Downscaling is the process of reducing the resolution of an image or video to improve performance and save storage space while maintaining visual quality. It plays a crucial role in various applications such as streaming, gaming, and machine learning, where managing resource constraints is essential. Discover how downscaling techniques can optimize your media experience by reading the rest of the article.
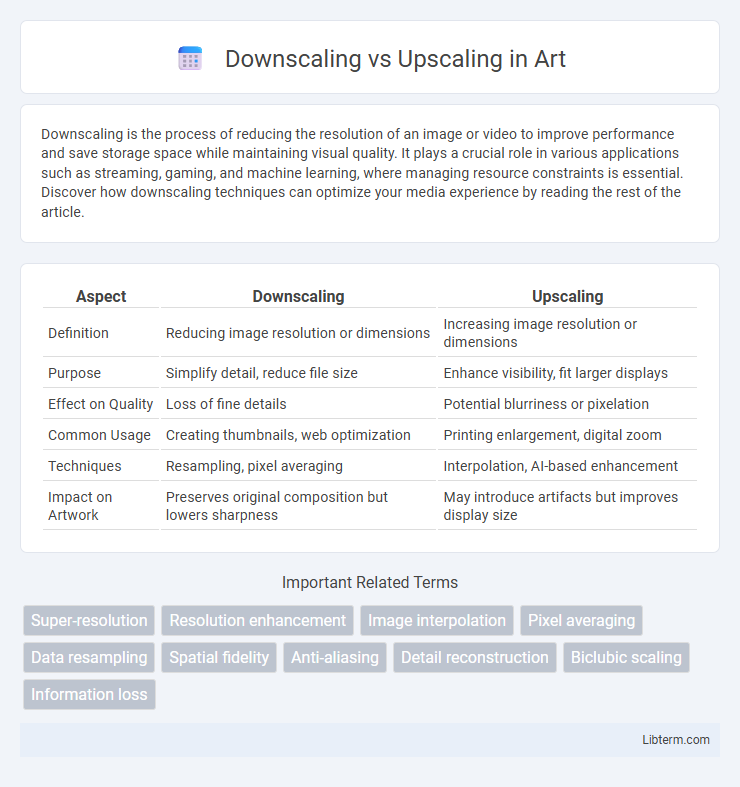
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Downscaling | Upscaling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing image resolution or dimensions | Increasing image resolution or dimensions |
| Purpose | Simplify detail, reduce file size | Enhance visibility, fit larger displays |
| Effect on Quality | Loss of fine details | Potential blurriness or pixelation |
| Common Usage | Creating thumbnails, web optimization | Printing enlargement, digital zoom |
| Techniques | Resampling, pixel averaging | Interpolation, AI-based enhancement |
| Impact on Artwork | Preserves original composition but lowers sharpness | May introduce artifacts but improves display size |
Understanding Downscaling and Upscaling
Downscaling involves reducing the resolution of an image or video to fit smaller displays or to save storage space, preserving essential visual details while minimizing file size. Upscaling increases the resolution by interpolating pixels to enhance image clarity on larger screens, often using advanced algorithms like AI-based super-resolution to maintain quality. Understanding the balance between downscaling and upscaling is crucial for optimizing visual content across diverse devices and media formats.
Key Differences Between Downscaling and Upscaling
Downscaling reduces the resolution of an image or video by removing pixels, resulting in smaller file sizes and faster processing times ideal for web use and mobile devices. Upscaling increases resolution by interpolating new pixels to expand image size, which can enhance display on higher-resolution screens but may cause loss of sharpness and introduce artifacts. The key difference lies in downscaling's goal to simplify and optimize for smaller displays versus upscaling's aim to enlarge and improve visual quality on larger or higher-resolution displays.
How Downscaling Works
Downscaling works by reducing the resolution of an image or video by removing pixels and condensing the remaining ones to fit a smaller display area, which enhances processing speed and decreases file size. This process often employs interpolation algorithms such as bilinear or bicubic to merge pixel information while maintaining as much detail and sharpness as possible. Effective downscaling preserves visual clarity on lower-resolution screens by optimizing pixel density and minimizing artifacts like blurring or aliasing.
The Process of Upscaling Explained
Upscaling involves increasing the resolution of an image or video by adding new pixels through algorithms such as bicubic interpolation, deep learning-based super-resolution, or neural networks, enhancing detail and sharpness beyond the original quality. This process predicts pixel data by analyzing existing visual information, enabling a higher-resolution output suitable for larger displays or printing. Advanced upscaling techniques maintain image clarity while minimizing artifacts and blurriness, making it essential for modern media and graphic applications.
Applications of Downscaling in Real-World Scenarios
Downscaling is crucial in climate modeling, enabling localized weather predictions by translating global climate data into high-resolution regional forecasts essential for agriculture and urban planning. In remote sensing, downscaling improves satellite imagery clarity, allowing precise monitoring of environmental changes and disaster management. This technique also enhances image processing in medical diagnostics, providing detailed scans for accurate disease detection and treatment planning.
Practical Uses of Upscaling Across Industries
Upscaling enhances the resolution of images, videos, and audio to meet higher quality standards essential in industries such as entertainment, healthcare, and manufacturing. In entertainment, upscaling restores classic films and improves streaming content quality, while in healthcare, it refines medical imaging for accurate diagnostics. Manufacturing benefits from upscaling through improved visual inspections and detailed product imaging, supporting quality control and precision engineering.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Downscaling
Downscaling reduces image resolution, leading to smaller file sizes and faster processing, which benefits web performance and storage management. However, downscaling can cause loss of detail and clarity, resulting in blurred or pixelated visuals, especially when reducing highly detailed images. Despite these drawbacks, downscaling improves compatibility across lower-resolution displays and helps optimize bandwidth usage.
Advantages and Limitations of Upscaling
Upscaling enhances image resolution by increasing pixel count, which benefits applications like video streaming and gaming by improving visual clarity on high-definition displays. However, upscaling often introduces artifacts such as blurring and pixelation due to the interpolation algorithms used to generate new pixels, limiting true image quality. Advanced AI-based upscaling methods mitigate some issues by predicting details more accurately but require extensive computational resources and may still not replicate native high-resolution content perfectly.
Choosing Between Downscaling and Upscaling
Choosing between downscaling and upscaling depends primarily on the original resolution of the image and the target display size. Downscaling reduces image dimensions to improve performance and reduce file size while maintaining clarity on smaller screens, whereas upscaling increases image resolution to fit larger displays but can introduce blurriness or artifacts if not using advanced algorithms like AI-based super-resolution. Selecting the appropriate method requires balancing image quality, processing power, and the specific use case such as web display, printing, or video streaming.
Future Trends in Image and Video Scaling Technologies
Future trends in image and video scaling technologies emphasize AI-driven algorithms that enhance both downscaling and upscaling processes with improved detail preservation and artifact reduction. Machine learning models like convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and generative adversarial networks (GANs) are increasingly utilized to predict and reconstruct high-resolution content from low-resolution inputs. Advances in real-time processing, combined with edge computing capabilities, are set to revolutionize scalability in streaming services, virtual reality, and ultra-high-definition displays.
Downscaling Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com