Genre painting captures everyday scenes and ordinary people engaged in common activities, offering a vivid glimpse into daily life. This art form emphasizes realism and narrative, often highlighting social customs and cultural nuances through detailed settings and expressive characters. Discover how genre painting reveals the subtleties of human experience by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
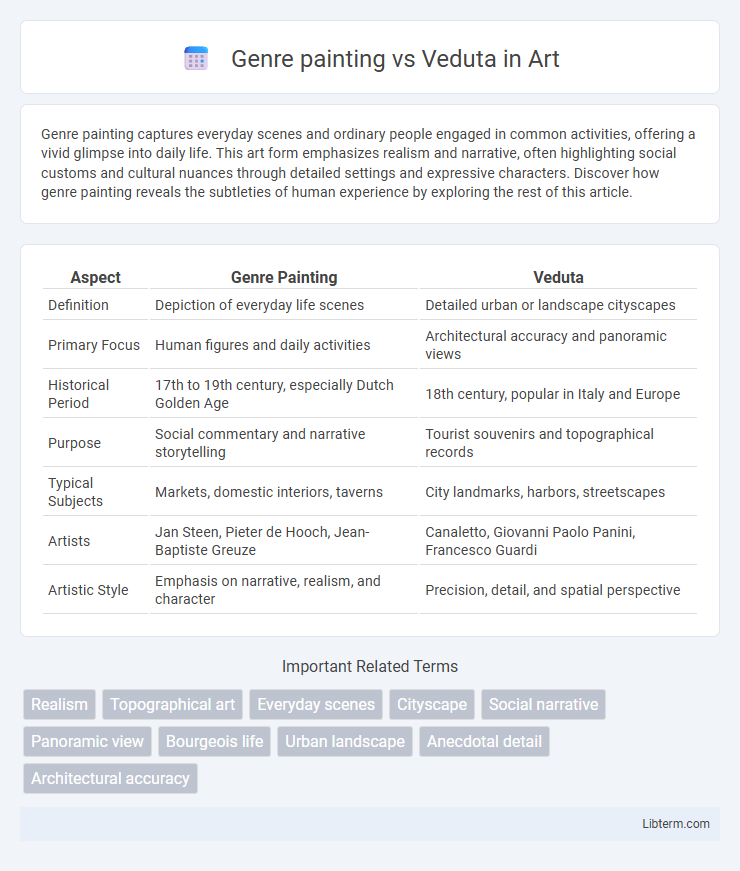
| Aspect | Genre Painting | Veduta |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Depiction of everyday life scenes | Detailed urban or landscape cityscapes |
| Primary Focus | Human figures and daily activities | Architectural accuracy and panoramic views |
| Historical Period | 17th to 19th century, especially Dutch Golden Age | 18th century, popular in Italy and Europe |
| Purpose | Social commentary and narrative storytelling | Tourist souvenirs and topographical records |
| Typical Subjects | Markets, domestic interiors, taverns | City landmarks, harbors, streetscapes |
| Artists | Jan Steen, Pieter de Hooch, Jean-Baptiste Greuze | Canaletto, Giovanni Paolo Panini, Francesco Guardi |
| Artistic Style | Emphasis on narrative, realism, and character | Precision, detail, and spatial perspective |
Introduction to Genre Painting and Veduta
Genre painting captures everyday scenes depicting ordinary people engaged in common activities, emphasizing social interaction and daily life details, often in intimate settings from the 17th century onwards. Veduta, originating in Italy during the Renaissance, refers to highly detailed and accurate cityscape or landscape paintings designed to showcase architectural and geographical precision. Both styles reflect distinct artistic intentions: genre paintings focus on narrative and human behavior, while vedutas prioritize topographical accuracy and visual documentation.
Historical Origins of Genre Painting
Genre painting originated in the 16th-century Netherlands, emphasizing scenes of everyday life and ordinary people engaged in domestic activities, work, and leisure. Unlike veduta, which developed in the 17th and 18th centuries primarily in Italy to depict highly detailed urban landscapes and cityscapes, genre painting captured intimate, narrative moments reflecting social customs and human behavior. This artistic approach gained prominence during the Dutch Golden Age, highlighting moralistic themes and the cultural atmosphere of the time.
The Evolution of Veduta Art
Veduta art evolved from precise, panoramic cityscapes into dynamic representations incorporating atmospheric effects and daily life, distinguishing it from genre painting, which centers on intimate scenes of ordinary people. Early vedutas emphasized architectural accuracy and topographical detail, while later artists infused emotional depth and narrative elements, bridging the gap between documentary and artistic expression. This evolution underscored veduta's shift from mere visual records to evocative artworks capturing the essence of urban experience.
Key Characteristics of Genre Painting
Genre painting captures everyday life scenes with a focus on ordinary people engaged in common activities, emphasizing realism and storytelling through detailed composition. Key characteristics include intimate settings, expressive facial expressions, and narrative elements that reflect social customs and domestic environments. Unlike Veduta, which is characterized by highly detailed urban landscapes and architectural accuracy, genre painting centers on human interaction and cultural representation.
Distinct Features of Veduta
Veduta paintings are characterized by their highly detailed and accurate depiction of cityscapes or landscapes, often rendered with precise architectural elements and panoramic views. Unlike genre painting, which focuses on scenes of everyday life and intimate moments, vedutas emphasize topographical accuracy and expansive perspectives to capture specific locations. This meticulous representation serves both artistic and documentary purposes, highlighting the grandeur and geography of urban environments.
Notable Artists in Genre Painting
Genre painting showcases everyday life scenes, with notable artists like Johannes Vermeer, Pieter de Hooch, and Jean-Baptiste-Simeon Chardin leading the movement. These artists emphasized domestic interiors, social activities, and ordinary people in their work, capturing detailed narratives rich in cultural context. Veduta, distinct from genre painting, focuses on highly detailed cityscapes and landscapes, with prominent vedutisti including Canaletto and Giovanni Paolo Panini.
Influential Vedutisti and Their Works
Influential vedutisti such as Canaletto and Giovanni Battista Piranesi transformed 18th-century art by meticulously capturing urban landscapes with architectural precision, contrasting the intimate, everyday scenes typical of genre painting. Canaletto's detailed views of Venice, like "The Grand Canal," emphasized perspective and vibrant city life, while Piranesi's etchings, such as "Carceri d'Invenzione," showcased imaginative and dramatic interpretations of classical ruins. Their works elevated veduta to a celebrated genre that combined documentary accuracy with artistic grandeur, distinguishing it from the narrative-driven approach of genre painting.
Genre Painting vs Veduta: Thematic Contrasts
Genre painting captures everyday scenes emphasizing human activity and social interactions, highlighting the ordinary lives of people. Veduta, in contrast, offers meticulously detailed cityscapes or landscapes, focusing on architectural accuracy and spatial perspective. Thematic contrasts arise as genre painting explores narrative and emotional depth, while veduta prioritizes visual documentation and geographic representation.
Techniques and Mediums Used in Both Styles
Genre painting typically employs oil on canvas or wood panels, utilizing fine brushwork to capture everyday scenes with detailed human expressions and textures. Veduta relies heavily on precise perspective techniques and often uses watercolor or oil mediums to depict expansive cityscapes and architectural details with topographical accuracy. Both styles emphasize meticulous detail, but genre paintings prioritize intimate realism, whereas vedute focus on spatial accuracy and linear perspective.
Lasting Influence on Contemporary Art
Genre painting, with its detailed depiction of everyday life and social interactions, has profoundly influenced contemporary narrative art by emphasizing relatable human experiences and cultural contexts. Veduta, characterized by precise, panoramic cityscapes, continues to inspire modern urban photography and digital art through its commitment to architectural accuracy and atmospheric detail. Both genres contribute uniquely to contemporary art's exploration of reality, space, and storytelling.
Genre painting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com