Cultural diffusion refers to the spread of cultural beliefs, practices, and innovations from one group to another, shaping societies and influencing traditions worldwide. It plays a crucial role in the development of languages, religions, and art forms by facilitating the exchange of ideas and customs. Explore the rest of the article to understand how cultural diffusion impacts your worldview and global connections.
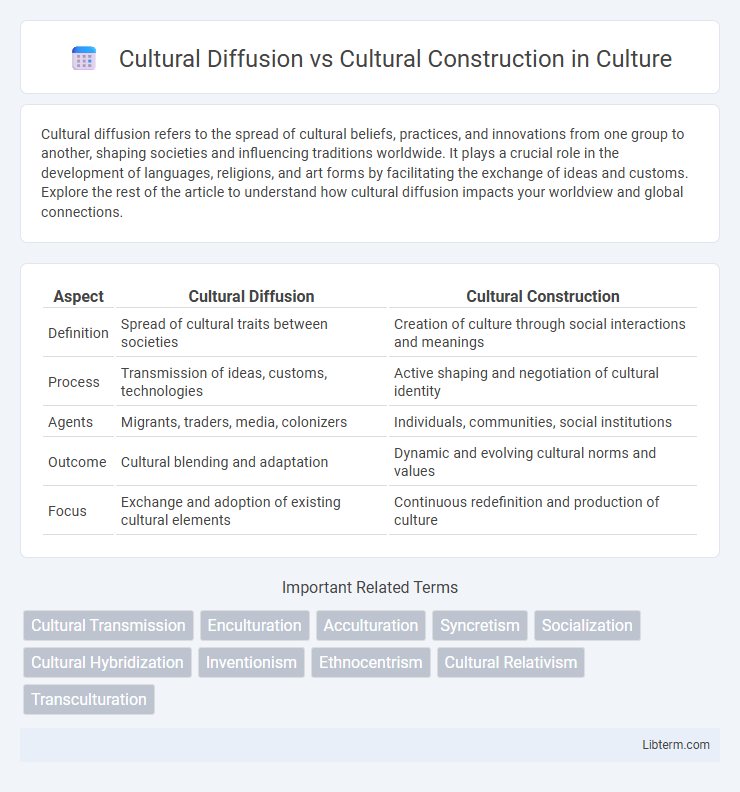
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cultural Diffusion | Cultural Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Spread of cultural traits between societies | Creation of culture through social interactions and meanings |
| Process | Transmission of ideas, customs, technologies | Active shaping and negotiation of cultural identity |
| Agents | Migrants, traders, media, colonizers | Individuals, communities, social institutions |
| Outcome | Cultural blending and adaptation | Dynamic and evolving cultural norms and values |
| Focus | Exchange and adoption of existing cultural elements | Continuous redefinition and production of culture |
Introduction to Cultural Diffusion and Cultural Construction
Cultural diffusion refers to the process through which cultural elements, such as beliefs, technologies, and practices, spread from one society to another, facilitating cross-cultural interactions and shared innovations. Cultural construction emphasizes how societies actively shape and redefine cultural meanings, identities, and social norms based on historical, social, and political contexts. Understanding the dynamics between cultural diffusion and construction highlights the interplay between external influences and internal reinterpretations in shaping cultural landscapes.
Defining Cultural Diffusion
Cultural diffusion refers to the process through which cultural elements such as beliefs, customs, technologies, and languages spread from one society to another, facilitating cultural exchange and adaptation. This phenomenon often occurs through trade, migration, conquest, or communication, resulting in the blending and transformation of cultural traits. Understanding cultural diffusion is crucial for analyzing how cultures influence each other and evolve over time in response to external interactions.
Key Mechanisms of Cultural Diffusion
Cultural diffusion occurs through mechanisms such as migration, trade, communication, and technological exchange, facilitating the spread of ideas, customs, and innovations across societies. These key processes enable cultural traits to be adopted, adapted, and integrated into different social contexts, promoting cross-cultural interaction. In contrast, cultural construction emphasizes how societies actively create and interpret cultural meanings based on internal social dynamics and historical contexts.
Understanding Cultural Construction
Cultural construction refers to the process through which societies create and assign meaning to cultural norms, values, and practices, shaping collective identity over time. This concept emphasizes that culture is not static but continuously formed and reformed through social interactions, power dynamics, and historical contexts. Understanding cultural construction allows for deeper insights into how cultural realities are actively negotiated and maintained within communities.
Processes Involved in Cultural Construction
Cultural construction involves active processes like social interaction, communication, and shared meaning-making that shape cultural norms, values, and identities within communities. It emphasizes how individuals and groups collectively create and negotiate culture through symbols, language, and rituals, reinforcing social cohesion and cultural continuity. Unlike cultural diffusion, which spreads existing cultural traits across societies, cultural construction highlights the dynamic formation and reinterpretation of culture from within.
Major Differences Between Cultural Diffusion and Construction
Cultural diffusion involves the spread of cultural elements such as ideas, styles, religions, and technologies from one society to another, often through trade, migration, or communication. In contrast, cultural construction refers to the process by which societies actively create and shape their own cultural meanings, norms, and identities internally over time. The major difference lies in diffusion being an external transmission of culture, whereas construction emphasizes internal development and social negotiation within a group.
Real-World Examples of Cultural Diffusion
Cultural diffusion occurs when elements of one culture, such as language, technology, or customs, spread to another, exemplified by the global adoption of sushi from Japan or the worldwide influence of American fast food chains like McDonald's. This contrasts with cultural construction, where societies actively create or redefine cultural meanings internally, such as the development of new national identities post-colonization. Real-world diffusion demonstrates the dynamic exchange of cultural traits across borders, shaping globalization and intercultural interactions.
Case Studies Illustrating Cultural Construction
Case studies of cultural construction reveal how societies actively create and shape cultural identities, values, and traditions through social practices and institutions. The Maasai of East Africa illustrate cultural construction by maintaining pastoralist customs and rituals that define their communal identity despite external pressures. Similarly, Japan's post-Meiji Restoration modernization represents cultural construction where selective Western influences merged with traditional Japanese values to forge a unique national culture.
Impact of Globalization on Culture
Globalization accelerates cultural diffusion by facilitating the rapid exchange of ideas, values, and practices across borders, leading to increased cultural hybridity and diversity worldwide. Simultaneously, cultural construction reinforces local identities by adapting global influences into unique cultural expressions shaped by historical, social, and political contexts. The dynamic interplay between diffusion and construction highlights globalization's role in both homogenizing and diversifying cultural landscapes.
Conclusion: The Interplay of Diffusion and Construction in Modern Societies
Modern societies continuously evolve through the dynamic interplay between cultural diffusion and cultural construction, where ideas, practices, and innovations spread globally while local communities adapt and reshape them according to unique social, historical, and environmental contexts. This interaction fosters hybrid identities and diverse cultural expressions, reflecting both external influences and internal creativity. Understanding this reciprocity is crucial for comprehending cultural transformation in an interconnected world.
Cultural Diffusion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com