Naturalism offers a philosophical perspective that emphasizes the role of natural causes and laws in explaining the universe, rejecting supernatural or spiritual explanations. It influences various fields such as science, literature, and ethics by grounding understanding in empirical evidence and observable phenomena. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Naturalism shapes your worldview and everyday thinking.
Table of Comparison
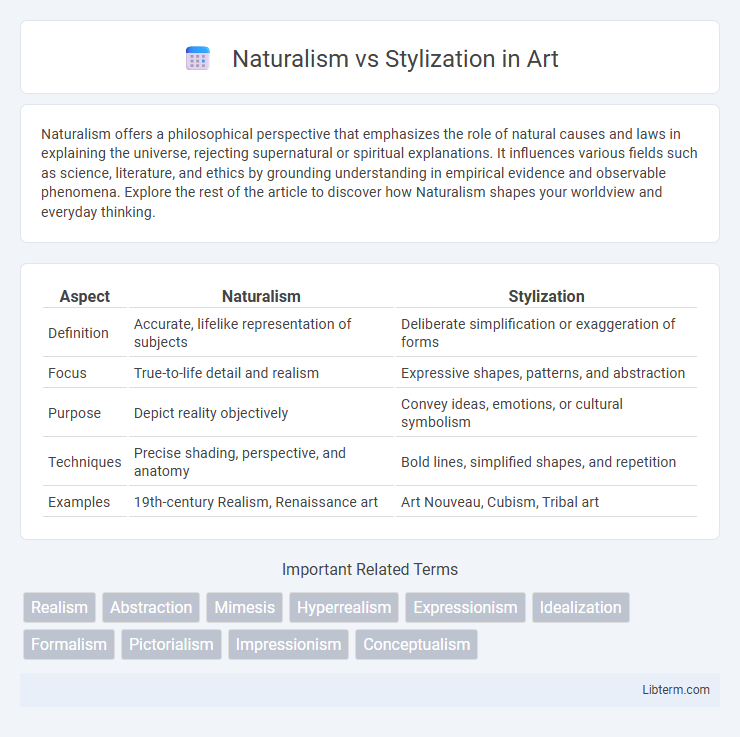
| Aspect | Naturalism | Stylization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Accurate, lifelike representation of subjects | Deliberate simplification or exaggeration of forms |
| Focus | True-to-life detail and realism | Expressive shapes, patterns, and abstraction |
| Purpose | Depict reality objectively | Convey ideas, emotions, or cultural symbolism |
| Techniques | Precise shading, perspective, and anatomy | Bold lines, simplified shapes, and repetition |
| Examples | 19th-century Realism, Renaissance art | Art Nouveau, Cubism, Tribal art |
Introduction to Naturalism and Stylization
Naturalism emphasizes realistic representation, capturing details, textures, and true-to-life proportions to reflect the natural world accurately. Stylization involves simplifying, exaggerating, or altering forms to convey artistic expression, emotion, or symbolic meaning rather than exact replication. Artists use naturalism to create lifelike art while stylization prioritizes visual impact and thematic abstraction.
Defining Naturalism in Art
Naturalism in art strives for accurate, detailed representation of subjects as they appear in the natural world, emphasizing lifelike colors, textures, and proportions. It focuses on depicting everyday scenes and human figures with realistic light and shadow effects to create a sense of depth and volume. This approach contrasts with stylization, which intentionally simplifies or exaggerates forms for symbolic or aesthetic purposes.
Understanding Stylization and Its Purpose
Stylization simplifies and exaggerates visual elements to emphasize emotion, mood, or thematic concepts, contrasting with naturalism's focus on replicating real-world accuracy. By distorting shapes, colors, or proportions, stylization enhances storytelling and conveys abstract ideas more effectively. This artistic approach supports creative expression and audience engagement by prioritizing interpretation over literal representation.
Historical Context: Evolution of Both Approaches
Naturalism emerged during the Renaissance, emphasizing realistic representation and accurate details inspired by direct observation of the natural world, while Stylization has roots in ancient art, where symbolic and exaggerated forms conveyed cultural or spiritual meanings. Throughout history, naturalism dominated Western art from the 17th to 19th centuries, coinciding with scientific advancements and the Enlightenment's focus on empirical accuracy. Stylization persisted in non-Western traditions and modern movements like Art Deco and Expressionism, evolving as a deliberate departure from realism to highlight emotional, abstract, or ideological content.
Techniques Used in Naturalism
Techniques used in naturalism emphasize realistic detail, accurate lighting, and precise textures to closely replicate real-life appearances. Artists employ observational skills, using methods such as chiaroscuro for depth and perspective techniques to create lifelike spatial relationships. The use of natural color palettes and fine brushwork further enhances the authenticity and meticulous representation inherent to naturalism.
Techniques Employed in Stylization
Stylization techniques in art prioritize exaggerated forms, simplified shapes, and bold colors to convey emotion or symbolic meaning rather than realistic representation. Methods such as abstraction, deformation, and selective detailing emphasize thematic elements and creative interpretation over naturalistic accuracy. These techniques enhance visual impact and allow artists to communicate subjective perspectives effectively.
Key Artists and Movements of Naturalism
Naturalism in art, characterized by its detailed, lifelike representation, found key proponents in artists such as Gustave Courbet, Jean-Francois Millet, and the Barbizon School, who emphasized realistic depictions of everyday life and nature. The movement emerged in the mid-19th century as a reaction against Romanticism, seeking to portray subjects with scientific accuracy and social realism, reflecting the influence of contemporary advancements in science and philosophy. Naturalism's emphasis on ordinary people and environments distinctly contrasts with Stylization, which prioritizes abstracted, exaggerated, or decorative forms seen in movements like Art Nouveau or Expressionism.
Influential Figures in Stylized Art
Influential figures in stylized art, such as Henri Matisse and Pablo Picasso, revolutionized the artistic landscape by prioritizing abstraction and expressive forms over naturalistic representation. Their innovative use of bold colors, simplified shapes, and exaggerated features established new aesthetic standards that challenged traditional realism. These artists' contributions significantly shaped movements like Fauvism and Cubism, further advancing stylization as a prominent and enduring art form.
Impact on Contemporary Art and Media
Naturalism emphasizes accurate, lifelike representation, influencing contemporary art and media by fostering realistic visual storytelling and immersive experiences. Stylization prioritizes abstraction and exaggeration, driving innovation in character design, animation, and graphic art through symbolic and expressive forms. Both approaches shape contemporary aesthetics, blending realism and creativity to engage diverse audiences and redefine artistic boundaries.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Naturalism and Stylization
Selecting between naturalism and stylization depends on the intended emotional impact and narrative purpose of the artwork. Naturalism emphasizes realistic detail and authenticity, enhancing viewer immersion through lifelike representation, while stylization prioritizes expressive form, abstraction, and symbolic interpretation to convey deeper thematic elements. Artists must evaluate the desired connection with their audience and the contextual demands of their medium to determine the optimal approach.
Naturalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com