Etching is a precise technique used to create intricate designs on metal surfaces by applying acid or other corrosive substances. This process allows artists and manufacturers to produce detailed patterns and textures that are both durable and visually striking. Discover how etching can transform your projects by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
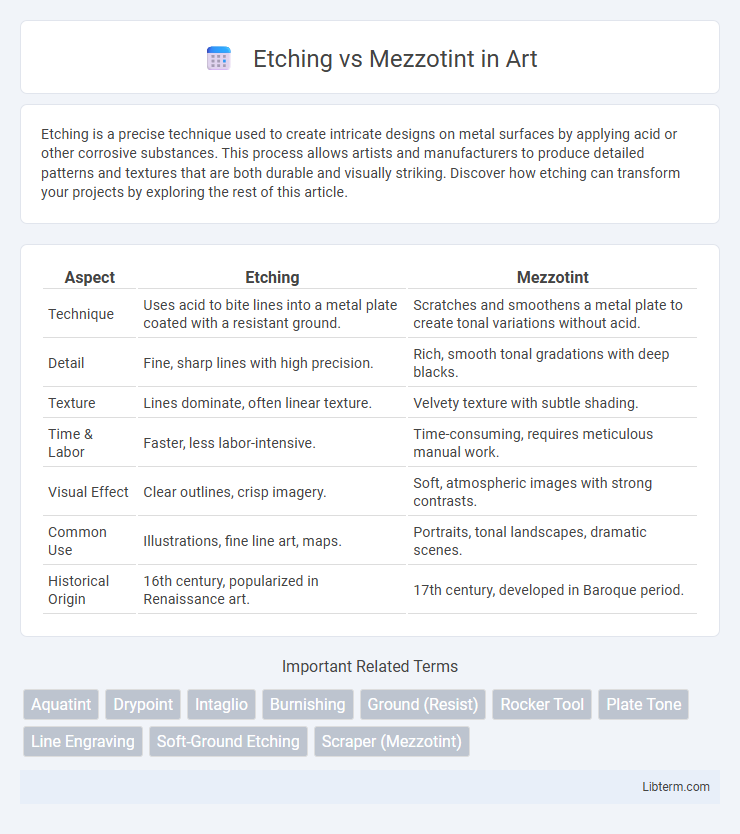
| Aspect | Etching | Mezzotint |
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Uses acid to bite lines into a metal plate coated with a resistant ground. | Scratches and smoothens a metal plate to create tonal variations without acid. |
| Detail | Fine, sharp lines with high precision. | Rich, smooth tonal gradations with deep blacks. |
| Texture | Lines dominate, often linear texture. | Velvety texture with subtle shading. |
| Time & Labor | Faster, less labor-intensive. | Time-consuming, requires meticulous manual work. |
| Visual Effect | Clear outlines, crisp imagery. | Soft, atmospheric images with strong contrasts. |
| Common Use | Illustrations, fine line art, maps. | Portraits, tonal landscapes, dramatic scenes. |
| Historical Origin | 16th century, popularized in Renaissance art. | 17th century, developed in Baroque period. |
Introduction to Etching and Mezzotint
Etching is a printmaking technique that uses acid to create detailed designs on a metal plate, offering fine lines and precise textures ideal for intricate artwork. Mezzotint, by contrast, creates tonal gradations by roughening the plate surface, producing rich, velvety blacks and smooth transitions suited for dramatic, high-contrast images. Both methods date back to the 17th century and remain essential techniques in intaglio printmaking, each providing unique artistic effects and textures.
Historical Background of Printmaking Techniques
Etching originated in the 16th century as a prominent intaglio printmaking technique where acid bites into a metal plate to create designs, widely used by artists like Rembrandt to achieve fine lines and detailed textures. Mezzotint, developed later in the 17th century, revolutionized tonal variation by creating gradients from dark to light through the roughening and smoothing of the metal surface, enabling rich, velvety blacks and subtle shading. Both techniques represent significant advancements in printmaking history, with etching emphasizing line work and mezzotint focusing on tonal depth, influencing artistic expression in the Baroque and Rococo periods.
What is Etching?
Etching is an intaglio printmaking technique where acid is used to bite into a metal plate, creating intricate designs by selectively corroding exposed areas. Artists coat a metal surface with an acid-resistant ground, scratch through it to reveal the metal, then submerge the plate in acid to produce detailed lines and textures. This process allows for fine, precise detail and tonal variation, distinguishing etching from mezzotint's focus on rich, velvety blacks and smooth gradations.
What is Mezzotint?
Mezzotint is a printmaking technique that produces rich tonal variations by roughening a metal plate with a rocker tool to create a textured surface that holds ink. Unlike etching, which uses acid to bite lines into the plate, mezzotint allows for smooth gradations from dark to light by selectively smoothing areas to reduce ink retention. This method is prized for its ability to render deep shadows and subtle highlights, making it ideal for producing highly detailed, atmospheric images.
Key Differences Between Etching and Mezzotint
Etching involves using acid to incise designs into a metal plate, enabling precise line work and fine detail, while mezzotint relies on roughening the plate's surface to create rich tonal gradients and deep blacks through a labor-intensive scraping and burnishing process. Etching allows for quicker production and sharper lines, ideal for intricate imagery, whereas mezzotint excels in producing velvety texture and smooth shading suitable for portraits and atmospheric effects. The fundamental difference lies in etching's chemical bite versus mezzotint's mechanical manipulation of the plate surface for tonal variation.
Tools and Materials Used in Each Process
Etching employs a metal plate coated with a resistant ground, a pointed etching needle to draw lines through the ground, and acid baths to bite into exposed metal areas, creating the image. Mezzotint uses a rocker tool with a curved blade to roughen the entire plate surface, producing a textured, ink-holding ground, followed by scrapers and burnishers to smooth specific areas for lighter tones. The distinct tools and materials--acid and etching needle for etching, rocker and burnisher for mezzotint--directly influence each technique's ability to render fine lines versus rich tonal gradations.
Artistic Effects and Visual Styles
Etching produces sharp, detailed lines with a crisp contrast, making it ideal for intricate designs and fine textures. Mezzotint offers rich tonal gradients and deep, velvety blacks, creating dramatic shadows and a painterly, soft appearance. Artists choose etching for precision and clarity, while mezzotint excels at achieving atmospheric depth and lush shading.
Applications in Contemporary Art
Etching and mezzotint are both intaglio printmaking techniques widely used in contemporary art for creating rich textures and tonal contrasts. Etching allows artists to produce detailed line work and intricate designs by using acid to bite into metal plates, making it ideal for fine narratives and graphic art. Mezzotint, known for its ability to generate deep, velvety shadows and smooth gradient tones, is often employed in contemporary portraiture and abstract works that require subtle tonal variation and atmospheric depth.
Pros and Cons of Etching vs Mezzotint
Etching offers precise line work and fine detail, making it ideal for intricate designs, but it tends to produce lighter tonal values compared to mezzotint. Mezzotint excels in creating rich, velvety blacks and smooth tonal gradients, perfect for dramatic contrasts, though it requires a more labor-intensive process and longer preparation time. While etching allows for quicker experimentation and easier correction, mezzotint delivers superior depth and texture at the expense of flexibility.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Artwork
Etching offers precise lines and detailed textures through acid-resistant grounds, ideal for artists seeking sharp, controlled imagery in their prints. Mezzotint provides rich tonal gradients and velvety blacks by roughening the plate's surface, perfect for creating dramatic contrasts and depth. Selecting between etching and mezzotint depends on whether your artwork emphasizes intricate line work or smooth tonal transitions to best convey your creative vision.
Etching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com