Literacy is a fundamental skill that enhances communication and comprehension in everyday life, boosting personal and professional success. Developing strong reading and writing abilities empowers you to access information, express ideas clearly, and participate fully in society. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective strategies for improving your literacy skills.
Table of Comparison
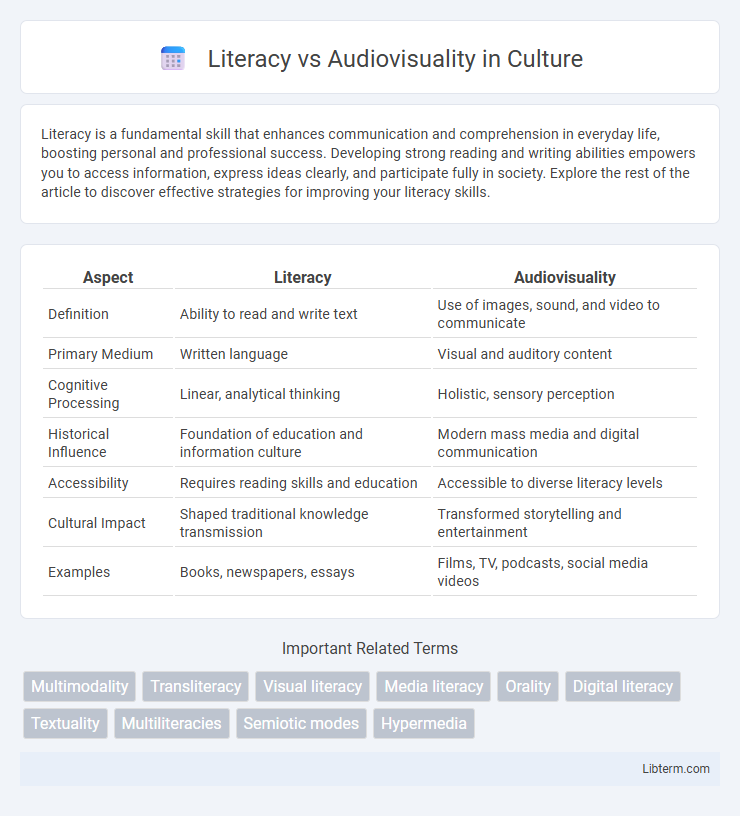
| Aspect | Literacy | Audiovisuality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to read and write text | Use of images, sound, and video to communicate |
| Primary Medium | Written language | Visual and auditory content |
| Cognitive Processing | Linear, analytical thinking | Holistic, sensory perception |
| Historical Influence | Foundation of education and information culture | Modern mass media and digital communication |
| Accessibility | Requires reading skills and education | Accessible to diverse literacy levels |
| Cultural Impact | Shaped traditional knowledge transmission | Transformed storytelling and entertainment |
| Examples | Books, newspapers, essays | Films, TV, podcasts, social media videos |
Understanding Literacy: Definition and Scope
Literacy encompasses the ability to read, write, and interpret written texts, forming the foundation for communication and knowledge acquisition in traditional educational frameworks. Audiovisuality expands this concept by integrating visual and auditory media, facilitating comprehension through images, sounds, and video, which engage multisensory learning processes. Understanding literacy today requires recognizing this scope shift from purely textual skills to multimodal competencies essential for navigating digital and media-rich environments.
What Is Audiovisuality? An Overview
Audiovisuality refers to the integration of visual and auditory elements to convey information or tell a story, often seen in media like films, videos, and digital content. Unlike traditional literacy, which relies on reading and writing, audiovisuality engages multiple senses simultaneously, enhancing comprehension and emotional impact. This multimodal approach leverages images, sound, and text to create a richer, more immersive communication experience in modern educational and entertainment contexts.
Historical Evolution: From Print to Screen
The historical evolution from print literacy to audiovisuality marks a significant shift in communication, tracing back to the invention of the printing press in the 15th century that disseminated written knowledge widely. The 20th century introduced film, television, and digital media, transforming information consumption from text-based to image and sound-based formats. This transition reflects advancements in technology and cultural adaptation, emphasizing multimodal literacy skills that integrate visual, auditory, and textual comprehension.
Cognitive Differences: Reading vs. Viewing
Reading enhances deep cognitive processing by engaging phonological, syntactic, and semantic pathways, promoting critical thinking and memory retention. In contrast, viewing audiovisual content primarily stimulates visual and auditory channels, enabling faster information absorption but often leading to more passive cognitive engagement. The interplay between literacy and audiovisuality reveals significant differences in attention span, comprehension depth, and cognitive load management during information intake.
Information Retention: Textual vs. Audiovisual Media
Textual media enhances information retention through active cognitive engagement and deeper semantic processing, fostering long-term memory formation. Audiovisual media leverages multisensory stimulation, aiding immediate comprehension and recall but often resulting in more transient retention. Studies indicate that combining textual and audiovisual elements optimizes retention by integrating detailed analysis with vivid contextual cues.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Learning
Literacy and audiovisuality offer distinct pathways to accessibility and inclusivity in learning by catering to diverse cognitive and sensory needs. Audiovisual materials enhance comprehension for learners with reading difficulties or language barriers by combining visual cues and auditory information, creating multisensory engagement. Literacy remains crucial for critical thinking and detailed understanding, but integrating audiovisual resources fosters a more inclusive educational environment that supports varied learning preferences and abilities.
Influence on Critical Thinking Skills
Literacy enhances critical thinking by promoting deep comprehension, analytical reasoning, and the ability to evaluate complex texts, fostering skills such as inference and synthesis. Audiovisuality supports critical thinking through visual literacy, encouraging interpretation of multimedia cues, contextual understanding, and emotional engagement, which can improve information processing speed and pattern recognition. Combined exposure to both literacy and audiovisual elements cultivates a multifaceted critical thinking approach, enabling better discernment and adaptability in diverse communication contexts.
Societal Impact: Cultural Shifts in Communication
Literacy's dominance historically enabled precise, structured communication fostering individual critical thinking and knowledge preservation, while audiovisuality introduces dynamic, multimodal expressions transforming collective cultural engagement. The rise of audiovisual media reshapes societal information consumption by promoting faster emotional resonance and inclusive accessibility, altering power dynamics in communication. This cultural shift influences education, public discourse, and identity formation, blending oral traditions with digital connectivity to redefine community and memory.
The Role of Technology in Literacy and Audiovisuality
Technology reshapes literacy by integrating digital tools that enhance reading and writing through interactive formats, while audiovisuality leverages multimedia platforms to convey information via images, sound, and video. Digital literacy encompasses skills to critically analyze and produce content across text, audio, and visual media, reflecting a convergence in communication methods. This technological fusion drives new educational paradigms, emphasizing multimodal comprehension and expression in contemporary learning environments.
Future Trends: Blending Literacy and Audiovisuality
Emerging educational models increasingly integrate literacy skills with audiovisual media to enhance comprehension and engagement, leveraging technologies such as virtual reality and interactive videos. The fusion of text-based reading with dynamic audiovisual content supports multisensory learning, adapting to diverse cognitive preferences and improving information retention. Future trends emphasize personalized learning environments that seamlessly blend traditional literacy with audiovisual elements to prepare learners for complex digital communication landscapes.
Literacy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com