Nika culture enriches communities with vibrant traditions, music, and art that celebrate identity and heritage. Yoruba culture, deeply rooted in West African history, is known for its rich mythology, spiritual practices, and intricate social structures. Explore the rest of this article to uncover how these cultural legacies shape modern expressions of identity and community.
Table of Comparison
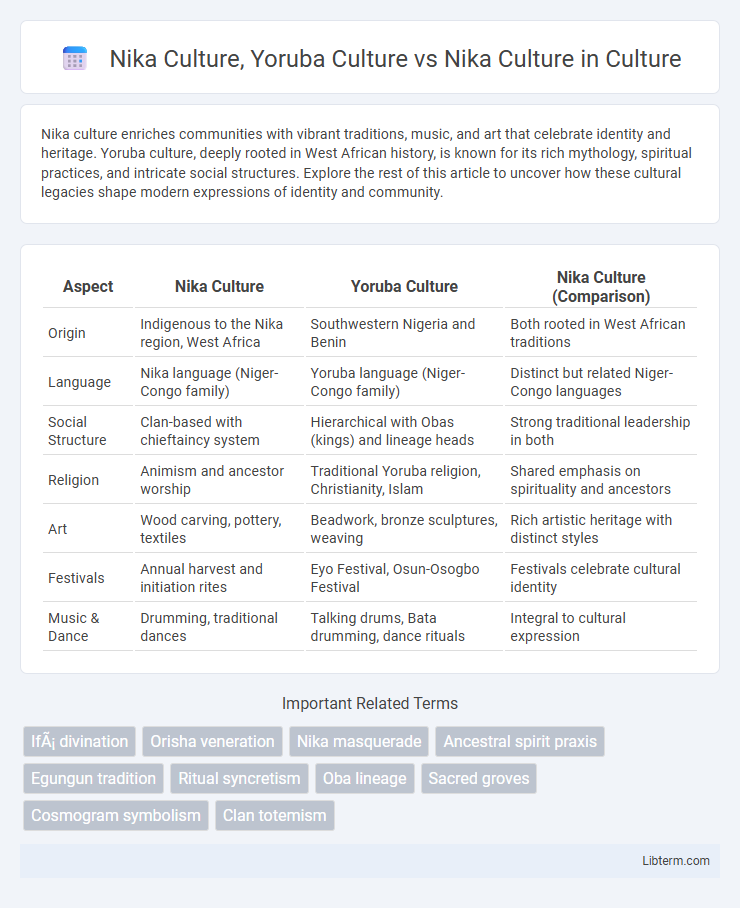
| Aspect | Nika Culture | Yoruba Culture | Nika Culture (Comparison) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Origin | Indigenous to the Nika region, West Africa | Southwestern Nigeria and Benin | Both rooted in West African traditions |
| Language | Nika language (Niger-Congo family) | Yoruba language (Niger-Congo family) | Distinct but related Niger-Congo languages |
| Social Structure | Clan-based with chieftaincy system | Hierarchical with Obas (kings) and lineage heads | Strong traditional leadership in both |
| Religion | Animism and ancestor worship | Traditional Yoruba religion, Christianity, Islam | Shared emphasis on spirituality and ancestors |
| Art | Wood carving, pottery, textiles | Beadwork, bronze sculptures, weaving | Rich artistic heritage with distinct styles |
| Festivals | Annual harvest and initiation rites | Eyo Festival, Osun-Osogbo Festival | Festivals celebrate cultural identity |
| Music & Dance | Drumming, traditional dances | Talking drums, Bata drumming, dance rituals | Integral to cultural expression |
Introduction to Nika Culture
Nika Culture represents an ancient African tradition known for its rich artistic expressions, intricate rituals, and strong community values. Unlike Yoruba Culture, which emphasizes a complex pantheon of deities and elaborate masquerade ceremonies, Nika Culture focuses on ancestral worship and the harmonious connection between nature and human life. The distinct symbolic practices and oral histories of Nika Culture provide unique insights into the spiritual and social structures that define this vibrant cultural identity.
Historical Overview of the Nika People
The Nika people, an ethnic group primarily located in West Africa, have a rich history marked by unique linguistic and cultural traditions that distinguish them from the Yoruba culture. Unlike the Yoruba, known for their extensive city-states and profound influence on art and religion, the Nika have maintained a more localized social structure with a strong emphasis on oral history and ancestral worship. Archaeological findings and oral traditions trace the Nika's origins to ancient migrations that shaped their distinct identity in the region.
Core Values and Beliefs of Nika Culture
Nika Culture centers on communal harmony, respect for ancestors, and a deep spiritual connection with nature, emphasizing collective responsibility and generational continuity. Yoruba Culture, while also valuing community and spirituality, places significant importance on individual destiny (Ayanmo) and a complex pantheon of deities guiding moral and social conduct. Both cultures uphold respect and reverence for elders but differ in the expression of core values, with Nika Culture prioritizing environmental symbiosis and Yoruba Culture focusing on personal destiny and divine influence.
Social Structure in Nika Society
Nika culture features a complex social structure centered around communal living, age-grade systems, and hierarchical leadership roles that emphasize collective responsibility and mutual support. Unlike Yoruba culture, which organizes society into distinct kingdoms and employs a stratified chieftaincy system integrating religion and governance, Nika social organization prioritizes egalitarian principles with flexible leadership based on consensus and communal welfare. The Nika society's social fabric is reinforced by ritual initiations and kinship ties that foster unity and sustain traditional norms across generations.
Overview of Yoruba Culture
Yoruba culture, rooted in southwestern Nigeria, is characterized by its rich traditions, intricate religious beliefs, and vibrant festivals such as Egungun and Osun-Osogbo. This culture emphasizes extended family structures, artistic expression through textiles and beadwork, and a hierarchical social system led by Obas (kings). In contrast, Nika culture, primarily found in the northeastern region of Nigeria, features distinct linguistic patterns, nomadic influences, and unique ritual practices centered around cattle herding and seasonal migration.
Key Differences Between Nika and Yoruba Traditions
Nika culture originates from the Afro-Cuban community with West African roots, emphasizing syncretic religious practices such as Santeria, which blend Yoruba deities with Catholic saints, whereas Yoruba culture is indigenous to Nigeria with deeply rooted traditional beliefs and deities like Orishas in their original Yoruba religion. Yoruba culture centers on ancestral worship, elaborate festivals like the Eyo Festival, and language-specific oral traditions, while Nika culture reflects fusion elements, influenced by the Haitian Vodou and Cuban Santeria, resulting in unique ceremonial music and dance styles distinct from Yoruba practices. Key differences lie in linguistic usage--Yoruba language is prevalent in West Africa and traditional ceremonies, whereas Nika culture primarily uses Afro-Cuban dialects and Spanish, shaping divergent ritual expressions and cultural identities.
Rituals and Festivals: Nika vs. Yoruba
Nika culture features rituals deeply rooted in ancestor worship and harvest celebrations, emphasizing communal harmony and spiritual balance through ceremonies like the Nika Harvest Festival. Yoruba culture presents a rich tapestry of festivals such as the Egungun masquerade, honoring ancestral spirits, and the Osun-Osogbo festival, dedicated to the river goddess Osun, highlighting the central role of divination and deities in ritual practices. Both cultures use vibrant music, dance, and symbolic attire in their rituals, though Yoruba ceremonies often incorporate complex Ifa divination systems absent in Nika traditions.
Language and Oral Traditions: A Comparative Analysis
Nika culture, predominantly found in Benin and Togo, employs the Nka language, characterized by complex tonal variations and a robust oral tradition of folklore, proverbs, and songs that preserve historical narratives. Yoruba culture, centered in Nigeria and surrounding regions, uses the Yoruba language, notable for its extensive vowel system and rich literary oral heritage encompassing Ifa divination verses, storytelling, and praise poetry. Comparative analysis reveals that both cultures emphasize oral transmission as a means of cultural preservation, with Nka language's tonal complexity paralleling Yoruba's intricate poetic structures, highlighting the integral role of language in sustaining identity and historical consciousness.
Art, Music, and Dress: Contrasts in Expression
Nika Culture showcases vibrant beadwork, intricate body tattoos, and dynamic dance forms that express spiritual and communal values, while Yoruba Culture emphasizes elaborate textile patterns such as Adire and Aso Oke, with drumming ensembles like the talking drum central to musical expression. Artistic expressions in Nika Culture lean toward organic materials and earth tones, contrasting with the Yoruba's bold color palettes and symbolic motifs that convey social status and mythology. Dress in Nika Culture uniquely incorporates natural elements like feathers and shells, differing from the Yoruba's structured garments that often signify cultural identity and ceremonial roles.
Modern Influences on Nika and Yoruba Cultures
Nika culture, rooted in the Ewe ethnic group of West Africa, showcases unique traditions and artisanal crafts that have evolved with modern influences such as globalization and digital communication, enhancing its visibility and economic potential. Yoruba culture, predominant in southwestern Nigeria, blends ancient religious practices, art, and language with contemporary elements like technology, urbanization, and popular music, fostering a dynamic cultural identity. Both cultures integrate traditional values with modern education and media, creating a fusion that preserves heritage while adapting to global trends.
Nika Culture, Yoruba Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com