A joint venture combines the strengths and resources of two or more businesses to achieve a specific goal while sharing risks and rewards. This strategic partnership allows companies to enter new markets, access innovative technologies, or increase operational efficiency. Discover how forming a joint venture can propel Your business forward by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
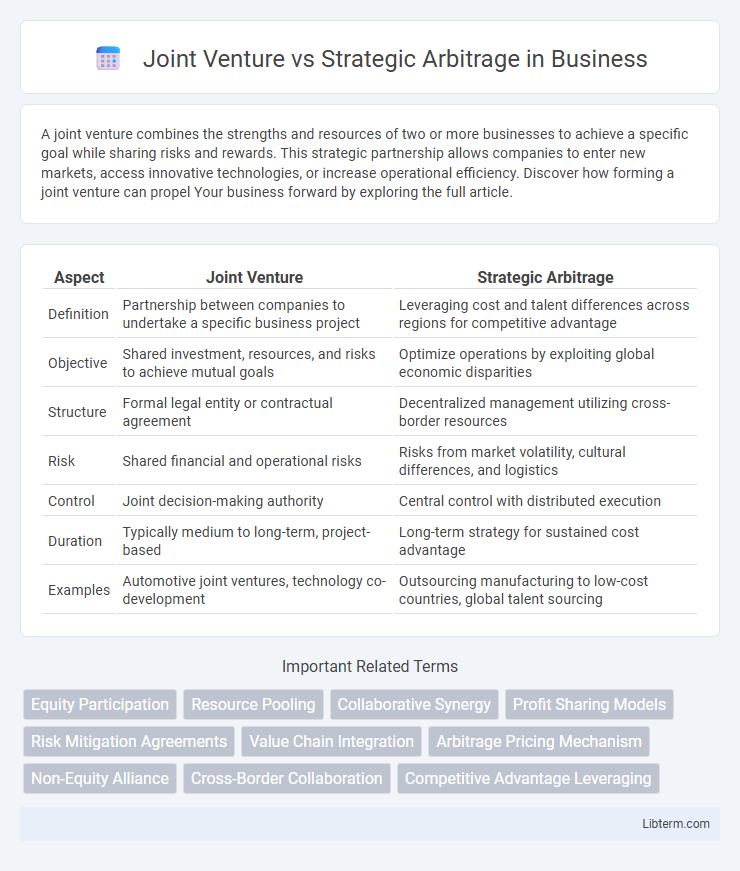
| Aspect | Joint Venture | Strategic Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Partnership between companies to undertake a specific business project | Leveraging cost and talent differences across regions for competitive advantage |
| Objective | Shared investment, resources, and risks to achieve mutual goals | Optimize operations by exploiting global economic disparities |
| Structure | Formal legal entity or contractual agreement | Decentralized management utilizing cross-border resources |
| Risk | Shared financial and operational risks | Risks from market volatility, cultural differences, and logistics |
| Control | Joint decision-making authority | Central control with distributed execution |
| Duration | Typically medium to long-term, project-based | Long-term strategy for sustained cost advantage |
| Examples | Automotive joint ventures, technology co-development | Outsourcing manufacturing to low-cost countries, global talent sourcing |
Understanding Joint Ventures: Key Concepts
A joint venture involves two or more companies creating a separate legal entity to combine resources for a specific business objective, sharing profits, losses, and control. Key concepts include shared ownership, risk allocation, and collaborative management, which enable partners to leverage complementary strengths and access new markets. Understanding the legal structure, governance mechanisms, and strategic alignment is crucial for maximizing joint venture success.
Strategic Arbitrage: Definition and Core Principles
Strategic arbitrage involves leveraging differences in market conditions, resources, or capabilities between two or more regions or industries to create competitive advantage and generate higher returns. This approach focuses on exploiting global inefficiencies through coordinated operations, resource allocation, and value chain integration across diverse geographies. Core principles include identifying unique location-specific advantages, optimizing cost structures, and aligning cross-border business strategies to maximize synergies and innovation potential.
Main Differences Between Joint Venture and Strategic Arbitrage
Joint ventures involve formal partnerships where two or more companies share resources, risks, and profits to achieve a specific business goal, often creating a new entity. Strategic arbitrage, by contrast, exploits differences in markets, costs, or expertise across countries or regions without forming a new legal entity, focusing on leveraging global advantages for competitive gains. The main differences lie in structure, legal commitment, and operational integration, with joint ventures requiring collaboration and shared management, while strategic arbitrage focuses on decentralized optimization of global resources.
Benefits of Forming a Joint Venture
Forming a joint venture enables companies to combine resources, expertise, and market access, facilitating shared risks and accelerating innovation. This partnership structure enhances competitive advantage by leveraging complementary strengths and local knowledge in target markets. Joint ventures also provide greater control over operations compared to strategic arbitrage, leading to improved coordination and long-term value creation.
Advantages of Employing Strategic Arbitrage
Strategic arbitrage allows companies to leverage cross-border differences in labor costs, regulations, and market dynamics to optimize efficiency and profitability. Unlike joint ventures, it enables full control over operations without sharing ownership or profits, facilitating faster decision-making and resource allocation. This approach enhances competitive advantage by exploiting global disparities while maintaining operational flexibility and minimizing partnership complexities.
Risks and Challenges in Joint Ventures
Joint ventures carry significant risks such as cultural clashes between partners, misaligned objectives, and complex governance structures that can lead to conflicts and operational inefficiencies. Challenges also include potential intellectual property disputes, unequal resource contributions, and difficulties in decision-making processes, which may undermine the joint venture's performance. Unlike strategic arbitrage, which leverages cost or resource differences across markets with fewer partnership dependencies, joint ventures require intensive collaboration and risk sharing, increasing exposure to joint liabilities and management risks.
Common Pitfalls of Strategic Arbitrage
Strategic arbitrage often faces common pitfalls such as misaligned objectives between partners, inadequate cultural integration, and underestimated operational complexities. Companies may struggle with overestimating cost savings while ignoring risks related to regulatory compliance and quality control in foreign markets. Failure to conduct thorough due diligence and establish clear communication channels can lead to suboptimal outcomes and damaged relationships.
Case Studies: Joint Venture Success Stories
Joint Ventures often demonstrate success through well-documented case studies such as the collaboration between Starbucks and Tata Global Beverages, which enabled Starbucks to enter the Indian market effectively by leveraging Tata's local expertise and supply chain. These success stories highlight how Joint Ventures foster mutual benefit by combining resources, sharing risks, and aligning strategic goals to achieve market penetration. In contrast, Strategic Arbitrage focuses more on exploiting cost and talent differences across borders but may lack the deep collaborative integration seen in Joint Ventures.
Notable Examples of Strategic Arbitrage in Action
Strategic arbitrage involves leveraging global differences in costs, regulations, or capabilities to create competitive advantages, as seen in companies like Apple, which designs products in the U.S. while manufacturing in China to optimize quality and cost efficiency. Another notable example is Toyota, which enters joint ventures in emerging markets to access local expertise and reduce production expenses, blending strategic arbitrage with localized partnerships. Pharmaceutical giants such as Pfizer utilize strategic arbitrage by outsourcing clinical trials to countries with lower healthcare costs while maintaining research and development domestically.
Choosing Between Joint Venture and Strategic Arbitrage: Decision Criteria
Choosing between a joint venture and strategic arbitrage depends on factors such as resource commitment, risk tolerance, and market control objectives. Joint ventures are suitable when local expertise and shared investment reduce risks, whereas strategic arbitrage excels in optimizing cost efficiencies across global markets without direct partnerships. Decision criteria should emphasize alignment with long-term business goals, regulatory environment, and the desired degree of operational integration.
Joint Venture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com