Syncretism refers to the blending of different religious, cultural, or philosophical beliefs into a cohesive system, often resulting in enriched traditions and practices. This fusion often occurs when diverse cultures interact, leading to the adaptation and merging of rituals, symbols, and ideologies. Explore the rest of the article to understand how syncretism shapes societies and influences your worldview.
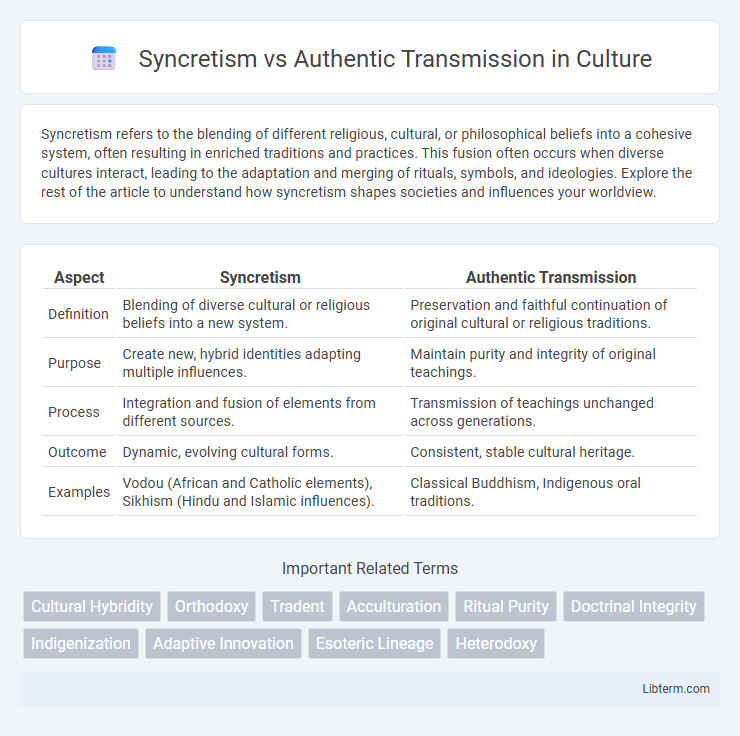
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Syncretism | Authentic Transmission |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Blending of diverse cultural or religious beliefs into a new system. | Preservation and faithful continuation of original cultural or religious traditions. |
| Purpose | Create new, hybrid identities adapting multiple influences. | Maintain purity and integrity of original teachings. |
| Process | Integration and fusion of elements from different sources. | Transmission of teachings unchanged across generations. |
| Outcome | Dynamic, evolving cultural forms. | Consistent, stable cultural heritage. |
| Examples | Vodou (African and Catholic elements), Sikhism (Hindu and Islamic influences). | Classical Buddhism, Indigenous oral traditions. |
Defining Syncretism and Authentic Transmission
Syncretism involves blending diverse religious or cultural beliefs to create a hybrid system, often merging elements from multiple traditions. Authentic transmission refers to the faithful preservation and passing down of original teachings within a tradition, maintaining doctrinal purity and continuity. The distinction lies in syncretism's adaptive fusion versus authentic transmission's emphasis on preserving core, unaltered truths.
Historical Roots of Syncretism in Religion and Culture
Syncretism in religion and culture traces its historical roots to ancient civilizations where diverse belief systems and practices converged through trade, conquest, and migration, resulting in blended spiritual traditions. This fusion often emerged from the interaction of indigenous faiths with dominant religions, such as Hellenistic influences merging with local pagan rituals or Buddhism integrating with local Asian customs. Authentic transmission, in contrast, seeks to preserve the original doctrines and rituals without external modification, emphasizing lineage, textual fidelity, and unaltered spiritual truths passed down through generations.
Authentic Transmission: Preserving Original Traditions
Authentic transmission ensures the preservation of original traditions by maintaining the integrity of teachings passed down through generations without alteration or fusion. This method emphasizes faithful adherence to historical practices, rituals, and doctrines, guarding against syncretism's blending of diverse beliefs that can dilute core values. Preservation of authentic transmission supports cultural continuity and deepens the understanding of heritage in its purest form.
Key Differences Between Syncretism and Authentic Transmission
Syncretism blends elements from multiple religious or cultural traditions, often resulting in hybrid practices that diverge from original doctrines. Authentic transmission preserves teachings and rituals exactly as handed down through recognized lineages or authorities, ensuring doctrinal purity and continuity. Key differences lie in syncretism's adaptive, integrative nature contrasting with authentic transmission's emphasis on strict fidelity to foundational texts and teachings.
Syncretism in Modern Spiritual Movements
Syncretism in modern spiritual movements blends diverse religious beliefs and practices, creating hybrid systems that emphasize inclusivity and personal experience. This fusion often involves integrating elements from Eastern spirituality, New Age concepts, and indigenous traditions, resulting in fluid and adaptable frameworks that resonate with contemporary seekers. Critics argue syncretism can dilute original doctrines, but proponents value its role in fostering cross-cultural understanding and spiritual innovation.
Risks and Challenges of Authentic Transmission
Authentic transmission faces risks such as distortion over time, loss of original context, and challenges in maintaining fidelity to source materials across generations. The challenge includes ensuring accurate interpretation, avoiding syncretic dilution, and preserving the integrity of core teachings amid cultural adaptations. Maintaining authentic transmission requires rigorous scholarship, critical analysis, and adherence to traditional frameworks to prevent misrepresentation or unauthorized alterations.
Case Studies: Syncretism in World Religions
Syncretism in world religions often emerges through the fusion of indigenous beliefs with dominant spiritual frameworks, as seen in Vodou's blend of West African spirituality and Catholicism, or Sikhism's integration of Hindu and Islamic elements. Authentic transmission, by contrast, emphasizes preserving doctrinal purity and historical continuity, illustrated by conservative branches of Buddhism maintaining canonical teachings without external modifications. Case studies reveal that syncretism facilitates cultural adaptation and religious evolution, while authentic transmission safeguards traditional identity and theological integrity.
The Role of Authority and Lineage in Transmission
Authority in transmission depends on recognized lineage tracing back to original sources or founders, ensuring authenticity and preserving doctrinal integrity. Syncretism often challenges this by mixing elements from multiple traditions, which can dilute or alter the original teachings. Maintaining a clear, authoritative lineage is crucial for authentic transmission and for safeguarding spiritual or intellectual heritage from syncretic reinterpretation.
Cultural Adaptation vs. Dilution of Tradition
Cultural adaptation allows religious and philosophical traditions to evolve by integrating elements from diverse contexts, fostering relevance and engagement across generations. Syncretism can enrich practices by blending beliefs, yet excessive fusion risks diluting core doctrines and compromising authentic transmission. Maintaining a balance ensures that traditions preserve their foundational integrity while remaining dynamic and resonant within contemporary cultural landscapes.
Striking a Balance: Contemporary Perspectives
Striking a balance between syncretism and authentic transmission involves integrating diverse cultural elements while preserving the core principles of original traditions. Contemporary perspectives emphasize the importance of contextual adaptation without distorting foundational teachings, allowing traditions to remain dynamic and relevant. This approach fosters inclusivity and continuity, promoting mutual respect amid evolving cultural landscapes.
Syncretism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com