Current refers to the flow of electric charge through a conductor, measured in amperes (amps). It plays a crucial role in powering devices, enabling communication systems, and driving industrial machinery. Explore the detailed explanation of current, its types, and practical applications in the full article.
Table of Comparison
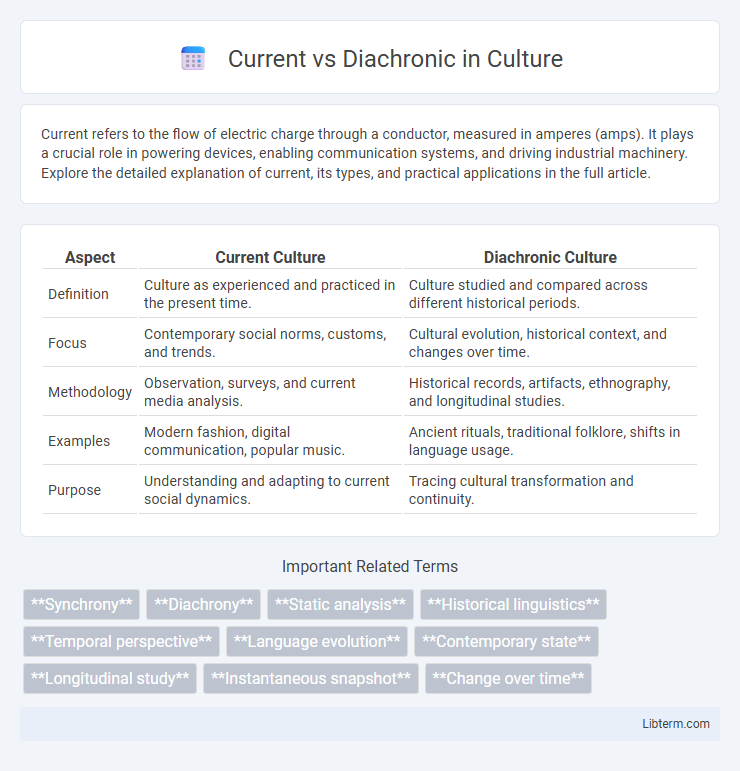
| Aspect | Current Culture | Diachronic Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Culture as experienced and practiced in the present time. | Culture studied and compared across different historical periods. |
| Focus | Contemporary social norms, customs, and trends. | Cultural evolution, historical context, and changes over time. |
| Methodology | Observation, surveys, and current media analysis. | Historical records, artifacts, ethnography, and longitudinal studies. |
| Examples | Modern fashion, digital communication, popular music. | Ancient rituals, traditional folklore, shifts in language usage. |
| Purpose | Understanding and adapting to current social dynamics. | Tracing cultural transformation and continuity. |
Introduction to Current and Diachronic Perspectives
Current perspectives analyze language, culture, or phenomena as they exist at a specific point in time, emphasizing contemporary usage and conditions. Diachronic perspectives study the evolution and historical development of these elements over extended periods, tracing changes and patterns. Understanding both viewpoints enriches insights into the dynamics between present states and their historical trajectories.
Defining Current Analysis
Current analysis examines language use as it exists at a specific point in time, capturing contemporary linguistic features without considering historical development. This approach prioritizes synchronic data, such as modern speech patterns, vocabulary, and grammar structures, enabling linguists to understand the language system in its present state. It contrasts with diachronic analysis, which studies language evolution across different periods.
Understanding Diachronic Analysis
Diachronic analysis examines linguistic or cultural changes over time, tracking the evolution of language, behaviors, or societal trends across historical periods. This longitudinal approach contrasts with current (synchronic) analysis, which focuses on understanding phenomena at a specific point in time. Understanding diachronic analysis provides insights into how and why shifts occur, revealing patterns of development and transformation in language structure, usage, or cultural practices.
Historical Evolution of Concepts
Current analysis examines concepts as they exist in contemporary contexts, while diachronic study traces their historical evolution and transformation over time. Understanding the diachronic development of ideas, such as linguistic meanings or cultural practices, reveals shifts influenced by historical events, social changes, and technological advancements. This approach deepens insights into how concepts adapt and reemerge, shaping present interpretations and future trajectories.
Methodological Differences
Current linguistic analysis examines language data from a specific point in time using synchronic methods, emphasizing structural and functional aspects without historical context. Diachronic studies employ a historical approach, tracing language evolution and changes across different periods by analyzing diachronic corpora and comparative data. Methodologically, current research relies on descriptive and corpus-based techniques, while diachronic research incorporates historical documentation, reconstruction, and comparative linguistics to understand language change.
Applications in Linguistics
Current linguistics analyzes language structures and usage at a specific point in time, providing insights into contemporary speech patterns and syntax, which aids in developing natural language processing (NLP) algorithms for real-time communication technologies. Diachronic linguistics examines language evolution and historical changes, crucial for tracing etymology, reconstructing proto-languages, and understanding semantic shifts that influence modern language interpretation. Both approaches inform computational linguistics and lexicography, enabling more accurate machine translation systems and improved language teaching methodologies.
Relevance in Social Sciences
Current analysis examines social phenomena as they exist in the present, providing insights into contemporary behaviors and structures essential for policy-making and social interventions. Diachronic analysis tracks changes over time, revealing patterns, trends, and evolutions critical for understanding historical context and long-term social dynamics. Social sciences use both approaches to balance immediate relevance with deeper temporal understanding, enhancing the precision of research outcomes and theoretical frameworks.
Case Studies: Current vs Diachronic Approaches
Case studies in current linguistic approaches analyze language use in real-time contexts, emphasizing contemporary usage patterns and social interactions. Diachronic case studies track language evolution over extended periods, revealing shifts in syntax, semantics, and phonology influenced by historical and cultural changes. Comparing these methods highlights the dynamic interplay between language stability and transformation across time.
Advantages and Limitations
Current linguistic analysis provides precise snapshots of language use, enabling detailed examination of contemporary grammar, vocabulary, and phonetics, which aids in understanding real-time communication patterns. Diachronic linguistics offers invaluable insights into language evolution, revealing historical shifts and the development of linguistic structures over long periods. However, current analysis may overlook historical context and language origins, while diachronic studies often face challenges due to incomplete data and the complexity of tracing linguistic changes through time.
Future Directions and Research
Future research in Current vs Diachronic studies aims to integrate advanced computational models and large-scale linguistic databases to better capture language evolution over time. Emphasis on cross-linguistic comparisons and real-time data analysis will enhance understanding of language variation and change mechanisms. Interdisciplinary approaches combining sociolinguistics, psycholinguistics, and corpus linguistics promise to refine theoretical frameworks and predictive models for future language dynamics.
Current Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com