Expressive art taps into deep emotions and personal experiences, allowing you to communicate feelings beyond words. This creative process fosters mental well-being and self-discovery through vibrant colors, dynamic shapes, and spontaneous forms. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how expressive art can transform your emotional landscape.
Table of Comparison
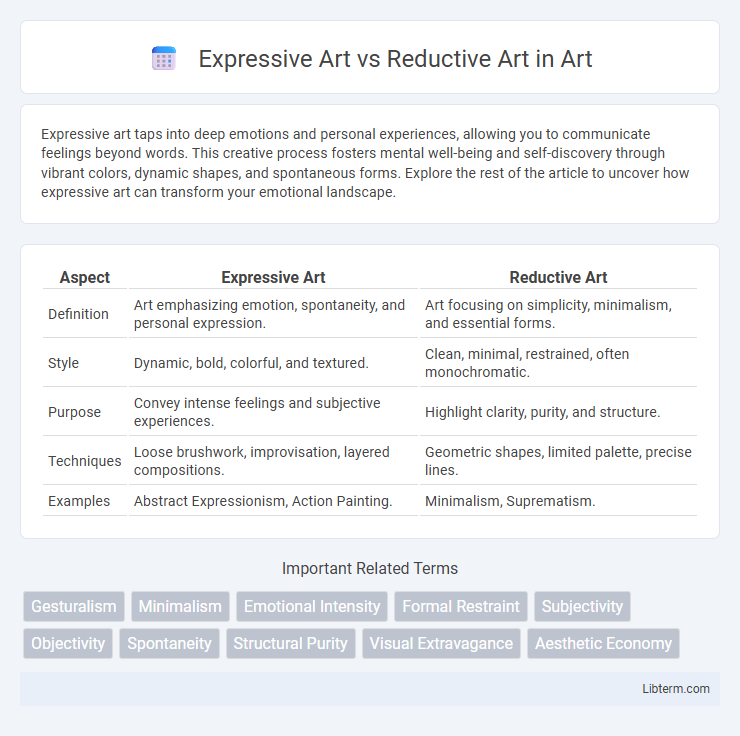
| Aspect | Expressive Art | Reductive Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art emphasizing emotion, spontaneity, and personal expression. | Art focusing on simplicity, minimalism, and essential forms. |
| Style | Dynamic, bold, colorful, and textured. | Clean, minimal, restrained, often monochromatic. |
| Purpose | Convey intense feelings and subjective experiences. | Highlight clarity, purity, and structure. |
| Techniques | Loose brushwork, improvisation, layered compositions. | Geometric shapes, limited palette, precise lines. |
| Examples | Abstract Expressionism, Action Painting. | Minimalism, Suprematism. |
Defining Expressive Art
Expressive art emphasizes the artist's emotions, individuality, and subjective experience, often using bold colors, dynamic brushstrokes, and abstract forms to convey deeper psychological or emotional states. This art form prioritizes personal expression and spontaneity over realistic representation, allowing for a free-flowing, intuitive creative process. By contrast, reductive art minimizes elements to focus on simplicity, order, and clarity, stripping away extraneous details to emphasize basic shapes, lines, and color fields.
Understanding Reductive Art
Reductive art emphasizes simplicity and clarity by stripping away non-essential elements, focusing on fundamental shapes, colors, and forms to convey meaning. This minimalist approach seeks to evoke emotions and ideas through precision, balance, and subtlety rather than elaborate detail or ornamentation. Understanding reductive art involves recognizing its power to communicate complex concepts through restraint and visual economy.
Historical Origins of Each Movement
Expressive Art originated in the early 20th century as part of the German Expressionism movement, emphasizing emotional experience and subjective interpretation through bold colors and distorted forms. Reductive Art emerged in the mid-20th century with roots in Minimalism, focusing on simplicity, geometric shapes, and the elimination of personal expression to highlight pure form and materiality. Both movements shaped modern art by challenging traditional representation but diverged in their philosophical approach to emotional content and artistic restraint.
Key Characteristics of Expressive Art
Expressive art emphasizes bold colors, dynamic brushstrokes, and emotional intensity to convey the artist's inner feelings and subjective experiences. It often features distorted forms, exaggerated shapes, and spontaneous techniques that prioritize personal expression over realistic representation. This style seeks to evoke emotional responses in viewers, making the emotional impact more important than precise detail or technical accuracy.
Core Principles of Reductive Art
Reductive Art emphasizes simplicity, minimalism, and the elimination of non-essential elements to highlight form, color, and texture. Core principles include the use of limited color palettes, geometric shapes, and a focus on purity of composition to create a sense of order and clarity. This approach contrasts with Expressive Art, which prioritizes emotional intensity and spontaneous creativity.
Influential Artists in Both Styles
Expressive art, characterized by vibrant colors and emotional intensity, finds key influencers in artists like Vincent van Gogh and Edvard Munch, whose works emphasize personal emotion and dynamic brushwork. Reductive art, focused on simplicity and minimalism, is shaped by pioneers such as Kazimir Malevich and Agnes Martin, who experiment with geometric forms and muted palettes to convey purity and essence. These influential artists define distinct artistic philosophies that continue to impact contemporary art movements globally.
Emotional Impact and Audience Engagement
Expressive art emphasizes bold colors, dynamic brushstrokes, and exaggerated forms to evoke intense emotional responses, creating a visceral connection that deeply engages the audience. Reductive art relies on simplicity, minimalism, and limited color palettes to strip away distractions, encouraging introspection and a focused emotional dialogue with viewers. The emotional impact of expressive art often manifests as immediate, overwhelming feelings, whereas reductive art fosters a subtler, contemplative engagement that invites prolonged reflection.
Techniques and Materials Used
Expressive Art employs dynamic brushstrokes, vivid colors, and mixed media such as acrylics, oils, and textured materials to evoke emotion and personal interpretation. Reductive Art emphasizes simplicity and precision, often using minimal techniques like monochromatic palettes, clean lines, and materials including ink, graphite, and smooth surfaces like canvas or paper. Techniques in Reductive Art focus on negative space and form reduction, while Expressive Art prioritizes spontaneity and layered textures.
Contemporary Trends in Art Expression
Contemporary trends in art expression highlight a dynamic tension between expressive art, which emphasizes emotional intensity, vibrant colors, and spontaneous forms, and reductive art, characterized by minimalism, geometric precision, and restrained palettes. Artists in the expressive movement often harness abstract expressionism and gestural painting to evoke raw human experience, while reductive practitioners explore spatial relationships through reductionism and conceptual clarity. This divergence reflects a broader dialogue within the art world about complexity versus simplicity, where expressive art channels personal narrative and emotion, and reductive art interrogates form and essence through minimal elements.
Choosing Between Expressive and Reductive Approaches
Choosing between expressive and reductive art approaches depends on the artist's intent and emotional goals. Expressive art emphasizes vivid colors, dynamic forms, and emotional intensity to convey feelings, while reductive art relies on minimalism, abstraction, and simplicity to highlight essential elements. Artists must consider whether they aim to evoke strong emotional responses or create contemplative, stripped-down visuals that emphasize purity and clarity.
Expressive Art Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com