Formal norms establish clear expectations for behavior in professional and social settings, promoting consistency and respect among participants. These guidelines help maintain order and ensure interactions proceed smoothly, safeguarding both individual rights and community standards. Delve into the rest of the article to explore how formal norms shape your daily interactions and organizational culture.
Table of Comparison
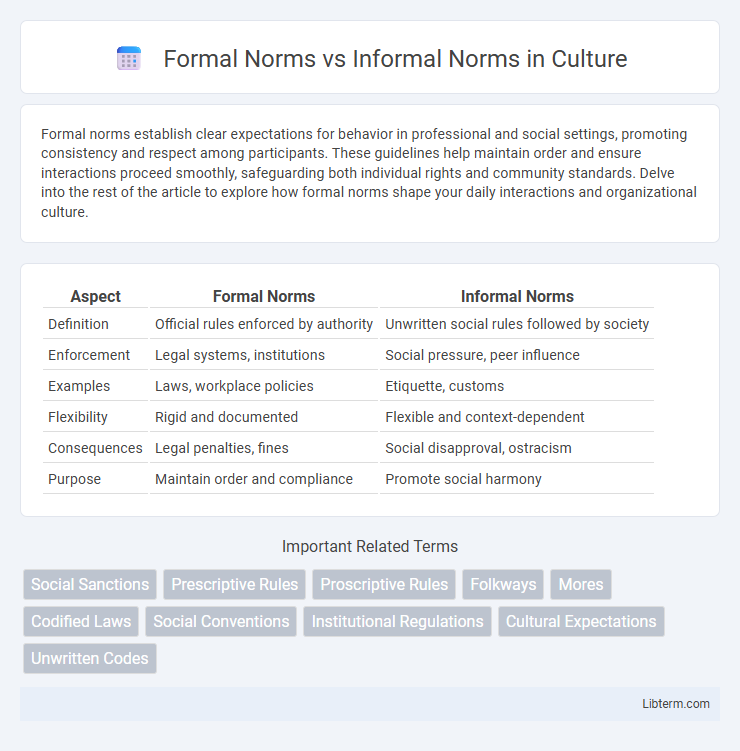
| Aspect | Formal Norms | Informal Norms |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official rules enforced by authority | Unwritten social rules followed by society |
| Enforcement | Legal systems, institutions | Social pressure, peer influence |
| Examples | Laws, workplace policies | Etiquette, customs |
| Flexibility | Rigid and documented | Flexible and context-dependent |
| Consequences | Legal penalties, fines | Social disapproval, ostracism |
| Purpose | Maintain order and compliance | Promote social harmony |
Understanding Formal and Informal Norms
Formal norms are explicit rules and laws established by institutions to regulate behavior, ensuring social order and consistency. Informal norms consist of unwritten social expectations and customs guiding everyday interactions, often reinforced through social approval or disapproval. Understanding the distinction between formal norms and informal norms is crucial for navigating societal expectations and fostering cohesive communities.
Defining Formal Norms
Formal norms are explicit, written rules established by institutions or authorities to regulate behavior within a society, such as laws, policies, and regulations. These norms carry specific sanctions or penalties for violations, ensuring compliance through legal or official enforcement mechanisms. Examples include traffic laws, workplace regulations, and academic codes of conduct, which provide clear guidelines and consequences to maintain order and predictability.
Characteristics of Formal Norms
Formal norms are explicitly written rules established by institutions, carrying clear sanctions for violations to ensure compliance. They regulate behavior through laws, regulations, and official policies, providing a structured framework for social order. These norms are typically enforced by authorized bodies, making them predictable and consistent across a society or organization.
Defining Informal Norms
Informal norms are unwritten social rules and shared expectations that govern behavior within a group without formal enforcement mechanisms. These norms influence everyday interactions by shaping values, customs, and traditions that are learned through socialization rather than official codes. Unlike formal norms, informal norms rely on social approval or disapproval to maintain order and cohesion within communities.
Key Features of Informal Norms
Informal norms are unwritten rules and social expectations that guide behavior in everyday interactions without official enforcement. These norms rely on social approval or disapproval, such as praise or gossip, to encourage conformity. They are flexible, evolving with cultural changes and vary widely across different social groups and communities.
Differences Between Formal and Informal Norms
Formal norms are established rules and laws officially codified and enforced by institutions, such as legal systems and organizations, ensuring predictable behavior through explicit sanctions. Informal norms consist of unwritten social expectations and customs that guide everyday interactions, maintained by social approval or disapproval rather than formal penalties. The primary differences lie in their codification, enforcement mechanisms, and the contexts in which they operate, with formal norms being explicit and institutionalized, whereas informal norms are implicit and culturally embedded.
The Role of Formal Norms in Society
Formal norms establish codified laws, regulations, and institutional rules that maintain social order and ensure predictable interactions within society. These norms are enforced by official authorities such as governments and judicial systems, providing clear consequences for violations and promoting stability. By defining acceptable behavior in legal and organizational contexts, formal norms support the functioning of complex societies and protect individual rights.
The Influence of Informal Norms on Behavior
Informal norms significantly shape individual and group behavior by establishing unwritten rules that guide daily interactions and social expectations. Unlike formal norms, which are codified and enforced by laws or regulations, informal norms rely on social approval, peer pressure, and cultural traditions to influence conformity and discourage deviance. Understanding the role of informal norms is essential for analyzing social dynamics, as they often dictate behavior more effectively than formal rules in environments such as workplaces, communities, and online platforms.
Examples of Formal and Informal Norms
Formal norms include laws, workplace policies, and school regulations that are officially documented and enforced by authorities. Informal norms encompass social customs such as dress codes, greetings, and table manners, which are understood and followed without written rules. For example, abiding by traffic laws represents formal norms, while shaking hands when meeting someone illustrates informal norms.
The Impact of Norms on Social Order
Formal norms, codified in laws and regulations, establish clear guidelines that maintain social order by ensuring predictable and consistent behavior through official enforcement mechanisms. Informal norms, rooted in cultural practices and social expectations, regulate behavior through social approval or disapproval, fostering community cohesion and informal social control. The interplay of formal and informal norms supports societal stability by balancing legal authority with community-based moral standards.
Formal Norms Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com