Digital portraits combine cutting-edge technology with artistic expression to create lifelike images that capture the essence of the subject. Using software tools, artists can manipulate colors, textures, and lighting to enhance every detail, resulting in a unique and personalized artwork. Explore the rest of the article to discover how your digital portrait can be transformed into a masterpiece.
Table of Comparison
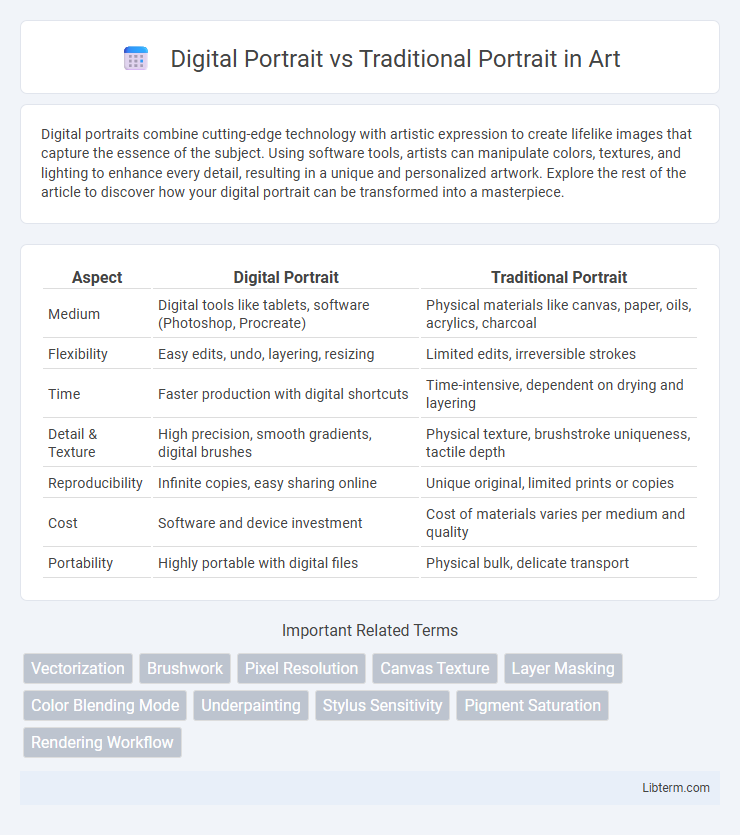
| Aspect | Digital Portrait | Traditional Portrait |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Digital tools like tablets, software (Photoshop, Procreate) | Physical materials like canvas, paper, oils, acrylics, charcoal |
| Flexibility | Easy edits, undo, layering, resizing | Limited edits, irreversible strokes |
| Time | Faster production with digital shortcuts | Time-intensive, dependent on drying and layering |
| Detail & Texture | High precision, smooth gradients, digital brushes | Physical texture, brushstroke uniqueness, tactile depth |
| Reproducibility | Infinite copies, easy sharing online | Unique original, limited prints or copies |
| Cost | Software and device investment | Cost of materials varies per medium and quality |
| Portability | Highly portable with digital files | Physical bulk, delicate transport |
Understanding Digital Portraits
Digital portraits leverage advanced software like Adobe Photoshop and Procreate, allowing artists to manipulate images with layers, brushes, and digital effects that traditional media cannot replicate. Digital tools offer precise control over color, texture, and lighting, enabling quick edits and experimentation without damaging the original artwork. Understanding digital portraits requires familiarity with graphic tablets, stylus sensitivity, and software interfaces to fully utilize the medium's creative potential.
Exploring Traditional Portraits
Traditional portraits capture the essence of subjects through mediums like oil, charcoal, and watercolor, reflecting unique textures and brushstrokes that digital art often seeks to emulate. The tactile interaction between artist and canvas emphasizes craftsmanship and individual style, preserving historical and cultural contexts. Exploring traditional portraits reveals the depth of artistic techniques and emotional expression rooted in centuries of visual storytelling.
Tools and Techniques: Digital vs Traditional
Digital portraits utilize software like Adobe Photoshop, Procreate, and Corel Painter, leveraging tools such as digital brushes, layers, and undo functions to enhance precision and creativity. Traditional portraits rely on physical media including graphite pencils, charcoal, oil paints, and canvas, requiring manual techniques like blending, shading, and layering. Digital techniques enable faster adjustments and experimentation, while traditional methods emphasize tactile skills and texture achieved through physical brushstrokes and materials.
Time Efficiency and Workflow Comparison
Digital portraits significantly reduce time spent on setup and revisions due to tools like undo functions and layers, enhancing overall workflow efficiency. Traditional portraits demand longer preparation, drying times, and iterative corrections, which can extend project duration. Digital workflows integrate easily with software for quick color adjustments and effects, streamlining the creative process compared to the manual techniques in traditional art.
Flexibility and Editing Capabilities
Digital portraits offer unparalleled flexibility with layers, undo options, and easy color adjustments, enabling artists to experiment freely and correct mistakes without damaging the original image. Traditional portraits, created with mediums like oil or charcoal, lack such editing capabilities, requiring precision and careful planning from the start. The ability to digitally manipulate details enhances creativity and efficiency in portrait creation, making digital art highly adaptable compared to the more permanent and tactile nature of traditional portraits.
Cost Factors and Accessibility
Digital portraits generally offer lower cost factors due to reduced material expenses and faster production times compared to traditional portraits, which require costly art supplies and extensive labor. Accessibility is enhanced in digital portraits through widespread availability of software and online platforms, allowing more artists and clients to connect globally without geographical constraints. Traditional portraits often demand physical studio access and in-person sessions, limiting accessibility and increasing logistical costs.
Preservation and Longevity of Artwork
Digital portraits offer enhanced preservation and longevity compared to traditional portraits, as digital files are immune to physical degradation like fading, cracking, or discoloration over time. Traditional portraits, created with materials such as oil, watercolor, or charcoal, require controlled environments and regular maintenance to prevent deterioration caused by light exposure, humidity, and pollution. Digital storage also allows for easy replication and backup, ensuring the artwork's integrity is maintained indefinitely without the risk of irreversible damage.
Audience Perception and Value
Digital portraits offer dynamic versatility and can be easily shared and reproduced, appealing to tech-savvy audiences who value accessibility and innovation. Traditional portraits often evoke a deeper emotional connection due to their tactile nature and historical craftsmanship, resonating with collectors and art enthusiasts who prioritize authenticity and timelessness. Both mediums hold unique cultural significance, but audience perception heavily depends on the context and intended use, influencing perceived value and desirability.
Environmental Impact Considerations
Digital portraits significantly reduce environmental impact by eliminating the need for physical materials such as canvas, paints, and paper, which often involve resource-intensive production and disposal processes. Traditional portraits consume natural resources, generate chemical waste from paints and solvents, and contribute to carbon emissions through transportation and storage. Opting for digital art supports sustainability efforts by minimizing waste and lowering the carbon footprint associated with portrait creation.
Choosing the Right Portrait Style for You
Choosing the right portrait style depends on your personal aesthetic and purpose; digital portraits offer versatility with easy edits and vibrant effects, while traditional portraits provide timeless texture and unique brushwork. Digital portraits suit clients seeking quick turnaround and modern flair, whereas traditional portraits appeal to those valuing classic artistry and original craftsmanship. Assess your preference for customization, medium longevity, and artistic feel when deciding between digital and traditional portrait styles.
Digital Portrait Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com