Intarsia is a woodworking technique that involves fitting together pieces of wood veneer to create intricate, mosaic-like patterns or images, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of furniture and decorative objects. This detailed craft requires precision and skill to seamlessly blend different wood tones and grains, adding depth and texture to the final design. Explore the rest of this article to discover how intarsia can transform your woodworking projects with timeless elegance.
Table of Comparison
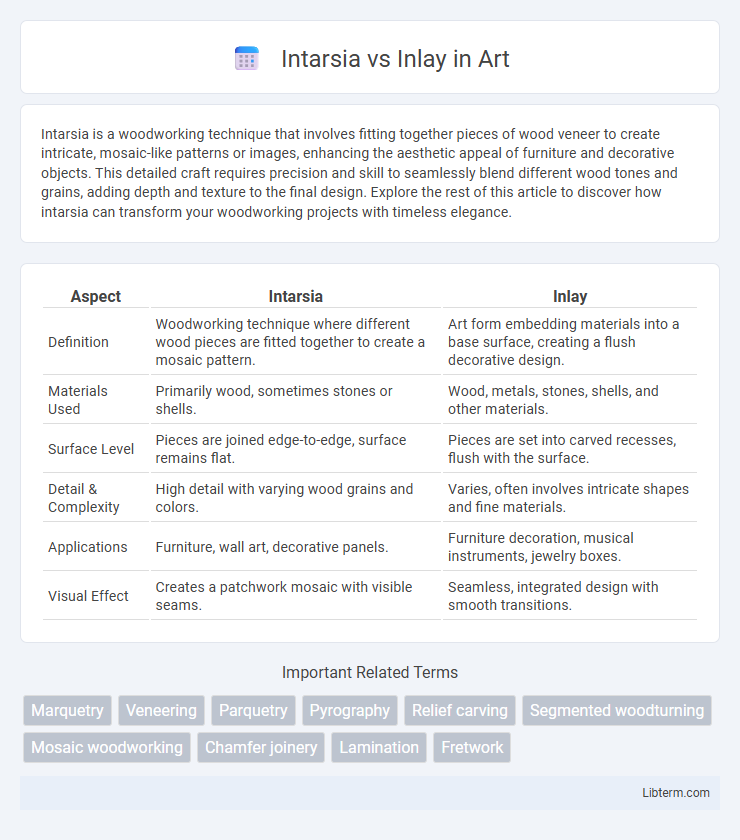
| Aspect | Intarsia | Inlay |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Woodworking technique where different wood pieces are fitted together to create a mosaic pattern. | Art form embedding materials into a base surface, creating a flush decorative design. |
| Materials Used | Primarily wood, sometimes stones or shells. | Wood, metals, stones, shells, and other materials. |
| Surface Level | Pieces are joined edge-to-edge, surface remains flat. | Pieces are set into carved recesses, flush with the surface. |
| Detail & Complexity | High detail with varying wood grains and colors. | Varies, often involves intricate shapes and fine materials. |
| Applications | Furniture, wall art, decorative panels. | Furniture decoration, musical instruments, jewelry boxes. |
| Visual Effect | Creates a patchwork mosaic with visible seams. | Seamless, integrated design with smooth transitions. |
Understanding Intarsia and Inlay: Key Definitions
Intarsia involves fitting pieces of wood veneer or other materials into a surface to create a mosaic-like pattern, emphasizing detailed craftsmanship and varied textures. Inlay refers to embedding contrasting materials such as metals, shells, or stones flush into a base surface, producing a smooth and often ornamental design. Both techniques enhance decorative woodwork but differ fundamentally in method and visual effect.
Historical Roots: Evolution of Intarsia and Inlay
Intarsia and inlay both trace their historical roots to ancient craftsmanship, with intarsia evolving from the intricate wood mosaic techniques popularized during the Italian Renaissance in the 15th century, while inlay dates back even further to ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, where artisans embedded precious materials into wood and metal surfaces. Intarsia developed as a distinct art form emphasizing precise fitting of wood pieces to create pictorial representations, contrasting with inlay, which traditionally involves embedding contrasting materials such as mother-of-pearl, ivory, or metal into cut cavities for decorative enhancement. The evolution of both techniques reflects shifts in artistic focus and material availability, leading to their enduring applications in furniture, jewelry, and architectural ornamentation.
Materials Used in Intarsia and Inlay Work
Intarsia typically involves using various types of wood, such as walnut, cherry, maple, and oak, to create intricate patterns by fitting together shaped pieces like a puzzle. Inlay work often incorporates diverse materials including wood, metal, shell, ivory, and gemstones, embedded into a solid base to form decorative designs. Both techniques require precision but differ in material layering; intarsia pieces are assembled side-by-side while inlays are set flush within the surface.
Techniques of Craftsmanship: Intarsia vs Inlay
Intarsia involves fitting together carefully shaped, differently colored wood pieces to create a mosaic-like image on a flat surface, emphasizing depth through wood grain and color variation. Inlay consists of embedding contrasting materials such as wood, metal, or shell into carved recesses on a base surface, producing intricate decorative patterns that are flush with the surface. Both techniques require precise cutting and fitting skills but differ in how dimensionality and texture are achieved within woodworking craftsmanship.
Design Possibilities: Intarsia vs Inlay Patterns
Intarsia offers intricate design possibilities by fitting differently shaped wood pieces together to create detailed, mosaic-like patterns with varied textures and colors. Inlay involves embedding contrasting materials such as metals, stones, or woods into a solid base, allowing for precise, decorative patterns that blend seamlessly with the surface. Both techniques enable unique artistic expression, but intarsia emphasizes three-dimensional depth while inlay focuses on surface-level embellishment.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Intarsia woodworking involves fitting together individual wood pieces, creating a durable surface less prone to damage over time due to the thickness and solid nature of each piece. Inlay technique embeds thin materials like wood, metal, or shell into a substrate, which can be more susceptible to wear and requires careful maintenance to avoid lifting or cracking. Intarsia generally demands less frequent maintenance, while inlay surfaces need regular sealing and gentle cleaning to preserve their intricate details and durability.
Aesthetic Differences and Visual Impact
Intarsia features distinct wooden pieces fitted together to create intricate, mosaic-like patterns that emphasize texture and depth, offering a sculptural quality to the surface. Inlay uses contrasting materials such as metal, shell, or different wood veneers embedded flush within the base wood, producing a smooth, decorative contrast that accentuates fine details with subtle elegance. The visual impact of intarsia is bold and tactile, while inlay provides refined, delicate embellishments that enhance the overall craftsmanship.
Popular Applications in Modern Design
Intarsia is widely applied in woodworking and furniture design for creating intricate, mosaic-like patterns by fitting different wood pieces together, enhancing aesthetic appeal in cabinets and flooring. Inlay techniques are popular in jewelry and musical instruments, embedding materials such as mother-of-pearl, metal, or precious stones into surfaces to add decorative detail and value. Both methods remain favored in luxury interiors and custom craftsmanship, offering unique textural contrasts and artistic expression in contemporary design.
Cost and Time Investment Comparison
Intarsia woodworking typically requires more time and higher costs due to its intricate process of cutting and fitting multiple wood pieces to create detailed images, often involving various wood types and finishes. Inlay involves embedding contrasting materials like metal, shell, or wood into a base surface, generally resulting in lower material costs and faster completion times due to simpler preparation and installation. Both techniques demand skilled craftsmanship, but intarsia's complexity usually translates into greater time investment and expense compared to inlay projects.
Choosing Between Intarsia and Inlay: Key Factors
Choosing between intarsia and inlay depends on the desired depth and complexity of the design; intarsia involves fitting pieces of wood together to create a mosaic with a three-dimensional effect, while inlay consists of embedding materials into a solid surface for a flush finish. Consider the type of materials used, with intarsia often highlighting wood grain contrasts and inlay incorporating materials like metal, shell, or stone for decorative accents. The skill level and tools required also influence the choice, as intarsia demands precise cutting and assembly, whereas inlay requires careful routing and insertion, impacting project cost and time.
Intarsia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com