Appropriation involves adopting elements from another culture, often stirring debates about respect and exploitation. Understanding the fine line between cultural appreciation and appropriation can help you navigate these complex social dynamics thoughtfully. Explore the rest of this article to learn how appropriation impacts communities and what you can do to engage respectfully.
Table of Comparison
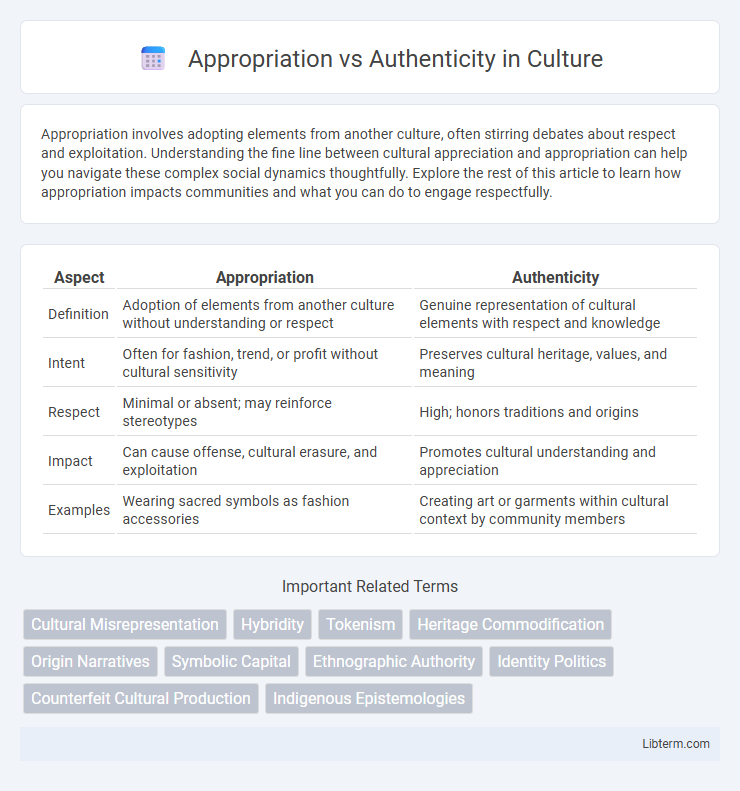
| Aspect | Appropriation | Authenticity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adoption of elements from another culture without understanding or respect | Genuine representation of cultural elements with respect and knowledge |
| Intent | Often for fashion, trend, or profit without cultural sensitivity | Preserves cultural heritage, values, and meaning |
| Respect | Minimal or absent; may reinforce stereotypes | High; honors traditions and origins |
| Impact | Can cause offense, cultural erasure, and exploitation | Promotes cultural understanding and appreciation |
| Examples | Wearing sacred symbols as fashion accessories | Creating art or garments within cultural context by community members |
Understanding Cultural Appropriation
Cultural appropriation involves adopting elements of a marginalized culture without permission, often ignoring the cultural significance and perpetuating stereotypes. Authenticity requires a respectful engagement and representation of cultural practices, acknowledging their origins and context. Understanding the difference is crucial to fostering cultural sensitivity and preventing exploitation.
Defining Cultural Authenticity
Cultural authenticity refers to the genuine representation and respect for a culture's traditions, symbols, and practices, ensuring that they are portrayed accurately and with proper context. It emphasizes the importance of originating from within the culture or being deeply knowledgeable and sensitive to its historical and social significance. Differentiating between cultural appropriation and authenticity involves assessing intent, respect, and the power dynamics underlying the use of cultural elements.
Historical Context of Appropriation
Appropriation in cultural contexts involves adopting elements from a culture, often without understanding or respecting their original meanings, which can lead to misrepresentation and harm, especially when power imbalances exist. Historically, appropriation has roots in colonialism, where dominant cultures extracted and commodified artifacts, symbols, and practices from marginalized groups, stripping them of their context and significance. Authenticity emphasizes genuine representation and respect for the source culture's history, values, and lived experiences, contrasting with appropriation's often superficial or exploitative use.
Signs of Authentic Cultural Representation
Signs of authentic cultural representation include respectful engagement with cultural symbols, accurate portrayal by members of the culture, and meaningful context that honors traditions and histories. Authentic representation avoids stereotypes and commodification, instead fostering genuine understanding and dialogue. The use of cultural elements is supported by community consent and collaboration, ensuring integrity and respect.
The Impact of Appropriation on Communities
Cultural appropriation often leads to misrepresentation and commodification of marginalized communities' heritage, resulting in the erosion of cultural identity and social tensions. Economic benefits from appropriated cultural elements usually bypass these communities, exacerbating inequality and alienation. Authenticity promotes respect and preservation of cultural expressions by ensuring community voices and traditions remain central to their portrayal and use.
Navigating Inspiration vs. Imitation
Navigating inspiration versus imitation requires a deep understanding of cultural contexts and respecting original expressions while creating new work. Appropriation involves using elements from another culture without permission or understanding, often leading to misrepresentation or harm. Authenticity emphasizes genuine engagement and honoring the source, fostering creativity that respects diversity and promotes meaningful connection.
Ethics in Cultural Exchange
Ethics in cultural exchange require a clear distinction between appropriation and authenticity, emphasizing respect, consent, and context. Cultural appropriation involves adopting elements of a culture without permission or understanding, often reinforcing stereotypes and power imbalances. Authentic engagement fosters genuine appreciation and collaboration, promoting cultural exchange grounded in mutual respect and integrity.
Case Studies: Appropriation in Media and Fashion
Case studies of appropriation in media and fashion reveal patterns where dominant cultures adopt elements from marginalized groups without proper acknowledgment or understanding, leading to controversy and accusations of cultural insensitivity. The fashion industry's frequent use of Indigenous patterns and symbols without collaboration highlights issues of exploitation and erasure, as seen in brands like Urban Outfitters and Dior facing backlash. Media representations often commodify cultural aesthetics, as in the use of African hairstyles or Native American imagery, sparking debates on the boundary between cultural appreciation and harmful appropriation.
Promoting Respectful Cultural Engagement
Promoting respectful cultural engagement requires understanding the distinction between appropriation and authenticity by honoring the origins, meanings, and contexts of cultural expressions. Educating communities about the importance of consent and collaboration with cultural representatives fosters genuine appreciation rather than exploitation. Emphasizing active listening and shared storytelling helps build bridges that sustain cultural integrity and mutual respect.
Moving Toward Genuine Authenticity
Navigating the delicate balance between appropriation and authenticity involves recognizing cultural elements respectfully while honoring their origins. Moving toward genuine authenticity requires deep understanding, intentional engagement, and collaboration with the source community to ensure representation is accurate and meaningful. This approach fosters cultural appreciation rather than exploitation, promoting mutual respect and enriching cross-cultural connections.
Appropriation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com