Understanding the complexities of law ensures you are better equipped to protect your rights and navigate legal challenges effectively. Whether dealing with contracts, criminal cases, or family disputes, knowledge of legal principles is essential. Explore the rest of the article to gain insights into key legal concepts that impact your daily life.
Table of Comparison
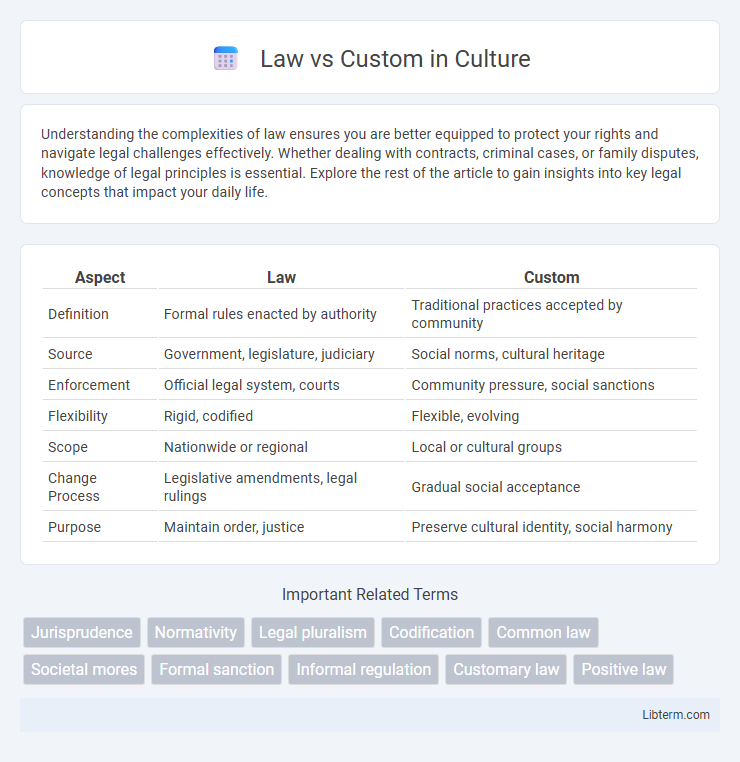
| Aspect | Law | Custom |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal rules enacted by authority | Traditional practices accepted by community |
| Source | Government, legislature, judiciary | Social norms, cultural heritage |
| Enforcement | Official legal system, courts | Community pressure, social sanctions |
| Flexibility | Rigid, codified | Flexible, evolving |
| Scope | Nationwide or regional | Local or cultural groups |
| Change Process | Legislative amendments, legal rulings | Gradual social acceptance |
| Purpose | Maintain order, justice | Preserve cultural identity, social harmony |
Understanding the Concepts: Law and Custom
Law comprises formal rules enacted and enforced by governmental institutions, ensuring societal order through codified statutes and regulations. Custom embodies traditional practices and unwritten norms developed over time within communities, influencing behavior based on collective acceptance rather than legal mandate. Understanding the distinction between law and custom is essential, as laws provide official guidelines subject to legal penalties, while customs shape social conduct through cultural continuity and moral obligation.
Historical Evolution of Law and Custom
Law and custom have evolved distinctly, with customary practices often serving as the foundation for formal legal systems in various societies. Historical evidence shows that customary law predates codified statutes, as early communities relied on traditions and social norms to regulate behavior and resolve disputes. Over time, these customs were institutionalized into formal laws through legislative processes and judicial recognition, reflecting a dynamic interplay between societal values and legal frameworks.
Key Differences Between Law and Custom
Law consists of formal rules established and enforced by governmental institutions, while custom represents informal practices developed within communities over time. Laws are codified, written, and carry legal authority with specific sanctions for violations, whereas customs are unwritten, flexible norms that gain social acceptance without formal penalties. The enforcement of law relies on judiciary systems, whereas customs depend on social pressure and collective recognition for compliance.
Sources and Foundations of Law
Law derives its authority primarily from formal sources such as constitutions, statutes, and judicial precedents, which establish a structured framework for legal governance. Custom, as a source of law, evolves from long-standing social practices and community traditions that gain normative force through consistent acceptance and observance. The foundational distinction lies in law's codification and enforceability by recognized institutions versus custom's informal, organic development rooted in societal consensus.
Origins and Development of Custom
Custom originates from long-established social practices deeply rooted in the collective behavior and traditions of a community, evolving organically over time without formal codification. Its development is influenced by cultural norms, collective memory, and repeated social actions that gain normative force, eventually guiding individual conduct and communal interactions. Unlike law, custom's authority derives from social acceptance and habitual observance rather than legislative enactment or judicial enforcement.
The Role of Law in Modern Societies
Law provides a formalized system of rules and regulations that govern behavior and resolve disputes, ensuring social order and stability in modern societies. It establishes universally accepted standards that protect individual rights, promote justice, and regulate interactions across diverse communities. Unlike customs, laws are codified, enforceable by official institutions, and adaptable to the evolving needs of contemporary populations.
The Influence of Custom on Social Behavior
Custom significantly shapes social behavior by establishing unwritten norms and practices that guide individuals within communities. These habitual patterns influence daily interactions, reinforcing group identity and social cohesion through consistent observance over time. Unlike formal laws, customs evolve organically, reflecting collective values and often serving as the foundation for legal principles.
Interaction Between Law and Custom
Law and custom interact as complementary forces shaping societal norms, where customs often influence the formation and interpretation of legal statutes. Legal systems may recognize customary practices as binding rules, especially in areas like family law, property, and dispute resolution among indigenous communities. This dynamic ensures that laws remain relevant and adaptable, reflecting the living traditions and values of the affected populations.
Advantages and Limitations of Law and Custom
Law provides clear, codified rules that ensure consistent enforcement and legal certainty, facilitating social order and dispute resolution. However, laws can be rigid and slow to adapt to societal changes, sometimes leading to conflicts with evolving cultural values. Custom embodies flexible, community-based practices that foster social cohesion and respect traditional norms but may lack formal recognition and enforceability in broader legal systems.
The Future of Law and Custom in a Changing World
The future of law and custom hinges on their dynamic interplay amid rapid social and technological changes, where legal systems increasingly integrate digital norms and cultural practices. Emerging fields such as cybersecurity law and indigenous rights exemplify how customary traditions influence modern legal frameworks, ensuring relevance and adaptability. Legal pluralism will continue to shape governance, balancing statutory mandates with evolving societal customs to address complex global challenges.
Law Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com