Naturalism emphasizes the portrayal of reality based on scientific principles, focusing on the influence of environment and heredity on human behavior. This literary movement seeks to depict life accurately and objectively, often highlighting the struggles of ordinary people within their social conditions. Explore the rest of the article to understand how naturalism shapes narratives and reflects human experience.
Table of Comparison
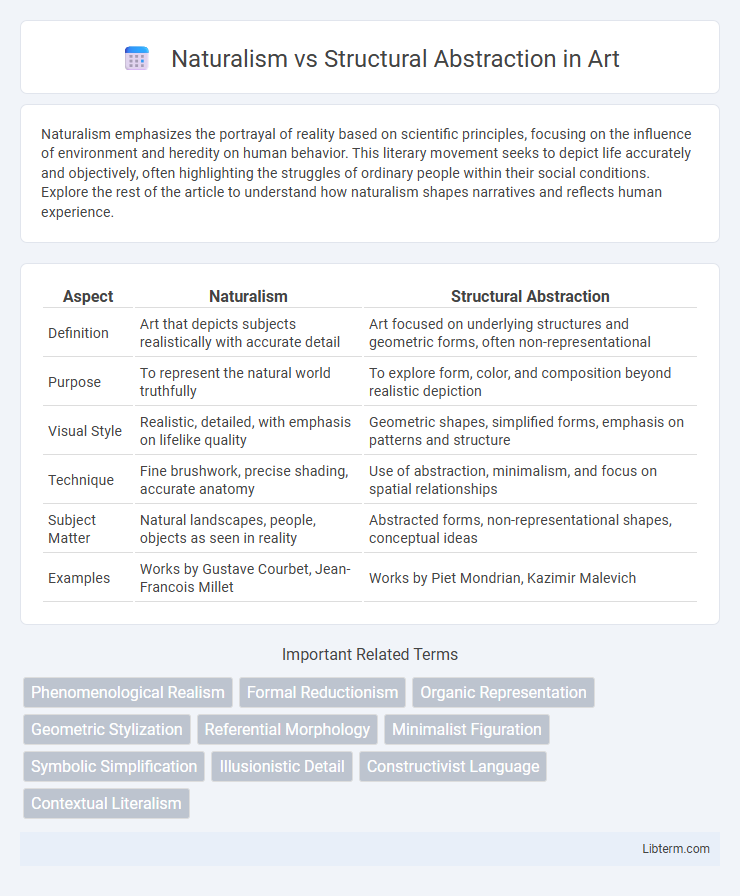
| Aspect | Naturalism | Structural Abstraction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art that depicts subjects realistically with accurate detail | Art focused on underlying structures and geometric forms, often non-representational |
| Purpose | To represent the natural world truthfully | To explore form, color, and composition beyond realistic depiction |
| Visual Style | Realistic, detailed, with emphasis on lifelike quality | Geometric shapes, simplified forms, emphasis on patterns and structure |
| Technique | Fine brushwork, precise shading, accurate anatomy | Use of abstraction, minimalism, and focus on spatial relationships |
| Subject Matter | Natural landscapes, people, objects as seen in reality | Abstracted forms, non-representational shapes, conceptual ideas |
| Examples | Works by Gustave Courbet, Jean-Francois Millet | Works by Piet Mondrian, Kazimir Malevich |
Introduction to Naturalism and Structural Abstraction
Naturalism emphasizes realistic representation by closely observing and depicting the natural world, capturing intricate details and textures to evoke authenticity. Structural Abstraction prioritizes the underlying forms and frameworks within subjects, distilling objects into geometric shapes and emphasizing composition over literal appearance. Both approaches influence modern art, contrasting detailed realism with simplified structural analysis.
Defining Naturalism in Art and Philosophy
Naturalism in art and philosophy emphasizes accurate, detailed representation of the natural world, rejecting idealization and supernatural elements to portray life objectively. This approach insists on observation-based depictions aligned with scientific understanding, capturing real-life scenarios and human conditions authentically. Distinct from structural abstraction, which breaks down forms into geometric or conceptual components, naturalism seeks to mirror reality with fidelity and precision.
Understanding Structural Abstraction
Structural abstraction emphasizes the simplification of forms by reducing objects to basic geometric shapes and underlying structures, facilitating clear communication of complex ideas. This approach contrasts with naturalism, which seeks to replicate the intricate details and textures of the natural world. Understanding structural abstraction involves recognizing its role in highlighting essential characteristics over realistic representation, enhancing interpretive clarity in art and design.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Naturalism emerged in the mid-19th century as an artistic movement emphasizing realistic representation influenced by scientific observation and social conditions, rooted in the works of artists like Gustave Courbet. Structural Abstraction developed in the early 20th century, focusing on geometric forms and structural relationships, influenced by Cubism and Constructivism, with pioneers such as Piet Mondrian and Kazimir Malevich. Both movements reflect evolving artistic responses to modernity, with Naturalism grounded in detailed reality and Structural Abstraction exploring conceptual frameworks beyond visual likeness.
Major Proponents and Influential Works
Naturalism in art and literature, championed by Emile Zola and Thomas Hardy, emphasizes realism and the detailed depiction of everyday life, with Zola's "Therese Raquin" and Hardy's "Tess of the d'Urbervilles" standing as seminal works. Structural Abstraction, rooted in modernist movements, is prominently advocated by artists like Piet Mondrian and Kazimir Malevich, whose works "Composition with Red, Blue, and Yellow" and "Black Square" introduced groundbreaking abstract forms emphasizing geometric structures and spatial relationships. These contrasting approaches underscore the shift from representational accuracy in Naturalism to the exploration of form and concept in Structural Abstraction.
Key Differences Between Naturalism and Structural Abstraction
Naturalism emphasizes lifelike representation, capturing realistic details and natural light to depict subjects as they appear in reality. Structural abstraction, conversely, deconstructs forms into geometric shapes and simplified elements, prioritizing conceptual structure over accurate representation. The key difference lies in naturalism's commitment to visual authenticity, while structural abstraction explores underlying forms and spatial relationships beyond surface appearances.
Applications in Visual Arts and Architecture
Naturalism in visual arts and architecture emphasizes accurate representation of reality, capturing lifelike details and organic forms to evoke emotional authenticity and human connection. Structural abstraction prioritizes geometric shapes, simplified forms, and spatial relationships, often employed in modernist architecture and abstract art to highlight functionality and conceptual clarity. Both approaches influence contemporary design, with naturalism enhancing experiential richness and structural abstraction promoting minimalism and systematic order.
Philosophical Implications and Worldview
Naturalism asserts that reality is solely composed of natural elements and phenomena, rejecting supernatural explanations and emphasizing empirical observation and scientific inquiry. Structural abstraction, in contrast, prioritizes relationships and patterns over tangible entities, suggesting that understanding the world hinges on conceptual frameworks rather than material substance. This philosophical divergence shapes distinct worldviews: Naturalism grounds knowledge in concrete facts and observable evidence, while Structural abstraction fosters an interpretive perspective where meaning arises from interconnected structures and symbolic systems.
Contemporary Trends and Hybrid Approaches
Contemporary trends in art reveal a dynamic interplay between naturalism and structural abstraction, where artists merge realistic representation with geometric forms to explore complex visual languages. Hybrid approaches often incorporate digital technologies, enabling seamless integration of organic textures and abstract frameworks, enhancing depth and conceptual layers. This fusion challenges traditional boundaries, fostering innovative expressions that resonate with diverse audiences and evolving cultural contexts.
Conclusion: The Interplay and Future of Both Movements
Naturalism and Structural Abstraction represent contrasting yet complementary approaches in art, with Naturalism emphasizing realistic representation and Structural Abstraction focusing on underlying forms and geometric simplification. Their interplay fosters a dynamic evolution in contemporary art, merging meticulous observation with innovative abstraction to challenge traditional perceptions. The future of both movements lies in their synthesis, where artists integrate naturalistic detail and abstract structures to explore new aesthetic possibilities and conceptual depths.
Naturalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com