Additive sculpture involves creating three-dimensional forms by progressively adding material, such as clay, metal, or plaster, to build up the desired shape. This technique allows artists to develop intricate textures and complex designs that showcase their creative vision. Discover more about how additive sculpture techniques can transform your artistic projects in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
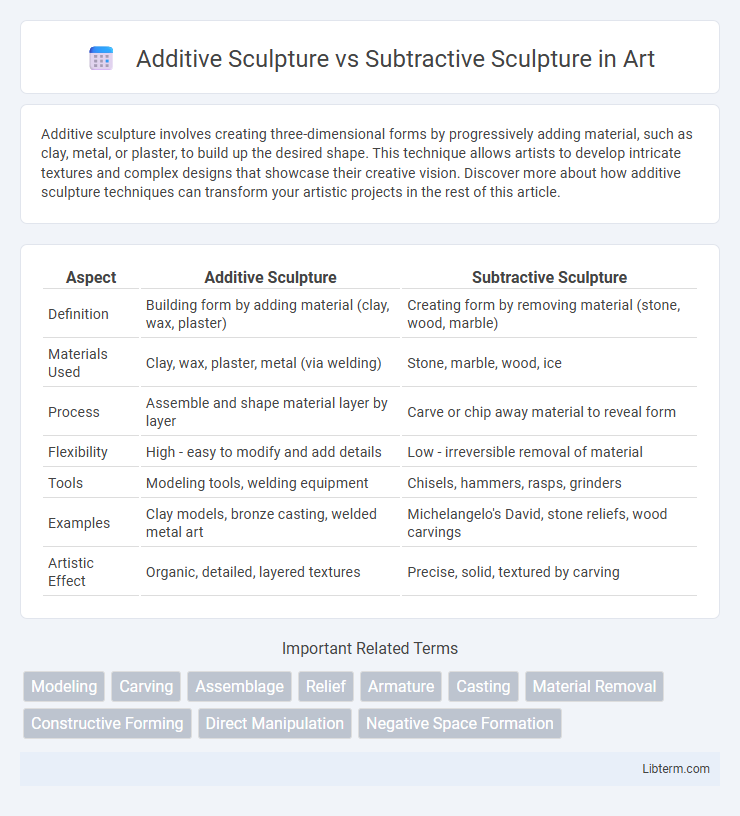
| Aspect | Additive Sculpture | Subtractive Sculpture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Building form by adding material (clay, wax, plaster) | Creating form by removing material (stone, wood, marble) |
| Materials Used | Clay, wax, plaster, metal (via welding) | Stone, marble, wood, ice |
| Process | Assemble and shape material layer by layer | Carve or chip away material to reveal form |
| Flexibility | High - easy to modify and add details | Low - irreversible removal of material |
| Tools | Modeling tools, welding equipment | Chisels, hammers, rasps, grinders |
| Examples | Clay models, bronze casting, welded metal art | Michelangelo's David, stone reliefs, wood carvings |
| Artistic Effect | Organic, detailed, layered textures | Precise, solid, textured by carving |
Introduction to Additive and Subtractive Sculpture
Additive sculpture involves building up material, such as clay, wax, or metal, to create a form, emphasizing construction and accumulation techniques. Subtractive sculpture requires removing material from a solid block like stone, wood, or marble through carving or chiseling to reveal the intended shape. Both approaches highlight different artistic processes and tools used in three-dimensional art creation.
Defining Additive Sculpture
Additive sculpture involves building up material by adding substances like clay, wax, or plaster to create a form, emphasizing construction and expansion. This technique allows artists to shape intricate details and organic forms by layering or assembling components. It contrasts with subtractive sculpture, where material is removed from a solid block to reveal the figure inside.
Defining Subtractive Sculpture
Subtractive sculpture is a technique where material is removed from a solid block, such as stone or wood, to reveal the desired form, emphasizing precision and careful planning. This process contrasts with additive sculpture, which involves building up material like clay or metal to create shapes. Subtractive methods demand a deep understanding of the material's properties to avoid irreversible mistakes during carving or chiseling.
Historical Evolution of Both Techniques
Additive sculpture, dating back to prehistoric times, involves building forms by adding materials such as clay, wax, or metal, exemplified by ancient civilizations like Mesopotamia and Egypt. Subtractive sculpture, traced to classical Greece and Egypt, entails carving or removing material from a solid block, such as marble or wood, to reveal the form within. Over centuries, both techniques evolved with technological advances and artistic movements, influencing the development of diverse sculptural styles from Renaissance marble statues to contemporary mixed-media installations.
Materials Used in Additive vs Subtractive Sculpture
Additive sculpture primarily uses materials such as clay, wax, plaster, metal, and modern synthetic compounds like polymer clay and resin, allowing artists to build up and shape form layer by layer. Subtractive sculpture typically involves carving or chiseling materials like marble, wood, stone, and ice, where the artist removes material to reveal the final form. The choice of material directly influences the techniques and tools employed, with additive processes favoring malleable, buildable substances and subtractive methods requiring solid, carveable blocks.
Key Differences in Artistic Process
Additive sculpture involves building up materials such as clay, wax, or metal to create a form, allowing artists to shape and add details progressively. Subtractive sculpture requires removing material from a solid block of stone, wood, or similar substances, demanding precision as mistakes are often irreversible. The key difference in the artistic process lies in the additive method's layering approach versus the subtractive method's carving and reduction technique.
Notable Artists and Iconic Examples
Additive sculpture, exemplified by artists like Auguste Rodin, involves building forms by adding materials such as clay or metal, with Rodin's "The Thinker" being a quintessential example. Subtractive sculpture removes material from a solid block, as seen in Michelangelo's marble masterpiece "David," showcasing the precision and skill required to reveal form through carving. Henry Moore's bronze additions contrast with Gian Lorenzo Bernini's baroque marble carvings, highlighting the distinction between additive and subtractive techniques in notable artistic practices.
Advantages and Challenges of Each Method
Additive sculpture offers the advantage of building complex, detailed forms by layering materials like clay, wax, or metal, allowing greater flexibility and error correction during creation. Subtractive sculpture, which involves removing material from a solid block such as stone or wood, provides a direct and precise approach that emphasizes craftsmanship and durability but requires careful planning due to its irreversible nature. While additive methods enable easier modification and incorporation of mixed media, subtractive techniques challenge artists with the risk of material wastage and difficulty in correcting mistakes once material is removed.
Modern Applications and Innovations
Additive sculpture techniques, such as 3D printing and clay modeling, enable artists to build forms layer by layer, fostering complex, intricate designs in contemporary art and industrial prototypes. Subtractive sculpture, including CNC milling and laser cutting, removes material from blocks like wood, stone, or metal, allowing precise, high-detail outputs in architectural models and fine art pieces. Advancements in digital technology have expanded both methods, blending traditional craftsmanship with modern innovation for enhanced creative expression and manufacturing efficiency.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Project
Selecting between additive and subtractive sculpture techniques depends on the material, desired detail, and project complexity, with additive methods ideal for flexible forms using clay or wax, while subtractive techniques suit hard materials like stone or wood. Consider the available tools and potential for error correction; additive sculpture allows gradual buildup and easier adjustments, whereas subtractive requires careful planning due to irreversible material removal. Evaluating the project's artistic goals and structural requirements ensures the chosen method aligns with both creative vision and practical execution.
Additive Sculpture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com