Individualism emphasizes personal freedom and self-reliance, encouraging people to prioritize their own goals and values over collective norms. This philosophy fosters creativity and innovation by valuing unique perspectives and personal responsibility. Explore the rest of the article to understand how individualism influences society and your everyday decisions.
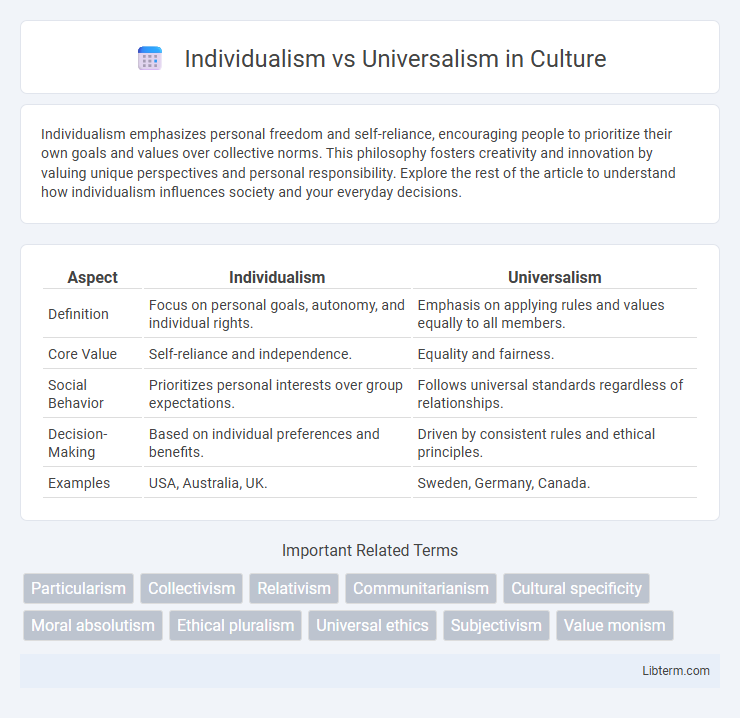
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Individualism | Universalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focus on personal goals, autonomy, and individual rights. | Emphasis on applying rules and values equally to all members. |
| Core Value | Self-reliance and independence. | Equality and fairness. |
| Social Behavior | Prioritizes personal interests over group expectations. | Follows universal standards regardless of relationships. |
| Decision-Making | Based on individual preferences and benefits. | Driven by consistent rules and ethical principles. |
| Examples | USA, Australia, UK. | Sweden, Germany, Canada. |
Understanding Individualism and Universalism
Individualism emphasizes personal freedom, self-reliance, and individual rights, promoting unique identity and autonomy within societies. Universalism focuses on applying consistent principles and values equally to all individuals, advocating fairness and collective responsibility regardless of personal differences. Understanding the distinction helps navigate cultural norms, ethical decision-making, and global interactions by balancing personal goals with shared human values.
Historical Roots of Individualism
The historical roots of individualism trace back to the Renaissance and Enlightenment periods, where humanism and reason emphasized personal autonomy and self-expression. Philosophers like John Locke and Jean-Jacques Rousseau advocated for individual rights, liberty, and the social contract, shaping modern Western political thought. This foundation contrasts with universalism's emphasis on collective moral principles derived from shared human values.
The Evolution of Universalism
Universalism has evolved from rigid, one-size-fits-all moral frameworks to more inclusive, context-sensitive approaches that recognize diverse cultural values while upholding core ethical principles. This evolution reflects increased globalization and intercultural interaction, leading to a balance between respecting individual cultural identities and promoting universal human rights. Contemporary universalism emphasizes adaptive norms that address global challenges such as human dignity, equality, and environmental sustainability.
Key Differences Between Individualism and Universalism
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy and self-expression, prioritizing individual rights and responsibilities within society. Universalism advocates for applying consistent moral principles and norms to all people regardless of their background or situation, promoting equality and fairness. Key differences include individualism's focus on personal goals versus universalism's emphasis on collective standards and impartiality.
Cultural Perspectives on Individualism vs Universalism
Cultural perspectives on individualism versus universalism shape social behavior and ethical decision-making across societies. Individualistic cultures prioritize personal goals and autonomy, emphasizing self-expression and individual rights, while universalistic cultures uphold shared values and norms, promoting equality and group harmony. Understanding these contrasting cultural frameworks is essential for effective cross-cultural communication and fostering global cooperation.
Impact on Personal Identity and Society
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy and self-expression, fostering unique identities and diverse societal roles. Universalism promotes shared values and collective norms, encouraging social cohesion and common ethical standards. The tension between these cultural dimensions shapes how individuals relate to society and define their sense of belonging.
Individual Rights vs Collective Good
Individualism emphasizes the primacy of individual rights, autonomy, and personal freedom as fundamental to human dignity and societal progress. Universalism advocates for the collective good, promoting shared values and societal welfare that transcend individual interests to ensure social cohesion and equity. Balancing individual rights with the collective good remains a central challenge in ethical, legal, and political frameworks worldwide.
Challenges in Balancing Individualism and Universalism
Balancing individualism and universalism presents challenges such as reconciling personal freedoms with collective responsibilities, often leading to conflicts between self-expression and social cohesion. Diverse cultural contexts emphasize varying degrees of individual rights versus universal ethical principles, complicating policymaking and social integration. Navigating this balance requires frameworks that respect individual autonomy while promoting inclusive values that transcend cultural differences.
Case Studies Illustrating the Dichotomy
Case studies exemplifying the dichotomy between individualism and universalism highlight cultural differences in decision-making and social behavior across societies. In individualistic cultures like the United States, case studies showcase a preference for personal autonomy and self-expression, while universalistic societies such as Sweden emphasize consistent rules and equal treatment for all individuals. This contrast is evident in organizational management and legal systems, where individualistic approaches prioritize personal rights and achievements, whereas universalistic frameworks stress fairness and collective responsibility.
Future Trends: Toward Harmony or Conflict?
Future trends in the debate between Individualism and Universalism suggest a complex interplay shaped by globalization, technological advances, and cultural integration. Increasing digital connectivity promotes universal values like human rights, yet rising nationalism and identity politics emphasize individualistic self-expression and cultural uniqueness. Balancing these forces requires adaptive frameworks that foster mutual respect and cooperation while acknowledging diverse individual identities.
Individualism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com