Composition serves as the foundation for effective communication, blending ideas, structure, and style to convey a clear message. Mastering composition techniques enhances your ability to craft compelling narratives or persuasive arguments. Explore the rest of the article to unlock key strategies for improving your writing skills.
Table of Comparison
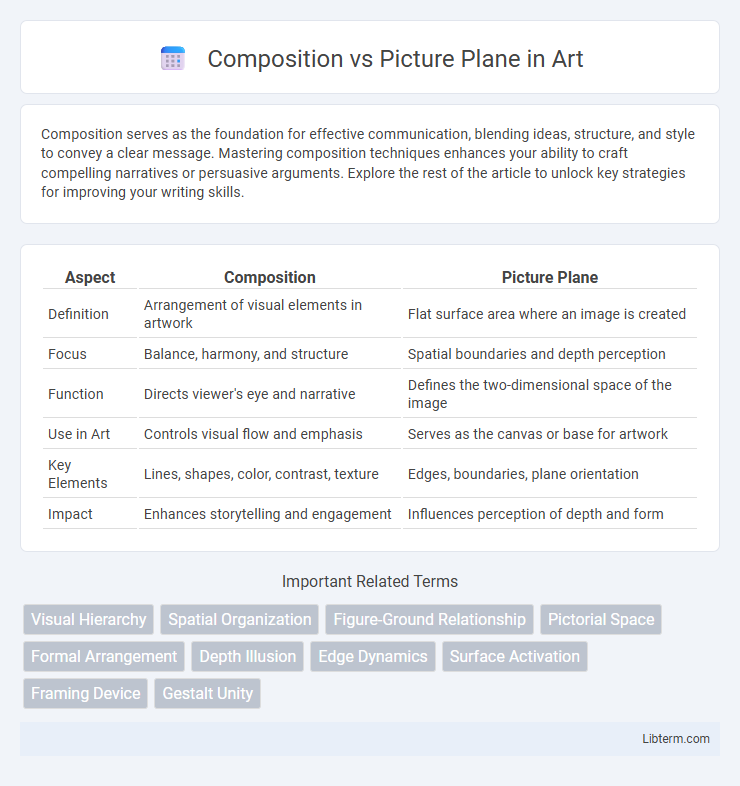
| Aspect | Composition | Picture Plane |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Arrangement of visual elements in artwork | Flat surface area where an image is created |
| Focus | Balance, harmony, and structure | Spatial boundaries and depth perception |
| Function | Directs viewer's eye and narrative | Defines the two-dimensional space of the image |
| Use in Art | Controls visual flow and emphasis | Serves as the canvas or base for artwork |
| Key Elements | Lines, shapes, color, contrast, texture | Edges, boundaries, plane orientation |
| Impact | Enhances storytelling and engagement | Influences perception of depth and form |
Understanding Composition in Art
Understanding composition in art involves arranging visual elements within the picture plane to create balance, harmony, and focal points that guide the viewer's eye. The picture plane serves as the flat surface upon which artists organize shapes, lines, colors, and textures to convey meaning and emotional impact. Mastering the relationship between composition and the picture plane enhances narrative clarity and aesthetic appeal in artworks.
Defining the Picture Plane
Defining the picture plane involves understanding it as the flat, two-dimensional surface onto which a composition is projected, serving as the interface between the artwork and the viewer. The picture plane acts as a conceptual boundary where spatial relationships and visual elements are organized to create depth, balance, and focus. Mastery of the picture plane allows artists to manipulate perspective, scale, and alignment, enhancing the overall impact and coherence of the composition.
Historical Evolution of Composition
The historical evolution of composition in art reflects a shift from the rigid, hierarchical structures of medieval and Renaissance works to more dynamic and fragmented arrangements in modern and contemporary art. Early compositions emphasized symmetry, balance, and the use of the picture plane as a window into a cohesive, orderly world, while movements like Cubism challenged this by dissolving traditional perspectives and flattening the picture plane to explore multiple viewpoints simultaneously. This evolution highlights the changing relationship between the composition elements and the picture plane, moving from illusionistic depth to surface interaction and abstract spatial organization.
The Role of the Picture Plane in Visual Perception
The picture plane serves as the two-dimensional surface where compositions are arranged, directly influencing visual perception by guiding the viewer's eye through spatial relationships and balance within the frame. It acts as the intermediary between the three-dimensional scene and its flat representation, helping to create depth, focus, and narrative through strategic placement of elements like lines, shapes, and colors. Mastery of the picture plane enables artists to manipulate perspective and viewer engagement, making it a crucial component in effective visual storytelling and composition.
Key Principles of Effective Composition
Effective composition relies on balance, focal point, and the rule of thirds to guide the viewer's eye across the picture plane. The picture plane serves as the flat surface where elements are arranged, emphasizing spatial relationships and depth through overlap, scale, and perspective techniques. Mastering contrast, alignment, and rhythm enhances visual interest and communicates the intended message within the two-dimensional frame.
Composition Techniques Across Art Movements
Composition techniques across art movements evolve in response to changing philosophies and aesthetics, influencing the relationship between the composition and the picture plane. Renaissance artists employed linear perspective to create depth and realistic spatial arrangements, while Cubists fragmented the picture plane to depict multiple viewpoints simultaneously. Abstract Expressionists often disregarded traditional composition constraints, emphasizing the picture plane as a flat surface that conveys emotion through color and form rather than representational depth.
Manipulating the Picture Plane for Artistic Impact
Manipulating the picture plane involves controlling spatial relationships, depth, and perspective within a two-dimensional surface to create dynamic compositions that engage viewers. Artists use techniques such as overlapping, scaling, and varied focal points to break traditional flatness, enhancing the visual impact and emotional resonance of the artwork. Strategic arrangement of elements on the picture plane can direct the viewer's eye and convey narrative or abstract meanings effectively.
Interplay Between Composition and Picture Plane
The interplay between composition and the picture plane is crucial in guiding the viewer's eye and establishing spatial depth within an artwork. Composition strategically arranges elements on the two-dimensional picture plane to create balance, tension, or rhythm, influencing perception and emotional response. Manipulating the picture plane through techniques like overlapping, perspective, and scale enhances the composition's impact by reinforcing focal points and spatial relationships.
Common Mistakes in Managing Picture Plane and Composition
Common mistakes in managing the picture plane and composition include neglecting spatial organization, which causes elements to appear flat or cluttered, disrupting visual harmony. Overlapping or inconsistent scaling of objects within the picture plane can confuse depth perception and weaken the overall structure. Failing to balance positive and negative space often leads to compositions that feel either overcrowded or empty, diminishing the intended impact.
Enhancing Storytelling Through Composition and Picture Plane
Enhancing storytelling through composition involves strategically arranging visual elements to guide the viewer's eye and emphasize narrative focal points, creating a coherent flow that supports the intended message. The picture plane serves as a conceptual boundary where artists manipulate depth, perspective, and spatial relationships to influence emotional engagement and thematic interpretation. Mastery of both composition and the picture plane enables creators to craft compelling visual stories that resonate through balanced structure and dynamic spatial awareness.
Composition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com