Popular culture shapes societal trends through music, fashion, movies, and social media, reflecting the values and interests of the masses. It influences identity, behavior, and communication across generations, making it a powerful force in everyday life. Explore the rest of this article to understand how popular culture impacts your world in unexpected ways.
Table of Comparison
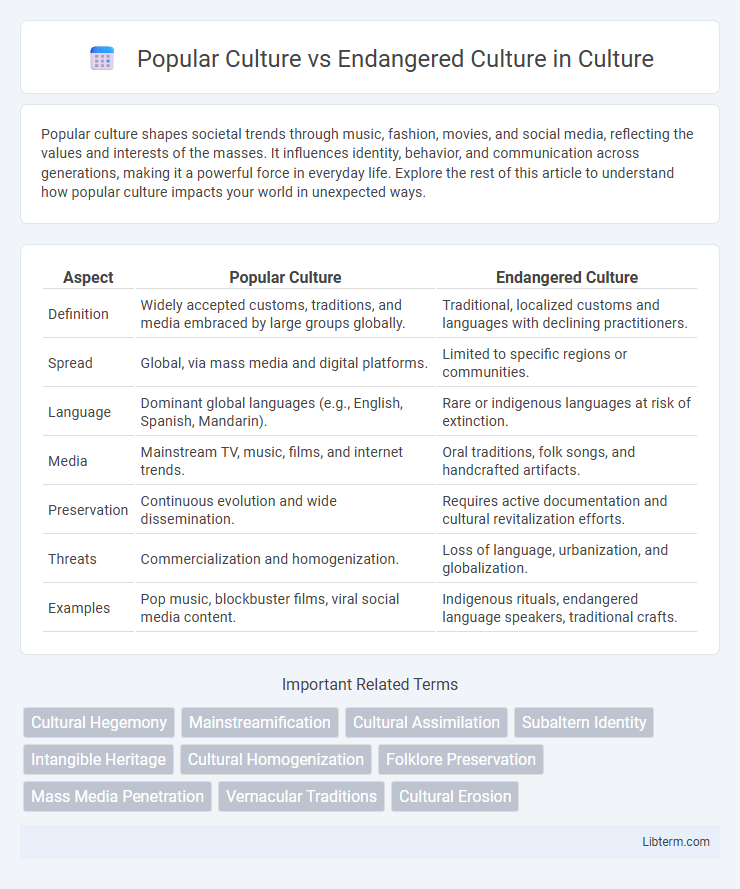
| Aspect | Popular Culture | Endangered Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Widely accepted customs, traditions, and media embraced by large groups globally. | Traditional, localized customs and languages with declining practitioners. |
| Spread | Global, via mass media and digital platforms. | Limited to specific regions or communities. |
| Language | Dominant global languages (e.g., English, Spanish, Mandarin). | Rare or indigenous languages at risk of extinction. |
| Media | Mainstream TV, music, films, and internet trends. | Oral traditions, folk songs, and handcrafted artifacts. |
| Preservation | Continuous evolution and wide dissemination. | Requires active documentation and cultural revitalization efforts. |
| Threats | Commercialization and homogenization. | Loss of language, urbanization, and globalization. |
| Examples | Pop music, blockbuster films, viral social media content. | Indigenous rituals, endangered language speakers, traditional crafts. |
Introduction: Defining Popular and Endangered Cultures
Popular culture encompasses mainstream trends, practices, and expressions widely embraced by large populations, often driven by mass media and global connectivity. Endangered culture refers to traditions, languages, and customs at risk of disappearing due to social, economic, and political pressures. Understanding these definitions highlights the dynamic tension between cultural dominance and preservation efforts worldwide.
Evolution of Popular Culture in the Modern Age
The evolution of popular culture in the modern age is characterized by rapid technological advancements and global connectivity, which have accelerated the dissemination and transformation of cultural trends worldwide. Digital media platforms, social networks, and streaming services play pivotal roles in shaping and popularizing music, fashion, and entertainment, often leading to homogenization of cultural expressions. This dynamic nature of popular culture contrasts sharply with endangered cultures, which risk losing their unique traditions and languages amid globalization and cultural assimilation pressures.
Causes of Cultural Endangerment
Cultural endangerment arises from factors such as globalization, which promotes dominant popular cultures at the expense of smaller, indigenous traditions. Urbanization and economic development lead to the displacement of communities and loss of native languages, rituals, and art forms. Media homogenization and political marginalization further accelerate the decline of endangered cultures by limiting their visibility and transmission to future generations.
Media Influence on Popular and Endangered Traditions
Media significantly amplifies popular culture by broadcasting mainstream music, films, and fashion globally, shaping collective identities and consumer behavior. In contrast, endangered cultures often receive limited media exposure, resulting in reduced awareness and accelerated cultural erosion. Efforts to digitally document and share indigenous rituals and languages through social platforms can aid in preserving these vulnerable traditions.
Globalization: Cultural Exchange or Cultural Erosion?
Globalization accelerates cultural exchange through technology, media, and migration, enabling popular culture to spread rapidly across borders. However, this dominance often leads to the erosion of endangered cultures by marginalizing local traditions and languages, undermining cultural diversity. Efforts to balance cultural preservation with global integration are essential to sustain endangered cultures amid the pervasive influence of popular culture.
The Impact of Technology on Cultural Preservation
Technology drives the preservation of endangered cultures by digitizing oral histories, traditional music, and rare languages, making them accessible to global audiences. Popular culture benefits from rapid content dissemination through social media, which simultaneously accelerates the spread and transformation of cultural expressions. Digital archives, virtual reality, and AI tools empower communities to document, revive, and teach endangered cultural practices, counteracting the homogenizing effects of globalization.
Case Studies: Endangered Cultures Around the World
Endangered cultures face extinction due to globalization, urbanization, and loss of native languages, as seen in the decline of the Ainu people of Japan, the Sentinelese of the Andaman Islands, and the Quechua-speaking communities in the Andes. These case studies highlight the vulnerability of traditional practices and indigenous knowledge systems under pressure from dominant popular culture influences such as media, technology, and economic development. Preservation efforts include language revitalization programs, legal protections, and community-driven initiatives to sustain cultural heritage and biodiversity.
Youth Engagement in Popular vs. Endangered Practices
Youth engagement in popular culture thrives through widespread digital platforms and social media, fostering active participation in music, fashion, and entertainment trends. In contrast, endangered cultures struggle to attract younger generations due to limited exposure and modernization pressures, risking cultural knowledge loss. Empowering youth involvement in traditional practices through educational programs and community initiatives is crucial for preserving endangered cultural heritage.
Strategies for Reviving Endangered Cultures
Reviving endangered cultures requires implementing community-based initiatives, such as language revitalization programs and traditional arts workshops, which foster cultural pride and transmission to younger generations. Leveraging digital platforms and social media amplifies these efforts by documenting endangered practices and connecting dispersed community members globally. Government support through policy-making and funding for cultural preservation projects ensures sustainable infrastructure to protect and promote threatened cultural heritages.
Balancing Cultural Diversity in a Globalized Society
Balancing cultural diversity in a globalized society requires preserving endangered cultures while acknowledging the widespread influence of popular culture. Efforts to maintain linguistic, artistic, and traditional heritage safeguard unique identities threatened by homogenizing global trends. Promoting intercultural dialogue and inclusive policies helps create a dynamic coexistence where diverse cultural expressions thrive alongside mainstream popular culture.
Popular Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com