the background, optimizing content engagement and clarity.
Backgrounding: Providing Context and Depth
Backgrounding enriches content by offering detailed context and depth, enabling readers to understand the broader significance behind key facts or events. This technique involves incorporating historical information, underlying causes, or related developments that frame the main narrative. Effective backgrounding improves comprehension and engagement by connecting isolated details to a cohesive, meaningful storyline.
Techniques for Effective Highlighting
Effective highlighting techniques involve using consistent colors or styles to differentiate key information, improving text clarity and retention. Employing selective emphasis on keywords or phrases with tools like bolding, underlining, or color-coding enhances comprehension without overwhelming readers. Combining visual cues with concise annotations further reinforces important concepts, aiding active reading and information recall.
When to Use Backgrounding in Your Writing
Backgrounding is essential when providing context or supporting information that enriches the main narrative without overshadowing key points. Use backgrounding to set the scene, explain historical developments, or clarify complex concepts, allowing readers to grasp the significance of highlighted details. This technique enhances readability by balancing emphasis and context, ensuring the primary message remains clear while offering comprehensive understanding.
Impact of Highlighting and Backgrounding on Reader Engagement
Highlighting directs reader attention to key information, increasing retention and comprehension by making important details stand out visually. Backgrounding de-emphasizes less critical content, preventing cognitive overload and allowing readers to focus on prioritized concepts. Effective use of highlighting and backgrounding enhances reader engagement by guiding information processing and improving overall readability in texts and digital content.
Common Mistakes in Highlighting and Backgrounding
Common mistakes in highlighting include overusing bold or bright colors, which can overwhelm the reader and obscure key information. In backgrounding, errors often arise from choosing low-contrast or distracting backgrounds that reduce text readability and viewer engagement. Effective visual design balances highlighting important elements while maintaining a clean, unobtrusive background to ensure clear communication.
Tools and Strategies for Balancing Highlighting and Backgrounding
Highlighting involves emphasizing key information using tools such as color-coded markers, digital annotations, and summary notes, while backgrounding incorporates contextual details through marginalia, footnotes, or layered digital comments. Effective strategies for balancing highlighting and backgrounding include using hierarchical color schemes to differentiate main ideas from supporting information, integrating interactive tools like digital sticky notes to provide background context, and employing spaced repetition software to review both highlighted facts and supplementary background material. Leveraging applications like OneNote, Evernote, or Adobe Acrobat enhances the ability to visually distinguish and organize highlighted content alongside comprehensive background data for improved comprehension and retention.
Case Studies: Successful Use of Highlighting vs Backgrounding
Case studies of successful highlighting demonstrate how emphasizing key information improves user engagement by directing attention to critical content, often increasing retention and comprehension rates by up to 30%. In contrast, backgrounding in design effectively de-emphasizes non-essential elements, creating a cleaner interface that reduces cognitive load and enhances overall user experience, as shown in platforms like Spotify and Apple's website redesign. Data from A/B testing reveals that strategic use of highlighting increases click-through rates by 25%, while well-executed backgrounding contributes to a 15% improvement in task completion time.
Highlighting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com