Taboos play a crucial role in shaping social norms and behaviors, influencing what is considered acceptable or forbidden within different cultures. Understanding these cultural restrictions can help you navigate social interactions more respectfully and avoid misunderstandings. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how taboos impact society and daily life.
Table of Comparison
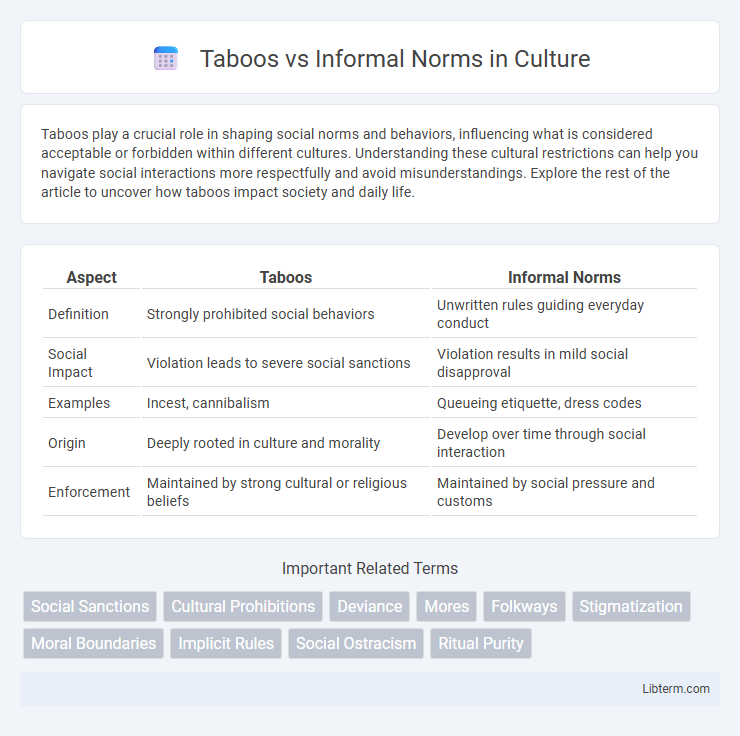
| Aspect | Taboos | Informal Norms |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strongly prohibited social behaviors | Unwritten rules guiding everyday conduct |
| Social Impact | Violation leads to severe social sanctions | Violation results in mild social disapproval |
| Examples | Incest, cannibalism | Queueing etiquette, dress codes |
| Origin | Deeply rooted in culture and morality | Develop over time through social interaction |
| Enforcement | Maintained by strong cultural or religious beliefs | Maintained by social pressure and customs |
Understanding Taboos and Informal Norms
Taboos are prohibitions against behaviors considered extremely offensive or unacceptable within a society, often rooted in moral or cultural beliefs, leading to strong social sanctions if violated. Informal norms guide everyday social behavior through unwritten rules and expectations, promoting social cohesion without formal enforcement. Understanding taboos requires recognizing their deep cultural significance and potential psychological impact, while informal norms help maintain fluid social interactions by shaping routine conduct.
Key Differences Between Taboos and Informal Norms
Taboos are strong social prohibitions against behaviors deemed morally or culturally unacceptable, often invoking severe sanctions or ostracism, while informal norms are unwritten rules guiding everyday social interactions with milder consequences for violations. Taboos are universally or culturally fixed and deeply ingrained, whereas informal norms are flexible, context-dependent, and subject to change over time. The key difference lies in the intensity of societal reaction and the nature of enforcement, with taboos carrying greater moral weight and informal norms relying on social approval for compliance.
Cultural Roots of Taboos
Taboos stem from deep cultural roots reflecting society's collective values, prohibiting actions seen as morally or spiritually offensive, such as incest or cannibalism. Informal norms guide everyday social behavior through unwritten rules that vary by culture but lack the severe sanctions associated with taboos. Understanding the cultural origins of taboos reveals their role in maintaining social cohesion by enforcing boundaries tied to identity, religion, and historical experience.
How Informal Norms Shape Social Behavior
Informal norms, unwritten rules governing everyday behavior, shape social behavior by establishing expectations for appropriate conduct within different communities. These norms influence interactions by promoting conformity through social approval or disapproval, thereby reinforcing group cohesion and shared values. Unlike taboos, which prohibit specific actions under threat of strong sanctions, informal norms guide routine social practices and help maintain order in social relationships.
Examples of Taboos Across Cultures
Taboos vary widely across cultures, with some examples including the prohibition of eating beef in Hindu communities, the avoidance of pork in Islamic and kosher dietary laws, and the strict social rules against incest or cannibalism globally. In contrast to informal norms, which govern everyday behaviors like dress codes or greetings, taboos carry severe social sanctions and moral condemnation, deeply embedded in religious or cultural traditions. These forbidden behaviors highlight the boundaries of acceptable conduct that maintain social cohesion and cultural identity.
Everyday Informal Norms in Society
Everyday informal norms in society guide routine social interactions, shaping behaviors such as greetings, dress codes, and etiquette without formal enforcement. These norms vary across cultures and communities, influencing social cohesion by promoting mutual understanding and predictability. Unlike taboos, which invoke strong moral prohibitions and sanctions, informal norms rely on social approval and subtle peer pressure to maintain order.
Consequences of Breaking Taboos
Breaking taboos often results in severe social sanctions such as ostracism, legal penalties, or moral condemnation, reflecting the deep-rooted cultural and psychological impact of these prohibitions. Whereas informal norms may invite mild disapproval or social correction, violating taboos can threaten an individual's identity and societal cohesion, leading to stigmatization or exclusion. The consequences serve to reinforce societal boundaries and protect core values that are deemed essential for cultural survival.
Social Reactions to Violating Informal Norms
Violating informal norms often results in mild social sanctions such as disapproval, gossip, or subtle exclusion, contrasting with the severe consequences linked to breaking taboos, which may provoke shame, ostracism, or legal penalties. Informal norms govern everyday behaviors like dress codes or punctuality, and social reactions serve to reinforce conformity through peer pressure rather than formal enforcement. Understanding these distinctions highlights how social cohesion relies on informal mechanisms to regulate behavior without delegating authority to institutions.
Changing Taboos and Evolving Norms
Changing taboos reflect society's shifting values, as behaviors once forbidden may become accepted over time due to cultural, technological, or generational influences. Evolving informal norms adapt gradually, shaped by collective experiences and social interactions, influencing everyday conduct without formal enforcement. Understanding these dynamics reveals how social boundaries expand or contract, impacting community cohesion and individual behavior.
The Importance of Taboos and Informal Norms in Social Order
Taboos and informal norms play a crucial role in maintaining social order by regulating behavior and establishing clear boundaries within communities. Taboos, rooted in deep cultural or moral beliefs, prohibit actions that could cause significant harm or offense, ensuring group cohesion and moral integrity. Informal norms guide everyday interactions and social expectations, promoting harmony and predictability without the need for formal legal enforcement.
Taboos Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com