Monochrome designs emphasize simplicity by using a single color or varying tones of one hue, creating a cohesive and elegant visual impact. This approach enhances focus, making your content or decor appear sophisticated and unified without distractions. Discover how embracing monochrome can transform your style by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
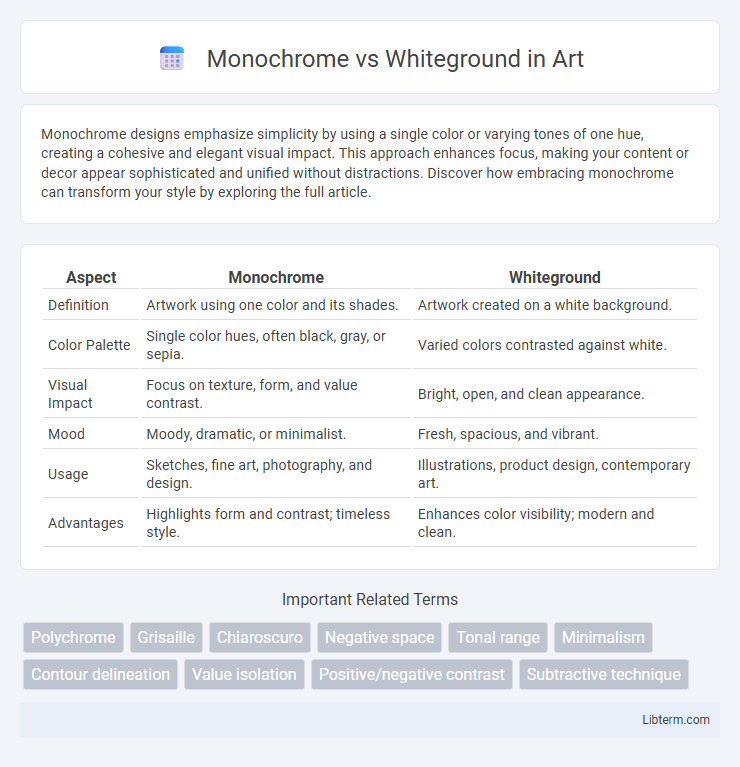
| Aspect | Monochrome | Whiteground |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Artwork using one color and its shades. | Artwork created on a white background. |
| Color Palette | Single color hues, often black, gray, or sepia. | Varied colors contrasted against white. |
| Visual Impact | Focus on texture, form, and value contrast. | Bright, open, and clean appearance. |
| Mood | Moody, dramatic, or minimalist. | Fresh, spacious, and vibrant. |
| Usage | Sketches, fine art, photography, and design. | Illustrations, product design, contemporary art. |
| Advantages | Highlights form and contrast; timeless style. | Enhances color visibility; modern and clean. |
Introduction to Monochrome and Whiteground
Monochrome design uses varying shades of a single color, creating a cohesive and visually harmonious aesthetic that emphasizes simplicity and depth. Whiteground, by contrast, employs a white background to enhance clarity, focus, and contrast, allowing foreground elements to stand out sharply. Both approaches prioritize minimalism but differ in their method of achieving visual balance and emphasis.
Defining Monochrome Art
Monochrome art utilizes a single color or varying shades of one hue to create depth and contrast, emphasizing texture and form rather than a spectrum of colors. This style accentuates minimalism and abstraction by stripping away distractions and focusing on tonal variations and composition. Whiteground, in contrast, typically involves artworks set against a stark white background to highlight the subject without color complexity.
Understanding Whiteground Techniques
Whiteground techniques in ancient Greek pottery involve painting figures in opaque white slip on a light background, allowing for detailed and delicate portrayals distinct from monochrome styles that use a single color tone. This method enables greater emphasis on fine line work and realistic depiction of mythological and everyday scenes, enhancing visual clarity and narrative depth. Understanding whiteground requires analyzing pigment composition and firing processes that preserve the white slip's brightness and intricate brushstrokes.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Monochrome design traces its origins to early photography and printmaking in the 19th century, where limited color palettes necessitated the use of a single color or shades of one hue. Whiteground, emerging from classical art and later minimalism in the 20th century, emphasizes the use of white or neutral backgrounds to enhance contrast and focus on form. Both styles evolved through technological advances and shifting artistic philosophies, influencing contemporary graphic and digital design approaches.
Visual Impact: Monochrome vs Whiteground
Monochrome enhances visual impact by creating a unified, dramatic effect through consistent shades of a single color, emphasizing texture and form. Whiteground provides a clean, minimalist backdrop that highlights subjects with clarity and contrast, promoting a sense of spaciousness and focus. Both techniques manipulate viewer perception differently, with monochrome offering emotional depth and whiteground delivering crisp simplicity.
Popular Artists and Influences
Monochrome art, favored by artists like Kazimir Malevich and Yves Klein, emphasizes single-color palettes to explore form and emotion without distraction, profoundly influencing abstract expressionism and minimalism. Whiteground techniques, employed by painters such as Robert Ryman and Agnes Martin, use white backgrounds to highlight subtle texture and tone variations, shaping contemporary art's focus on purity and spatial depth. Both approaches have significantly impacted modern visual culture by redefining perception and encouraging introspective viewer experiences.
Techniques and Materials Used
Monochrome artworks typically utilize a single color or varying shades of one hue, often employing techniques such as layering, glazing, and texture manipulation to create depth and visual interest. Artists working with whiteground pottery use a white slip as a base, applying fine, detailed painting with mineral-based pigments before firing, which allows for delicate, intricate designs and a smooth finish. Both methods emphasize precise control over materials to achieve distinctive aesthetic effects, with monochrome focusing on tonal variation and whiteground highlighting clarity and detail.
Emotional and Psychological Effects
Monochrome imagery evokes a sense of nostalgia and introspection by emphasizing contrast and texture, often enhancing emotional depth through its stripped-down color palette. Whiteground backgrounds promote clarity and openness, creating a calming psychological effect that reduces visual distractions and fosters focus. The stark simplicity of monochrome can intensify mood, while whiteground spaces encourage mental clarity and a sense of spaciousness.
Contemporary Applications and Trends
Monochrome design emphasizes a single color palette to create sleek, cohesive visuals often seen in modern branding, website interfaces, and product packaging. Whiteground techniques leverage white or neutral backgrounds to enhance readability, highlight key elements, and foster minimalist aesthetics popular in contemporary UI/UX design and advertising. Recent trends blend monochrome schemes with whiteground layouts to balance boldness and clarity, driving engagement in digital media and print campaigns.
Choosing Between Monochrome and Whiteground
Choosing between Monochrome and Whiteground depends on the desired aesthetic and functional impact of the design. Monochrome enhances visual coherence through a unified color palette, emphasizing shape and texture, while Whiteground offers clarity and a clean, minimal backdrop that highlights content without distraction. Consider Monochrome for mood-driven, artistic expression and Whiteground for professional, versatile presentations focused on readability and simplicity.
Monochrome Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com