Piet Mondrian revolutionized abstract art by pioneering the De Stijl movement, characterized by bold grids and primary colors. His innovative approach to composition and balance continues to influence modern design and architecture worldwide. Discover how Mondrian's artistic philosophy shaped contemporary aesthetics in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
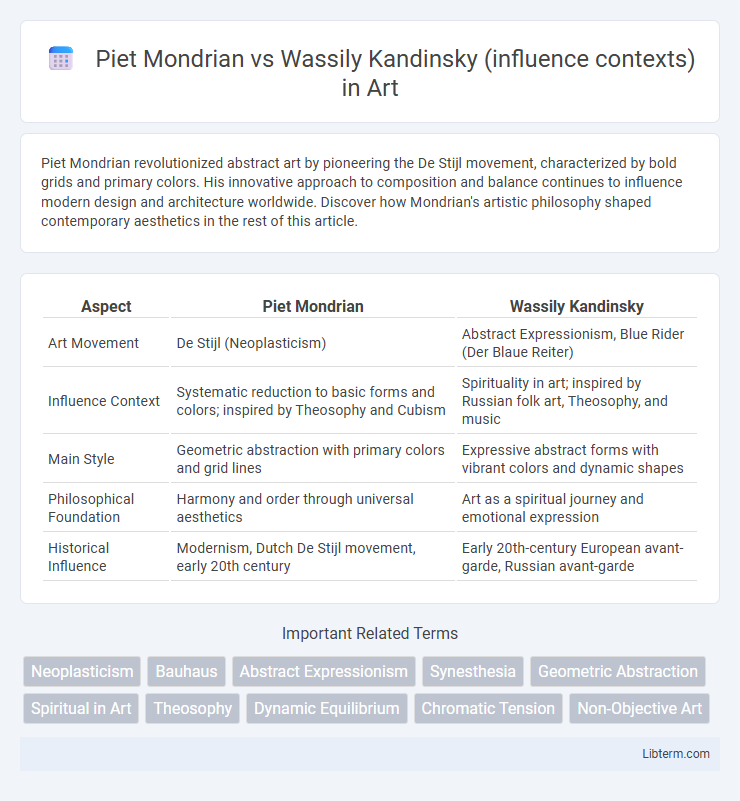
| Aspect | Piet Mondrian | Wassily Kandinsky |
|---|---|---|
| Art Movement | De Stijl (Neoplasticism) | Abstract Expressionism, Blue Rider (Der Blaue Reiter) |
| Influence Context | Systematic reduction to basic forms and colors; inspired by Theosophy and Cubism | Spirituality in art; inspired by Russian folk art, Theosophy, and music |
| Main Style | Geometric abstraction with primary colors and grid lines | Expressive abstract forms with vibrant colors and dynamic shapes |
| Philosophical Foundation | Harmony and order through universal aesthetics | Art as a spiritual journey and emotional expression |
| Historical Influence | Modernism, Dutch De Stijl movement, early 20th century | Early 20th-century European avant-garde, Russian avant-garde |
Early Life and Artistic Beginnings
Piet Mondrian's early life in the Netherlands deeply influenced his artistic beginnings, where his exposure to Dutch landscapes and theosophy shaped his pursuit of abstraction and geometric forms. Wassily Kandinsky's upbringing in Moscow and his studies in law and economics transitioned into his fascination with spirituality and music, leading to his pioneering work in abstract art inspired by synesthesia and emotion. Both artists' formative experiences were pivotal in developing their distinct approaches to abstraction, with Mondrian emphasizing structure and balance and Kandinsky exploring color and emotional resonance.
Philosophical Foundations of Their Art
Piet Mondrian's art draws heavily from theosophy and Neoplasticism, emphasizing universal harmony through geometric abstraction and primary colors to express a spiritual order beyond the visible world. Wassily Kandinsky's work is deeply influenced by his interest in mysticism and Theosophy, where he sought to evoke inner emotional and spiritual experiences through abstract forms and vibrant color symbolism. Both artists aligned their abstract styles with philosophical and spiritual frameworks, but Mondrian pursued structured harmony while Kandinsky explored expressive, dynamic spirituality.
Contributions to Abstract Art
Piet Mondrian revolutionized abstract art through his development of Neoplasticism, characterized by geometric precision, primary colors, and grid-based compositions, which influenced minimalist and modern design principles. Wassily Kandinsky pioneered abstract expressionism by exploring the emotional and spiritual resonance of color and form, integrating synesthetic concepts that linked visual art to music. Both artists fundamentally shaped abstract art by emphasizing non-representational forms, yet Mondrian focused on structural harmony while Kandinsky highlighted emotive and dynamic expression.
Use of Color and Form
Piet Mondrian's use of color emphasized primary colors and geometric forms to achieve harmony and balance, reflecting his pursuit of universal aesthetic principles through abstraction. Wassily Kandinsky employed vibrant, expressive colors and dynamic, irregular shapes to evoke emotional and spiritual responses, drawing heavily on synesthetic experiences and the psychological impact of color. Their contrasting approaches highlight Mondrian's structural precision versus Kandinsky's emotive fluidity in the development of modern abstract art.
Relationship with the Avant-Garde Movements
Piet Mondrian's work significantly shaped De Stijl, emphasizing geometric abstraction and a reduction to primary colors, influencing modern architecture and design. Wassily Kandinsky played a pioneering role in Expressionism and abstract art, linking color and form to spiritual and emotional experiences, foundational for the Blue Rider group. Both artists profoundly impacted the avant-garde by pushing boundaries of representation and abstraction in early 20th-century art movements.
Spiritual Influences in Their Work
Piet Mondrian's work was deeply influenced by theosophy and spiritual movements emphasizing harmony and universal order, which guided his shift toward abstract geometric forms and primary colors symbolizing higher spiritual realities. Wassily Kandinsky drew on anthroposophy and synesthesia theories, using vibrant colors and dynamic shapes to evoke emotional and spiritual experiences, aiming to reveal inner psychic states. Both artists sought to transcend materialism through abstraction, but while Mondrian pursued precise balance reflecting cosmic spirituality, Kandinsky embraced expressive abstraction to manifest spiritual awakening and emotional resonance.
Impact on Modernism
Piet Mondrian's influence on Modernism is deeply rooted in his pioneering work with abstraction and geometric forms, which established a visual language emphasizing simplicity, balance, and universality. Wassily Kandinsky's impact stems from his exploration of color theory and spiritual expression, positioning him as a key figure in abstract art who connected emotional resonance with visual innovation. Both artists significantly shaped Modernism by redefining artistic boundaries and inspiring movements such as De Stijl and Abstract Expressionism.
Legacy in Contemporary Art
Piet Mondrian's legacy in contemporary art is defined by his pioneering role in abstract geometric composition and the De Stijl movement, influencing minimalism and modern design principles globally. Wassily Kandinsky's contributions to abstract art emphasize vibrant colors and spiritual expression, shaping the development of expressionism and abstract expressionism in contemporary practices. Both artists' innovations continue to inform color theory, form, and conceptual frameworks in avant-garde and digital art forms today.
Critical Reception over Time
Piet Mondrian's critical reception has evolved from early skepticism to recognition as a pioneer of abstract art, particularly in neoplasticism, emphasizing geometric harmony and balance. Wassily Kandinsky's work, initially controversial for its abstract expressionism and spiritual themes, gained acclaim for pioneering color theory and emotional abstraction, influencing modern art movements. Over time, both artists have been celebrated for transforming visual language, with Mondrian praised for structural precision and Kandinsky for expressive dynamism.
Lasting Influence on Art Education
Piet Mondrian's exploration of geometric abstraction and primary colors profoundly shaped modern art education by emphasizing principles of balance, harmony, and the reduction of forms to their essentials. Wassily Kandinsky's pioneering work in expressionist abstraction introduced the study of color theory, emotional resonance, and the spiritual dimension of art, deeply influencing curricula focused on creativity and individual expression. Together, their legacies continue to inform art education frameworks that balance structured composition with personal artistic freedom.
Piet Mondrian Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com