Silhouette art captures the essence of a subject by using strong contrasts between light and dark, creating striking shapes without detailed features. This technique enhances visual storytelling by emphasizing contours and forms, making it a powerful tool in photography, design, and illustration. Discover how silhouettes can transform your creative projects by exploring the full article.
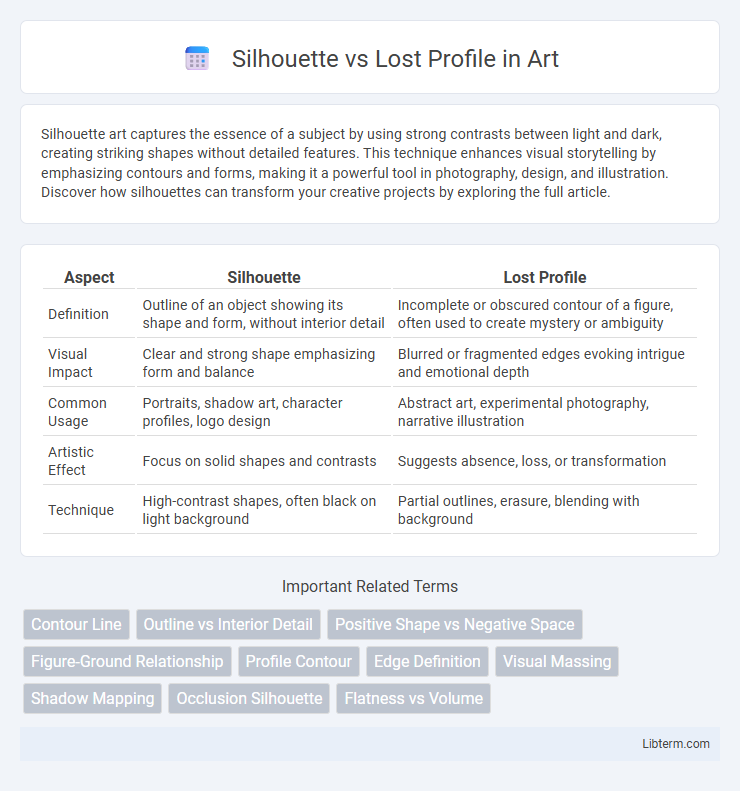
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Silhouette | Lost Profile |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Outline of an object showing its shape and form, without interior detail | Incomplete or obscured contour of a figure, often used to create mystery or ambiguity |
| Visual Impact | Clear and strong shape emphasizing form and balance | Blurred or fragmented edges evoking intrigue and emotional depth |
| Common Usage | Portraits, shadow art, character profiles, logo design | Abstract art, experimental photography, narrative illustration |
| Artistic Effect | Focus on solid shapes and contrasts | Suggests absence, loss, or transformation |
| Technique | High-contrast shapes, often black on light background | Partial outlines, erasure, blending with background |
Understanding Silhouette: Definition and Significance
Silhouette in design represents the outline or contour of an object, crucial for quick visual recognition and aesthetic appeal, especially in photography and graphic design. Its significance lies in conveying the shape and essence of a subject with minimal detail, enhancing clarity and emotional impact. Understanding silhouette helps artists and designers create strong, memorable images by emphasizing form without reliance on color or texture.
Lost Profile Explained: Key Characteristics
Lost Profile refers to a hair or facial contour where the natural outline fades seamlessly into the skin, creating a smooth, almost invisible edge. This aesthetic emphasizes subtle transitions with minimal contrast between the hairline or beard and the skin, often used to achieve a natural, soft appearance. Unlike a defined Silhouette, the Lost Profile avoids sharp borders, prioritizing gradual blending and understated detailing.
Historical Evolution of Silhouette and Lost Profile
The historical evolution of silhouette art traces back to the 18th century when profile portraits were created using black paper cutouts, serving as an affordable alternative to painted miniatures. Lost profile techniques evolved from traditional silhouette methods, incorporating photographic and digital methods to reconstruct or preserve profiles that were once impossible to capture accurately. This progression highlights a shift from manual craftsmanship to technological integration in preserving the essence of personal or cultural identity through profile imagery.
Visual Differences: Silhouette vs Lost Profile
The silhouette emphasizes a clear, solid shape with well-defined contours, creating an easily recognizable and bold visual impression. In contrast, the lost profile features fragmented or obscured edges, giving it a more abstract and less distinct appearance. These visual differences highlight the silhouette's role in clarity and simplicity while the lost profile conveys ambiguity and abstraction.
Applications in Fashion and Design
Silhouette emphasizes the overall shape and outline of a garment, making it essential for designing fashion collections with distinct profiles and seasonal trends. Lost profile techniques focus on detailed, hidden patterns and textures that emerge upon closer inspection, adding depth and uniqueness to fashion and accessory designs. Both approaches are crucial in contemporary design for creating visually compelling and innovative apparel that appeals to diverse consumer preferences.
Silhouette vs Lost Profile in Art and Photography
Silhouette and lost profile techniques in art and photography emphasize contour and shape while minimizing detail, creating powerful visual narratives through contrast and shadow. Silhouette captures the outline against a bright background, highlighting form without internal details, whereas lost profile obscures edges through soft blending, producing ambiguity and ethereal effects. Both methods exploit light and shadow interplay to evoke emotion and enhance subject mood, with silhouette offering sharper clarity and lost profile providing subtle, immersive depth.
Pros and Cons of Using Silhouette
Silhouette excels in user-friendly design and advanced vector editing tools, making it ideal for creating precise and intricate cutting projects. It supports a wide range of materials and integrates seamlessly with various printers and cutters, enhancing versatility and workflow efficiency. However, Silhouette's software can have a steeper learning curve for beginners and may require frequent updates or subscriptions for access to premium features.
Pros and Cons of Using Lost Profile
Lost Profile offers superior precision in fitting complex and irregular denture geometries, enhancing patient comfort compared to Silhouette. Its advanced 3D scanning technology reduces manual adjustments but may require longer initial setup time and higher software costs. While Lost Profile excels in accuracy, users might face a steeper learning curve and increased dependency on digital workflows versus the more user-friendly Silhouette system.
Choosing Between Silhouette and Lost Profile
Choosing between Silhouette and Lost Profile hinges on the specific needs of 3D scanning and modeling tasks, with Silhouette excelling in high-precision profile detection and Lost Profile offering advanced algorithms for reconstructing incomplete shapes. Silhouette provides superior edge detection and is ideal for applications requiring exact contour extraction, while Lost Profile is preferred for handling noisy or partial data through robust profile recovery techniques. Evaluating factors such as scan complexity, required accuracy, and processing speed will help determine the optimal solution for your 3D capture workflow.
Future Trends in Silhouette and Lost Profile Usage
Future trends indicate increasing adoption of Silhouette technology in fashion and design due to its precision in shape analysis and customization capabilities. Lost Profile methods, however, continue to advance in archaeological and forensic fields, leveraging AI to reconstruct incomplete data with higher accuracy. Integration of machine learning with both Silhouette and Lost Profile techniques promises enhanced predictive modeling and real-time application across diverse industries.
Silhouette Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com