Investment casting offers precise metal shaping by using wax patterns melted away during the process, ensuring high-quality and detailed components. This technique supports a wide range of alloys and complex geometries, making it ideal for aerospace, automotive, and medical industries. Discover how investment casting can elevate your manufacturing needs by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
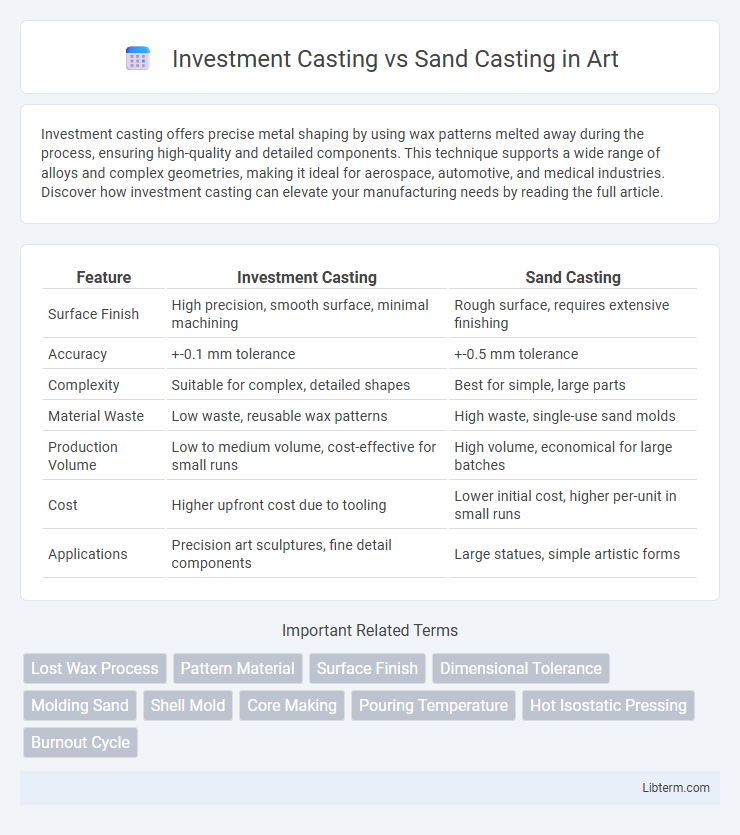
| Feature | Investment Casting | Sand Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Finish | High precision, smooth surface, minimal machining | Rough surface, requires extensive finishing |
| Accuracy | +-0.1 mm tolerance | +-0.5 mm tolerance |
| Complexity | Suitable for complex, detailed shapes | Best for simple, large parts |
| Material Waste | Low waste, reusable wax patterns | High waste, single-use sand molds |
| Production Volume | Low to medium volume, cost-effective for small runs | High volume, economical for large batches |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost due to tooling | Lower initial cost, higher per-unit in small runs |
| Applications | Precision art sculptures, fine detail components | Large statues, simple artistic forms |
Overview of Investment Casting and Sand Casting
Investment casting produces complex, precise metal parts by creating wax patterns coated with ceramic material that form a mold after wax removal, offering superior surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Sand casting involves pouring molten metal into sand molds, allowing for larger, less detailed components with a rougher surface texture and lower production cost. Both methods suit different manufacturing needs; investment casting excels in high-precision, intricate designs, while sand casting is preferred for larger, simpler shapes with cost efficiency.
Key Differences Between Investment and Sand Casting
Investment casting uses a wax pattern coated with ceramic material to form molds, enabling highly detailed and complex shapes with excellent surface finish, while sand casting employs sand molds that are less precise but more cost-effective for large parts. Investment casting typically offers tighter dimensional tolerances and smoother surfaces, making it ideal for intricate components, whereas sand casting is favored for producing large, heavy, and robust parts with lower tooling costs. The choice between these methods depends on factors such as required precision, production volume, material type, and budget constraints.
Materials Used in Investment vs Sand Casting
Investment casting primarily uses high-quality alloys such as stainless steel, aluminum, and superalloys, ensuring superior surface finish and intricate detail replication. Sand casting employs a broader range of materials including cast iron, steel, aluminum, and brass, accommodating larger, more complex shapes but with rougher surface textures. The choice of materials in investment casting favors precision and fine structures, while sand casting supports cost-effective production of robust, heavy components.
Process Steps: Investment Casting Explained
Investment casting involves creating a wax model that is coated with a ceramic shell, which is then heated to remove the wax and form a mold for molten metal. This process yields high-precision components with fine details and smooth surfaces, ideal for complex geometries. The key steps include wax pattern creation, shell building, dewaxing, casting, and shell removal.
Process Steps: Sand Casting Explained
Sand casting involves creating a mold by compacting sand around a pattern, which is then removed to form a cavity for molten metal. The process includes mold preparation, pouring molten metal into the mold cavity, cooling, and finally, breaking the sand mold to retrieve the solidified metal casting. This method is widely used for large, complex metal parts due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness compared to investment casting.
Surface Finish and Dimensional Accuracy Comparison
Investment casting offers superior surface finish with smoother textures and finer details, typically achieving surface roughness values as low as 1.6 micrometers. Dimensional accuracy in investment casting is high, often within +-0.1% of the nominal dimension, making it ideal for complex and precise components. Sand casting, by contrast, results in rougher surface finishes around 12.5 micrometers and lower dimensional accuracy, generally around +-0.5% to +-1%, due to the granular nature of the sand mold.
Cost Analysis: Investment Casting vs Sand Casting
Investment casting generally incurs higher upfront costs due to intricate mold creation and precision machining, making it suitable for complex, high-precision components with tight tolerances. Sand casting offers lower initial expenses, benefiting large-scale production with simpler geometries, but may require additional machining for detailed finishes, affecting the overall cost-efficiency. Evaluating total production volume and required detail level is critical in determining whether the higher cost of investment casting or the cost-effective flexibility of sand casting provides better value.
Applications and Industry Suitability
Investment casting excels in producing complex, precise components with excellent surface finishes, making it ideal for aerospace, medical, and automotive industries requiring high-tolerance parts. Sand casting suits large, heavy, and less intricate items such as engine blocks, pumps, and pipes, commonly used in construction, mining, and industrial machinery sectors. The choice depends on factors like part complexity, production volume, material type, and cost constraints, aligning investment casting with precision-driven industries and sand casting with bulkier, cost-sensitive manufacturing.
Advantages of Investment Casting Over Sand Casting
Investment casting offers superior dimensional accuracy and finer surface finish compared to sand casting, reducing the need for extensive machining and post-processing. Complex geometries and intricate details can be produced with investment casting, enabling the creation of thin walls and delicate features that sand casting cannot achieve efficiently. This process also minimizes material waste and allows for tighter tolerances, enhancing overall product quality and consistency.
Choosing the Right Casting Method for Your Project
Investment casting offers superior precision, excellent surface finish, and is ideal for complex geometries or small production runs, making it suitable for aerospace, medical, and automotive components. Sand casting provides cost-effective solutions for large parts and heavy metal components, with quick turnaround times favored in construction and industrial machinery. Selecting the right casting method depends on project requirements such as dimensional accuracy, production volume, material type, and budget constraints.
Investment Casting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com