Upscaling in digital art involves increasing the resolution of an image to enhance its detail and clarity without losing quality. Advanced algorithms and AI-powered tools are used to interpolate pixels, preserving sharpness and texture while expanding the artwork. Explore the full article to discover how upscaling can transform your digital creations.
Table of Comparison
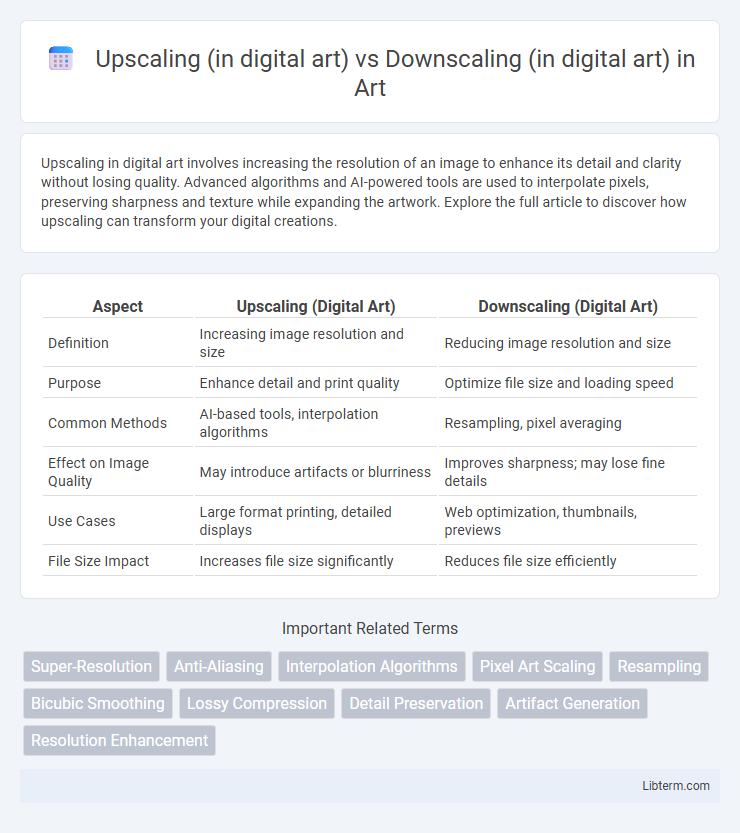
| Aspect | Upscaling (Digital Art) | Downscaling (Digital Art) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Increasing image resolution and size | Reducing image resolution and size |
| Purpose | Enhance detail and print quality | Optimize file size and loading speed |
| Common Methods | AI-based tools, interpolation algorithms | Resampling, pixel averaging |
| Effect on Image Quality | May introduce artifacts or blurriness | Improves sharpness; may lose fine details |
| Use Cases | Large format printing, detailed displays | Web optimization, thumbnails, previews |
| File Size Impact | Increases file size significantly | Reduces file size efficiently |
Introduction to Image Scaling in Digital Art
Image scaling in digital art involves modifying the resolution or dimensions of an artwork, with upscaling increasing image size to enhance detail for larger displays, while downscaling reduces size to optimize file performance or fit smaller screens. Upscaling often utilizes algorithms like bicubic interpolation or AI-powered super-resolution to preserve clarity and minimize pixelation. Downscaling improves loading speed and compatibility across devices by efficiently compressing pixel data without significant loss of visual quality.
Definition of Upscaling and Downscaling
Upscaling in digital art refers to the process of enlarging an image by increasing its resolution, often using algorithms to add pixels and enhance detail without compromising quality. Downscaling involves reducing the image's original resolution by decreasing the number of pixels, which can result in a loss of fine details but helps optimize file size for faster loading and easier sharing. Both techniques are essential for adapting digital artwork to different display requirements and maintaining visual fidelity across platforms.
Core Purposes of Image Resizing Techniques
Upscaling in digital art primarily aims to increase image resolution to enhance visual detail for larger displays or prints, using algorithms like AI-driven super-resolution to add pixels without losing quality. Downscaling reduces image size to improve loading times, optimize storage, and fit specific display requirements while preserving essential details to avoid blurring or pixelation. Both techniques balance maintaining image clarity with adapting dimensions to meet platform-specific needs, crucial in digital art production and presentation workflows.
Common Algorithms for Upscaling
Common algorithms for upscaling in digital art include bicubic interpolation, which smooths pixel transitions by considering the closest 16 pixels, and deep learning-based super-resolution methods like SRCNN and ESRGAN that enhance image details by reconstructing high-frequency patterns. These algorithms generate higher resolution images by estimating new pixel values, improving clarity and reducing pixelation compared to simple nearest-neighbor upscaling. Downscaling typically employs averaging or area-based resampling to reduce image size while preserving essential visual information, but the focus of upscaling algorithms remains on enhancing image quality and detail.
Common Algorithms for Downscaling
Common algorithms for downscaling digital art include bilinear, bicubic, and Lanczos resampling methods, which reduce image resolution while attempting to preserve detail and minimize artifacts. Bilinear interpolation offers fast processing by averaging pixel values, but may produce blurrier results compared to bicubic interpolation, which uses weighted averages of surrounding pixels for smoother transitions. Lanczos downscaling employs sinc function-based kernels to better maintain edge sharpness and texture clarity, making it a preferred choice for high-quality resampling in digital art reduction.
Effects on Image Quality: Upscaling vs Downscaling
Upscaling in digital art increases an image's resolution by adding pixels, often leading to a loss of sharpness and potential pixelation unless advanced algorithms or AI-assisted tools are used to preserve detail. Downscaling reduces the resolution, which can improve image clarity and reduce noise by consolidating pixel information, though excessive downscaling may result in significant detail loss and blurring. The quality impact of both processes depends heavily on the method applied, with interpolation techniques or deep learning models playing a critical role in maintaining fidelity during upscaling or preserving sharpness during downscaling.
Use Cases: When to Upscale or Downscale
Upscaling in digital art is ideal for enhancing low-resolution images to fit larger displays or print formats, preserving visual quality for detailed viewing or marketing materials. Downscaling is preferred when optimizing high-resolution images for faster web loading times, reducing file size while maintaining essential detail for thumbnails or mobile use. Choosing between upscaling and downscaling depends on the final output requirements, such as display size, platform constraints, and performance needs.
Challenges and Limitations in Image Scaling
Upscaling in digital art often introduces challenges such as pixelation, loss of detail, and increased noise due to the interpolation of missing pixels, which can degrade image quality despite advanced AI algorithms. Downscaling can result in the loss of fine details and sharpness as the image resolution decreases, making it difficult to preserve texture and important visual information. Both processes are limited by the original image resolution and quality, as scaling beyond inherent pixel data results in artifacts and diminished fidelity.
Best Practices for Maintaining Visual Quality
Upscaling digital art requires using advanced interpolation algorithms like bicubic or AI-based super-resolution to enhance resolution while minimizing pixelation and artifacts. Downscaling should be performed with careful resampling methods such as Lanczos or bilinear filtering to preserve edge sharpness and prevent aliasing. Maintaining visual quality depends on balancing resolution changes with proper anti-aliasing, color profile management, and preserving original aspect ratios.
Future Trends in Digital Art Scaling Technologies
Future trends in digital art scaling technologies emphasize AI-driven algorithms that enable seamless upscaling by reconstructing fine details and textures without quality loss, while advanced downscaling techniques optimize pixel reduction for enhanced clarity on smaller displays. Deep learning models such as GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks) and neural networks are increasingly integrated into software tools, significantly improving resolution transformation processes. Enhanced scalability and real-time processing capabilities are expected to revolutionize digital workflows, supporting high-fidelity visual experiences across diverse digital platforms.
Upscaling (in digital art) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com