Technocratic authority relies on expertise and specialized knowledge to guide decision-making processes in organizations and governments. This form of authority prioritizes competence and empirical evidence over traditional or charismatic leadership styles. Explore the rest of this article to understand how technocratic authority shapes modern governance and your everyday life.
Table of Comparison
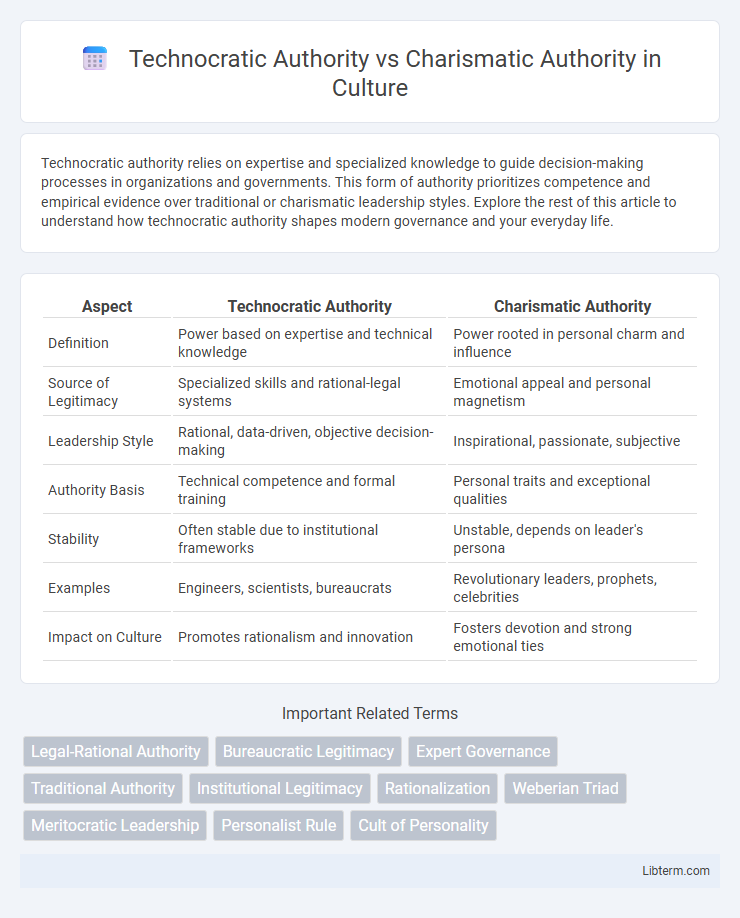
| Aspect | Technocratic Authority | Charismatic Authority |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Power based on expertise and technical knowledge | Power rooted in personal charm and influence |
| Source of Legitimacy | Specialized skills and rational-legal systems | Emotional appeal and personal magnetism |
| Leadership Style | Rational, data-driven, objective decision-making | Inspirational, passionate, subjective |
| Authority Basis | Technical competence and formal training | Personal traits and exceptional qualities |
| Stability | Often stable due to institutional frameworks | Unstable, depends on leader's persona |
| Examples | Engineers, scientists, bureaucrats | Revolutionary leaders, prophets, celebrities |
| Impact on Culture | Promotes rationalism and innovation | Fosters devotion and strong emotional ties |
Understanding Technocratic Authority
Technocratic authority relies on expertise, technical knowledge, and specialized skills to make decisions and govern effectively within organizations or governments. This form of authority is legitimized by the perceived competence and rationality of experts who apply data-driven methods and scientific principles. Unlike charismatic authority, which depends on personal appeal, technocratic authority emphasizes systematic problem-solving and evidence-based policies.
Defining Charismatic Authority
Charismatic authority is defined by the personal charm, vision, and influence of a leader, which inspires devotion and obedience from followers. It is established through the perceived extraordinary qualities and emotional connection a leader has with their audience, rather than formal rules or expertise. This form of authority contrasts with technocratic authority, which relies on specialized knowledge and technical competence to legitimize power.
Historical Contexts of Both Authorities
Technocratic authority emerged prominently during the Industrial Revolution and the rise of modern bureaucracies, emphasizing expertise, technical knowledge, and rational decision-making, especially in government and corporate institutions. Charismatic authority, rooted in Max Weber's sociological framework, historically proliferated during times of social upheaval or revolution, exemplified by leaders like Napoleon Bonaparte and Martin Luther King Jr., whose personal charisma inspired loyalty and social change. Both forms of authority shaped political and organizational structures differently, with technocratic rule prioritizing efficiency and expertise, while charismatic authority relied on personal magnetism and visionary leadership within specific historical contexts.
Core Principles and Foundations
Technocratic authority is grounded in expertise, technical knowledge, and rational-legal frameworks, emphasizing efficiency and specialized skills in decision-making processes. Charismatic authority derives its legitimacy from an individual's extraordinary personal qualities, inspiring devotion and emotional appeal beyond formal rules or institutional structures. While technocratic power prioritizes systematic competence and objective criteria, charismatic authority relies on personal trust and revolutionary vision to mobilize followers.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Technocratic authority relies on expertise, data analysis, and systematic procedures to guide decision-making, emphasizing rationality and efficiency. In contrast, charismatic authority depends on the leader's personal appeal, vision, and emotional influence, often resulting in more intuitive and flexible decisions. The technocratic approach prioritizes formal structures and objective criteria, while charismatic decision-making is shaped by individual charisma and follower loyalty.
Legitimacy and Public Perception
Technocratic authority derives legitimacy from expertise, specialized knowledge, and rational decision-making, often appealing to public trust in competency and evidence-based policies. Charismatic authority, by contrast, secures legitimacy through the leader's personal charm, vision, and emotional appeal, influencing public perception via loyalty and inspiration rather than formal credentials. Public perception of technocratic authority tends to favor stability and efficiency, while charismatic authority thrives on dynamic leadership and personal connection with followers.
Impact on Organizational Effectiveness
Technocratic authority enhances organizational effectiveness through data-driven decision-making, promoting consistency and efficiency in complex environments. Charismatic authority motivates employees by inspiring loyalty and commitment, driving innovation and adaptability during change. Organizations that balance technocratic expertise with charismatic leadership often achieve superior performance by blending structured processes with dynamic vision.
Risks and Limitations of Each Authority
Technocratic authority risks over-reliance on specialized knowledge, potentially leading to detachment from public needs and reduced democratic accountability. Charismatic authority faces limitations in its dependence on the leader's personal appeal, which can result in instability and challenges in sustaining long-term governance once the leader departs. Both forms of authority can create vulnerabilities: technocratic systems may struggle with bureaucratic rigidity, while charismatic systems risk leader-centric decision-making and lack institutional checks.
Case Studies: Technocratic vs Charismatic Leadership
Technocratic authority is exemplified by leaders like Angela Merkel, whose decisions are grounded in expertise, data, and pragmatic problem-solving, fostering stability and efficiency in governance. Charismatic authority, seen in figures such as Martin Luther King Jr., relies on personal charm and emotional appeal to inspire mass movements and social change. Case studies reveal that technocratic leadership excels in policy implementation, while charismatic leadership drives transformative social influence through vision and motivation.
Future Trends in Authority Structures
Future trends in authority structures indicate a growing emphasis on technocratic authority, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, data analytics, and digital governance systems that prioritize expertise and efficiency. Charismatic authority, while still influential in political and social movements, faces challenges maintaining legitimacy amid increasing demand for transparent, evidence-based decision-making. Hybrid models combining technocratic precision with charismatic leadership traits are emerging to address complex societal needs by balancing emotional resonance with technical competence.
Technocratic Authority Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com