Graphite is a naturally occurring form of carbon characterized by its layered, hexagonal crystal structure, which provides exceptional electrical conductivity and lubricating properties. Widely used in industries ranging from electronics to aerospace, graphite plays a critical role in batteries, refractory materials, and as a sustainable alternative to metal-based components. Explore the rest of this article to understand how your use of graphite can enhance performance and innovation.
Table of Comparison
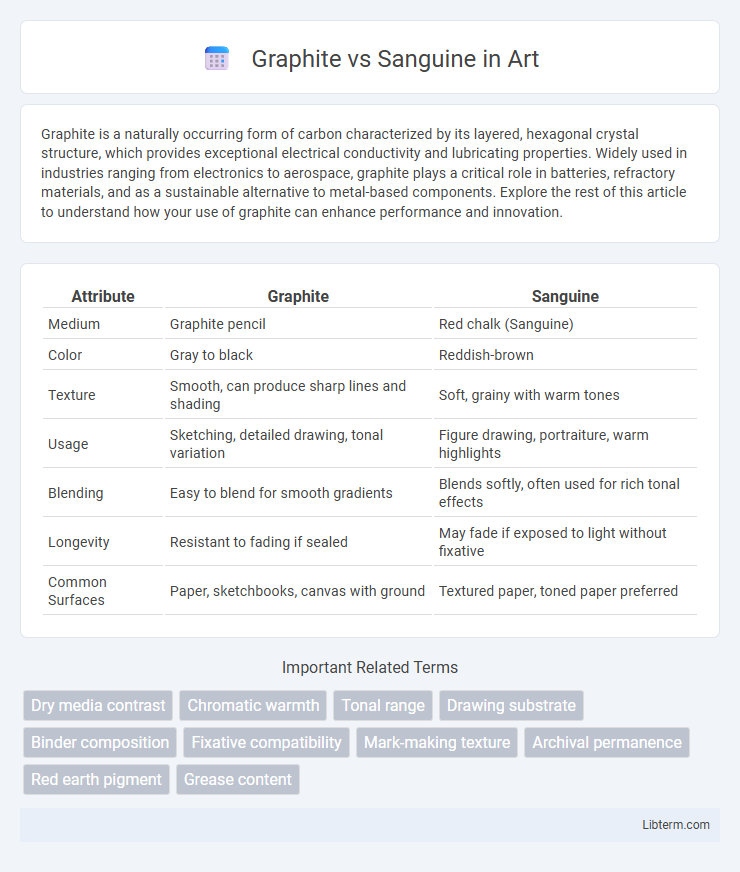
| Attribute | Graphite | Sanguine |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Graphite pencil | Red chalk (Sanguine) |
| Color | Gray to black | Reddish-brown |
| Texture | Smooth, can produce sharp lines and shading | Soft, grainy with warm tones |
| Usage | Sketching, detailed drawing, tonal variation | Figure drawing, portraiture, warm highlights |
| Blending | Easy to blend for smooth gradients | Blends softly, often used for rich tonal effects |
| Longevity | Resistant to fading if sealed | May fade if exposed to light without fixative |
| Common Surfaces | Paper, sketchbooks, canvas with ground | Textured paper, toned paper preferred |
Introduction to Graphite and Sanguine
Graphite is a powerful open-source monitoring tool designed for storing and graphing time-series data, widely used in performance metrics and system monitoring. Sanguine, on the other hand, is a lesser-known yet innovative platform that focuses on semantic data processing and visualization, catering to complex data correlation needs. Both tools serve distinct purposes in data analytics, with Graphite excelling in real-time metrics monitoring and Sanguine providing advanced semantic insights.
Historical Origins of Graphite and Sanguine
Graphite originated in the 16th century, initially discovered in Borrowdale, England, where it was mined for use in marking livestock and later adapted for writing and drawing. Sanguine, whose name derives from the Italian word for blood, traces back to the Renaissance period, prized by artists for its rich reddish-brown hue mimicking natural flesh tones. Both materials reflect distinct historical developments, with graphite linked to industrial mining and sanguine rooted in traditional chalk and ochre pigments used for fine art.
Material Composition and Characteristics
Graphite is composed of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, offering excellent electrical conductivity, high thermal resistance, and lubricating properties. Sanguine, typically a pigment made from iron oxide, consists mainly of hydrated iron oxide particles, known for its rich reddish-brown color and durability in artistic applications. The fundamental difference in material composition impacts their characteristics: graphite excels in industrial and technological uses due to its conductivity and stability, while sanguine is valued in art for its vibrant pigmentation and texture.
Color and Visual Impact
Graphite offers a deep, dark gray tone with a subtle metallic sheen that creates a sleek and modern visual impact, ideal for sophisticated and minimalist designs. Sanguine boasts a rich, warm reddish-brown hue with earthy undertones, delivering a bold and organic appearance that enhances warmth and depth in any space. The color contrast between Graphite's cool, neutral palette and Sanguine's warm, rustic character makes each ideal for distinct design moods and styles.
Techniques for Drawing with Graphite
Graphite drawing techniques emphasize blending, shading, and layering to create realistic textures and depth, utilizing various pencil grades from hard (H) to soft (B) for tonal variation. Techniques such as hatching, cross-hatching, stippling, and smudging enhance the dimensional quality of graphite artwork, enabling precise control over light and shadow. Mastery of graphite tools like kneaded erasers and blending stumps further refines details and smooth gradients, distinguishing graphite drawings from the bold, expressive lines typical of sanguine media.
Techniques for Drawing with Sanguine
Sanguine drawing techniques involve using a reddish-brown chalk or crayon to create warm, expressive sketches that emphasize light and shadow through soft shading and blending. Artists often apply sanguine with varied pressure to achieve rich textures and subtle gradations, enhancing the depth and dimensionality of figures and landscapes. Unlike graphite, which produces cooler tones and precise lines, sanguine excels in creating atmosphere and a lifelike warmth, often combined with white chalk to highlight and bring vibrancy to the artwork.
Popular Uses in Art and Illustration
Graphite is widely favored in art and illustration for its versatility in creating detailed sketches, shading, and realistic textures, making it ideal for preliminary drawings and fine line work. Sanguine, a natural reddish-brown chalk, is popular for figure drawing and portraiture, valued for its warm tones that add depth and a classical feel to artworks. Artists often choose graphite for precision and contrast, while sanguine excels in expressive, soft rendering, especially in traditional and academic studies.
Advantages and Limitations of Graphite
Graphite offers significant advantages such as high conductivity, excellent thermal stability, and a lightweight structure, making it ideal for applications in aerospace and electronics. It exhibits limitations including brittleness, susceptibility to oxidation at high temperatures, and lower strength compared to some metal alloys. Despite these drawbacks, Graphite's unique properties enable efficient heat dissipation and electrical performance in demanding environments.
Advantages and Limitations of Sanguine
Sanguine offers enhanced compatibility with decentralized finance (DeFi) applications compared to Graphite, enabling more efficient cross-chain asset management and liquidity provision. Its improved scalability addresses the throughput limitations commonly associated with Graphite, ensuring faster transaction processing and lower network congestion. However, Sanguine's relative novelty results in a smaller developer community and limited third-party integrations, potentially hindering widespread adoption and ecosystem maturity.
Choosing Between Graphite and Sanguine
Choosing between Graphite and Sanguine depends on the specific use case and project requirements. Graphite excels in time-series data monitoring with high scalability and efficient data storage, making it ideal for infrastructure performance metrics. Sanguine offers advanced visualization and interactive analytics features, better suited for business intelligence and exploratory data analysis.
Graphite Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com