Sinopia is a rich, deep red pigment historically used in fresco painting and as an underdrawing color in artwork. Its earthy tones provide warmth and depth, making it a favorite among artists seeking natural and rustic hues. Discover how Sinopia's unique qualities can enhance your artistic projects by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
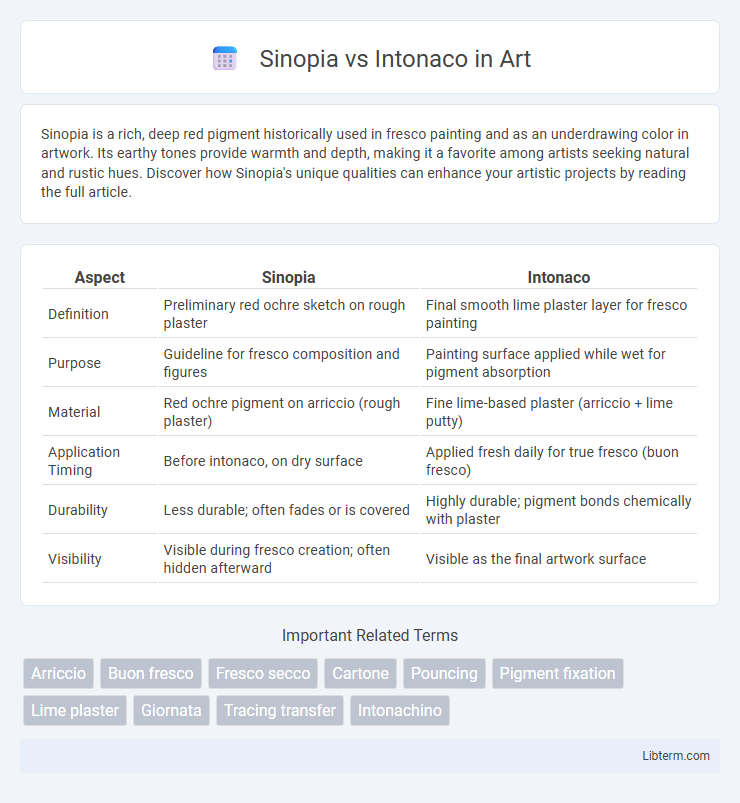
| Aspect | Sinopia | Intonaco |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Preliminary red ochre sketch on rough plaster | Final smooth lime plaster layer for fresco painting |
| Purpose | Guideline for fresco composition and figures | Painting surface applied while wet for pigment absorption |
| Material | Red ochre pigment on arriccio (rough plaster) | Fine lime-based plaster (arriccio + lime putty) |
| Application Timing | Before intonaco, on dry surface | Applied fresh daily for true fresco (buon fresco) |
| Durability | Less durable; often fades or is covered | Highly durable; pigment bonds chemically with plaster |
| Visibility | Visible during fresco creation; often hidden afterward | Visible as the final artwork surface |
Introduction to Sinopia and Intonaco
Sinopia is a traditional preparatory layer made from red earth pigment mixed with clay and water, used historically as an underdrawing on plaster surfaces before applying fresco paint. Intonaco is the smooth, wet plaster layer applied over the sinopia, serving as the actual painting surface for fresco artists, allowing pigments to bond chemically as it dries. Understanding the relationship between sinopia and intonaco is crucial for preserving and restoring frescoes, as each layer plays a distinct role in the fresco technique.
Historical Background and Origins
Sinopia originated in ancient Etruscan and Roman mural painting as the preparatory underdrawing for frescoes, named after the red ochre pigment sourced from Sinop, Turkey. Intonaco refers to the final smooth plaster layer applied over the sinopia, essential in true fresco technique to bind pigments with lime, a practice perfected during the Italian Renaissance. The differentiation between sinopia and intonaco highlights the meticulous layering process crucial for enduring fresco masterpieces in historical art.
Definition of Sinopia
Sinopia is a reddish-brown pigment traditionally used as an underdrawing or preliminary sketch on plaster surfaces before applying intonaco, the smooth, wet plaster layer in fresco painting. This preparatory layer is essential for transferring detailed designs onto the intonaco, ensuring accurate execution of the fresco. While sinopia serves as the detailed guide, intonaco forms the final surface that absorbs pigments, resulting in durable and vibrant frescoes.
Definition of Intonaco
Intonaco is the final, smooth layer of plaster applied to a wall or ceiling, typically made from lime, sand, and water, providing a durable and receptive surface for fresco painting. Sinopia refers to the preliminary reddish-brown underdrawing executed on the rough arriccio layer beneath the intonaco, guiding the artist's design. The intonaco layer must remain wet during painting to ensure the pigments chemically bond with the plaster, a key technique in true fresco art.
Materials and Techniques Used
Sinopia involves a preliminary reddish-brown pigment sketch applied directly onto the plaster surface to outline fresco designs, utilizing natural iron oxide pigments for durability. Intonaco refers to the final, smooth layer of wet lime plaster, typically composed of lime putty mixed with fine sand, which serves as the canvas for painting in fresco techniques. The sinopia sketch guides artists during the intonaco application, ensuring precise composition before pigments are absorbed into the fresh plaster for lasting color.
Role in Fresco Painting
Sinopia serves as the detailed underdrawing in fresco painting, outlining the composition and guiding the application of intonaco. Intonaco is the smooth, wet plaster layer applied over the sinopia, providing the essential surface onto which pigments chemically bond during the fresco process. The durability and vibrancy of fresco colors depend on the precise interaction between the sinopia's preparatory sketch and the intonaco's calcium carbonate matrix.
Key Differences Between Sinopia and Intonaco
Sinopia is a preparatory underdrawing made with red earth pigment used as a guide for fresco painting, while Intonaco is the final, smooth layer of wet plaster applied on walls to receive the fresco. Sinopia typically appears as a rough sketch or outline beneath the Intonaco, helping artists plan composition and details before applying paint on the fresh plaster surface. The durability of Intonaco makes it essential for fresco preservation, whereas Sinopia serves primarily as a transient guide for the artist's work.
Preservation and Restoration Challenges
Sinopia, the preparatory drawing for frescoes, is highly fragile and often deteriorates due to exposure during restoration, requiring meticulous conservation techniques to preserve its delicate pigment layers. Intonaco, the final layer of wet plaster applied for fresco painting, faces challenges such as substrate erosion and moisture damage, demanding precise environmental control to maintain its integrity. Effective preservation of both requires advanced methods like non-invasive imaging and controlled humidity to mitigate degradation and support restoration accuracy.
Artistic Significance and Impact
Sinopia serves as the essential preparatory underdrawing in fresco painting, providing artists with a precise guide that ensures accurate composition and detail fidelity during the intonaco application. Intonaco, the thin, fresh layer of plaster applied over the sinopia, is critical for the fresco's longevity and vibrant coloration, as pigments chemically bond with the wet surface. The interplay between sinopia and intonaco defines the fresco technique's artistic significance, merging meticulous planning with durable, luminous artistry that has influenced mural art across centuries.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Sinopia and Intonaco
Choosing between Sinopia and Intonaco depends on the specific requirements of the fresco project, with Sinopia serving as the detailed preliminary sketch that guides the artwork's layout, while Intonaco acts as the final wet plaster layer where pigments are applied for durability and vibrancy. For artists prioritizing precision in composition, Sinopia is essential, whereas Intonaco is crucial for achieving the fresco's lasting color and texture. Understanding their distinct functions ensures a successful fresco technique and preservation.
Sinopia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com