Stereotype threat occurs when individuals fear confirming negative stereotypes about their social group, which can impair their performance and confidence. This psychological phenomenon often impacts academic, professional, and social settings, limiting potential and reinforcing biases. Discover how stereotype threat affects your abilities and learn strategies to overcome its effects in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
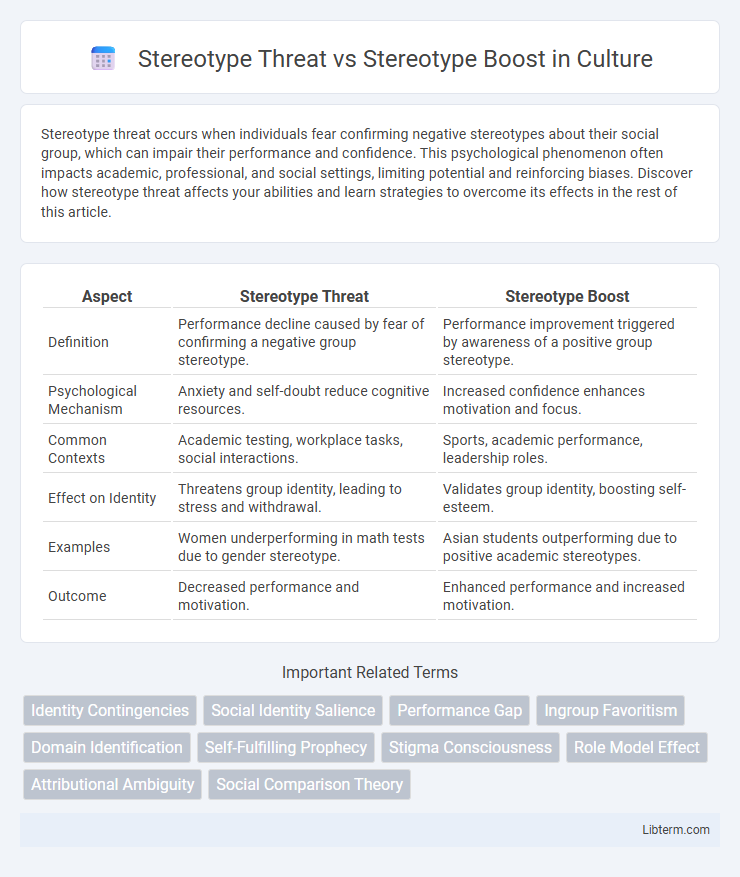
| Aspect | Stereotype Threat | Stereotype Boost |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Performance decline caused by fear of confirming a negative group stereotype. | Performance improvement triggered by awareness of a positive group stereotype. |
| Psychological Mechanism | Anxiety and self-doubt reduce cognitive resources. | Increased confidence enhances motivation and focus. |
| Common Contexts | Academic testing, workplace tasks, social interactions. | Sports, academic performance, leadership roles. |
| Effect on Identity | Threatens group identity, leading to stress and withdrawal. | Validates group identity, boosting self-esteem. |
| Examples | Women underperforming in math tests due to gender stereotype. | Asian students outperforming due to positive academic stereotypes. |
| Outcome | Decreased performance and motivation. | Enhanced performance and increased motivation. |
Understanding Stereotype Threat: Definition and Origins
Stereotype threat refers to the psychological risk of confirming negative stereotypes about one's social group, leading to impaired performance in relevant tasks. This concept, first identified by Claude Steele and Joshua Aronson in 1995, reveals how awareness of stereotypes can trigger stress and reduce cognitive resources. Understanding its origins highlights the interplay between social identity and performance, showing how situational cues activate stereotype-related anxiety.
What is Stereotype Boost? Concept and Mechanisms
Stereotype Boost refers to the enhanced performance individuals exhibit when they are aware of a positive stereotype about their social group, which activates confidence and motivation. This phenomenon occurs through mechanisms such as increased self-efficacy, reduced anxiety, and improved cognitive resource allocation. Understanding stereotype boost is crucial for leveraging positive social identities to improve outcomes in various domains like academics, sports, and workplace performance.
Psychological Impacts of Stereotype Threat
Stereotype threat significantly impairs cognitive performance by inducing anxiety and self-doubt when individuals fear confirming negative stereotypes about their group. This psychological stress depletes working memory resources, leading to decreased problem-solving abilities and lowered academic achievement. In contrast, stereotype boost enhances performance by reinforcing positive expectations linked to one's social identity, but its benefits are limited compared to the pervasive detrimental effects of stereotype threat on mental health and motivation.
Cognitive and Emotional Effects of Stereotype Boost
Stereotype boost enhances cognitive performance by increasing confidence and reducing anxiety in individuals who are reminded of positive stereotypes about their group. This boost triggers a greater release of dopamine, improving working memory and executive function, which enhances problem-solving and decision-making skills. Emotionally, stereotype boost fosters a sense of competence and motivation, leading to increased persistence and resilience in challenging tasks.
Real-World Examples of Stereotype Threat
Stereotype threat occurs when individuals underperform on tasks due to anxiety about confirming negative stereotypes about their social group, as seen in African American students scoring lower on standardized tests under evaluative pressure. Women in STEM fields often experience stereotype threat, leading to reduced math test scores and decreased interest in pursuing technical careers. Conversely, stereotype boost happens when positive stereotypes enhance performance, evident in Asian American students excelling in mathematics due to cultural expectations.
Positive Outcomes: Real-World Cases of Stereotype Boost
Stereotype boost occurs when individuals perform better than expected due to positive stereotypes associated with their social group, enhancing confidence and motivation. Real-world cases include women excelling in math tests when reminded of their gender group's strong math abilities and African American athletes outperforming in sports when racial athletic stereotypes are emphasized. These positive outcomes demonstrate how activating uplifting stereotypes can improve performance and foster success in educational and athletic domains.
Factors Influencing Stereotype Threat and Boost
Stereotype threat and stereotype boost are influenced by factors such as the relevance of the stereotype to the individual's identity, situational cues that highlight the stereotype, and the individual's level of identification with the domain involved, such as academic or athletic performance. Perceived stigma and anxiety from stereotype threat can impair task performance, while positive stereotypes and confidence enhancement lead to stereotype boost, improving outcomes. Environmental context, task framing, and prior experiences also mediate the intensity and presence of these phenomena.
Stereotype Threat vs Stereotype Boost: Key Differences
Stereotype threat refers to the risk of confirming negative stereotypes about an individual's social group, leading to decreased performance and increased anxiety. In contrast, stereotype boost occurs when positive stereotypes enhance an individual's confidence and performance in specific tasks. The key differences lie in the psychological impact: stereotype threat induces stress and underperformance, whereas stereotype boost fosters motivation and improved outcomes.
Strategies to Reduce Stereotype Threat in Education and Work
Strategies to reduce stereotype threat in education and work include fostering an inclusive environment that emphasizes individual abilities rather than group stereotypes. Implementing growth mindset interventions helps individuals view abilities as malleable, which mitigates fear of confirming negative stereotypes. Providing role models from diverse backgrounds and promoting self-affirmation exercises also enhance confidence and performance by counteracting stereotype-related anxiety.
Harnessing Stereotype Boost for Personal and Group Success
Stereotype boost occurs when positive stereotypes about one's group enhance individual performance and motivation in relevant tasks. Harnessing stereotype boost involves creating environments that emphasize strengths linked to group identity, thereby improving confidence and outcomes. Organizations and educators can leverage stereotype boost by promoting affirming narratives and role models to foster collective and personal achievement.
Stereotype Threat Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com