Synonymy refers to the phenomenon where different words share the same or nearly the same meaning, enhancing language richness and variety. Understanding synonymy can improve your writing by enabling more precise and engaging expression. Explore the rest of this article to discover how synonymy impacts communication and language learning.
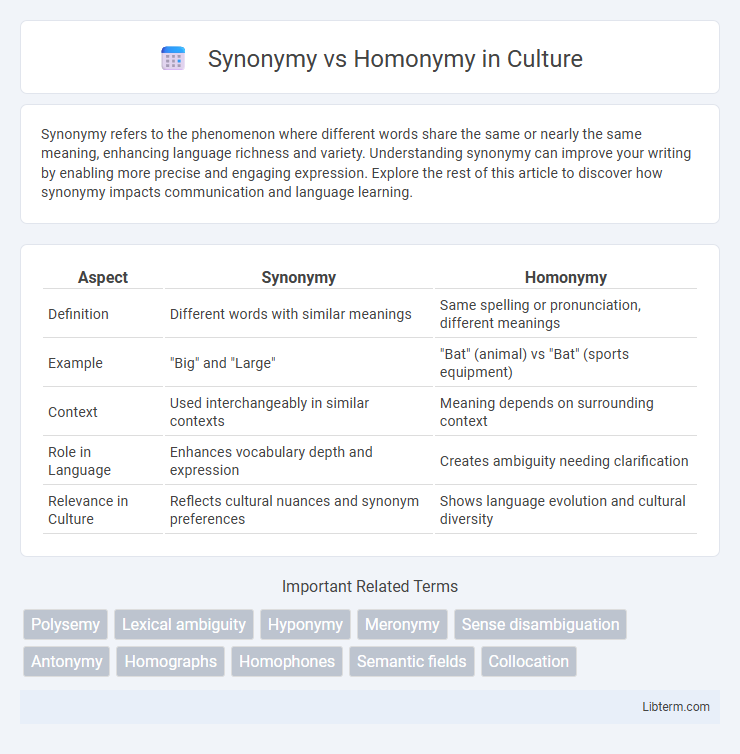
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Synonymy | Homonymy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Different words with similar meanings | Same spelling or pronunciation, different meanings |
| Example | "Big" and "Large" | "Bat" (animal) vs "Bat" (sports equipment) |
| Context | Used interchangeably in similar contexts | Meaning depends on surrounding context |
| Role in Language | Enhances vocabulary depth and expression | Creates ambiguity needing clarification |
| Relevance in Culture | Reflects cultural nuances and synonym preferences | Shows language evolution and cultural diversity |
Introduction to Synonymy and Homonymy
Synonymy refers to the relationship between words that have similar or identical meanings, such as "big" and "large," enhancing lexical variety and precision in language. Homonymy involves words that share the same spelling or pronunciation but have different meanings, like "bat" (an animal) and "bat" (a sports equipment), which can cause ambiguity in communication. Understanding these concepts is essential for effective language use, semantics, and natural language processing applications.
Defining Synonymy: Meaning and Examples
Synonymy refers to the relationship between words that share the same or very similar meanings, such as "big" and "large," allowing for interchangeable use in many contexts without significant change in meaning. This semantic equivalence enables more precise or stylistic choices in language, enriching vocabulary flexibility. Examples of synonymy include pairs like "happy" and "joyful," "quick" and "fast," which demonstrate subtle distinctions yet overall semantic overlap.
Understanding Homonymy: Concepts and Illustrations
Homonymy occurs when two or more words share the same spelling or pronunciation but have different meanings, such as "bat" (the animal) and "bat" (the sports equipment). Understanding homonymy involves recognizing context clues that differentiate these meanings within sentences. Examples like "bank" (financial institution) versus "bank" (river edge) illustrate how semantic ambiguity arises from homonymous terms.
Key Differences between Synonymy and Homonymy
Synonymy involves different words with similar or identical meanings, such as "big" and "large," while homonymy refers to a single word spelling or pronunciation associated with multiple unrelated meanings, like "bat" (the animal) and "bat" (used in sports). Synonyms enhance lexical choice and precision in language, whereas homonyms often create ambiguity requiring contextual disambiguation. Understanding the distinction between synonymy and homonymy is essential for effective communication and accurate language processing in linguistics.
Types of Synonymy in Linguistics
Synonymy in linguistics refers to words or phrases with similar meanings, categorized into types such as absolute synonymy, where words are interchangeable in all contexts, and partial synonymy, which applies when words share meanings only in specific usages. Homonymy occurs when a single word form has multiple unrelated meanings, divided into homographs, identical in spelling but different in meaning, and homophones, identical in pronunciation but different in meaning and spelling. Understanding these distinctions enhances semantic analysis and improves natural language processing applications.
Classification of Homonyms
Homonyms are classified into two main types: homographs, which share the same spelling but differ in meaning and sometimes pronunciation, and homophones, which share the same pronunciation but differ in meaning and spelling. A classic example of homographs is "lead" (to guide) and "lead" (a metal), whereas homophones include "flower" and "flour." This classification facilitates clearer semantic analysis and distinguishes lexical ambiguity in language processing.
Importance of Synonymy in Language and Communication
Synonymy enhances language precision and richness by providing multiple words with similar meanings, allowing speakers and writers to choose terms that best fit context and nuance. This variety supports effective communication, aids in avoiding ambiguity, and improves text clarity and stylistic diversity. Understanding synonymy is crucial for language learning, translation, and natural language processing, where subtle differences between synonyms can impact interpretation and meaning.
Challenges Posed by Homonymy in Understanding
Homonymy presents significant challenges in language understanding due to words sharing identical forms but differing meanings, causing ambiguity in both spoken and written contexts. Distinguishing between homonyms requires careful analysis of syntactic and semantic cues within sentences, complicating natural language processing tasks such as machine translation and information retrieval. Unlike synonymy, which involves multiple words with similar meanings, homonymy demands specialized disambiguation techniques to accurately interpret intended senses and prevent miscommunication.
Synonymy and Homonymy in Semantics
Synonymy in semantics refers to the relationship between words that share the same or very similar meanings, such as "big" and "large," enhancing lexical variety and precision in language. Homonymy involves words that have identical forms but distinct meanings, like "bat" (the animal) and "bat" (used in sports), posing challenges for semantic interpretation and disambiguation. Understanding synonymy and homonymy is crucial for natural language processing, lexicography, and semantic analysis as they affect meaning clarity and contextual usage.
Conclusion: The Role of Synonymy and Homonymy in Language
Synonymy enriches language by providing multiple words with similar meanings, enhancing expressiveness and nuance in communication. Homonymy, involving words that share form but differ in meaning, adds complexity and potential ambiguity, challenging contextual interpretation. Together, synonymy and homonymy play crucial roles in linguistic diversity, shaping semantics and influencing how meaning is constructed and understood.
Synonymy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com