Legal-rational authority is a concept where power is legitimized through established laws, rules, and procedures rather than personal charisma or traditional customs. This form of authority ensures decisions are made based on legal frameworks, promoting consistency and fairness in governance. Explore the article further to understand how legal-rational authority shapes organizations and government institutions.
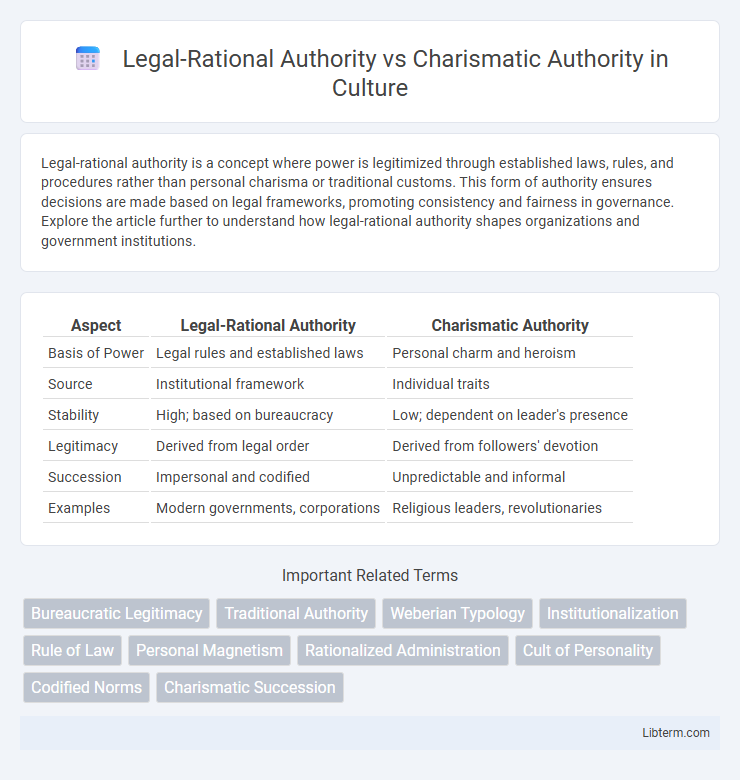
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Legal-Rational Authority | Charismatic Authority |
|---|---|---|
| Basis of Power | Legal rules and established laws | Personal charm and heroism |
| Source | Institutional framework | Individual traits |
| Stability | High; based on bureaucracy | Low; dependent on leader's presence |
| Legitimacy | Derived from legal order | Derived from followers' devotion |
| Succession | Impersonal and codified | Unpredictable and informal |
| Examples | Modern governments, corporations | Religious leaders, revolutionaries |
Introduction to Authority Types
Legal-rational authority is based on established laws, rules, and procedures that govern organizational or political systems, ensuring predictable and systematic governance. Charismatic authority arises from the personal appeal and extraordinary qualities of an individual leader, inspiring devotion and obedience from followers. These two authority types, identified by sociologist Max Weber, represent distinct foundations for legitimacy and power within societies.
Defining Legal-Rational Authority
Legal-rational authority is based on established laws, rules, and procedures that govern the legitimacy of power within organizations and governments. This type of authority relies on a formal system of codified norms and impersonal regulations, ensuring predictable and consistent decision-making processes. Max Weber identified legal-rational authority as the dominant form of legitimacy in modern bureaucratic institutions.
Understanding Charismatic Authority
Charismatic authority derives its legitimacy from the extraordinary personal qualities and vision of a leader, inspiring devotion and obedience among followers. Unlike legal-rational authority, which is based on established laws and procedures, charismatic authority relies on emotional appeal and the perceived heroism or exceptional character of the individual. This form of authority can be unstable as it depends heavily on the leader's personal influence and can dissolve once the leader departs or loses charisma.
Origins and Theoretical Foundations
Legal-rational authority originates from structured legal systems and codified rules, emphasizing bureaucratic institutions, as outlined by Max Weber's theory of authority. Charismatic authority stems from an individual's extraordinary personal qualities and the devotion they inspire, relying on emotional appeal rather than codified laws. Weber's theoretical foundations establish these as distinct types of legitimacy shaping political and organizational structures.
Key Characteristics of Legal-Rational Authority
Legal-rational authority is defined by a system of rules and laws that govern obedience rather than personal loyalty to an individual, establishing legitimacy through a structured bureaucracy and formal procedures. Key characteristics include a clear hierarchy of offices, a codified set of rules, and the impersonal application of regulations ensuring consistency and predictability in decision-making. This form of authority contrasts with charismatic authority, which relies on the personal charm and exceptional qualities of a leader to inspire devotion.
Distinct Features of Charismatic Authority
Charismatic authority is defined by the exceptional personal qualities and vision of a leader, inspiring loyalty and devotion beyond formal rules or legal frameworks. Unlike legal-rational authority, which relies on established laws and procedures, charismatic authority depends on the leader's ability to mobilize followers through emotional appeal and perceived extraordinary capabilities. This form of authority often emerges during times of crisis or social upheaval, where traditional legal systems lose legitimacy and the leader's personal magnetism becomes the primary source of power.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Authority
Legal-rational authority provides clear rules and procedures that ensure predictability, consistency, and accountability in governance, which facilitates large-scale administrative efficiency and stability. However, its reliance on formal structures can lead to rigidity, impersonality, and resistance to change. Charismatic authority inspires loyalty and fosters innovation through personal appeal and visionary leadership but risks instability and unpredictability due to dependence on the individual leader's presence and charisma.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Legal-rational authority is exemplified by institutions like the U.S. government, where power is derived from established laws and procedures, ensuring predictable governance and accountability. Charismatic authority appears in figures such as Martin Luther King Jr., whose influence stemmed from personal charisma and vision, inspiring social movements without formal legal backing. Case studies reveal that legal-rational systems provide stability and rule-based leadership, while charismatic authority drives rapid social change but often requires institutionalization to sustain long-term impact.
Impact on Organizations and Society
Legal-rational authority establishes stability and predictability in organizations through codified rules and procedures, promoting accountability and bureaucratic efficiency. Charismatic authority drives organizational and societal change by inspiring loyalty and motivating innovation, but can also lead to volatility and dependence on a single leader. The balance between these authority types affects organizational culture, leadership succession, and social order dynamics.
Conclusion: Comparing Authority Systems
Legal-rational authority is grounded in established laws, rules, and procedures, ensuring predictability and stability within organizations and governments. Charismatic authority depends on the personal qualities and extraordinary leadership of an individual, often resulting in rapid mobilization but potential instability. Comparing both systems reveals that legal-rational authority excels in institutional consistency, while charismatic authority drives dynamic change through personal influence.
Legal-Rational Authority Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com