Cultural competence enhances your ability to effectively interact with diverse populations by understanding and respecting different cultural perspectives. Developing this skill improves communication, reduces misunderstandings, and fosters inclusive environments in both personal and professional settings. Explore the rest of this article to learn practical strategies for building your cultural competence.
Table of Comparison
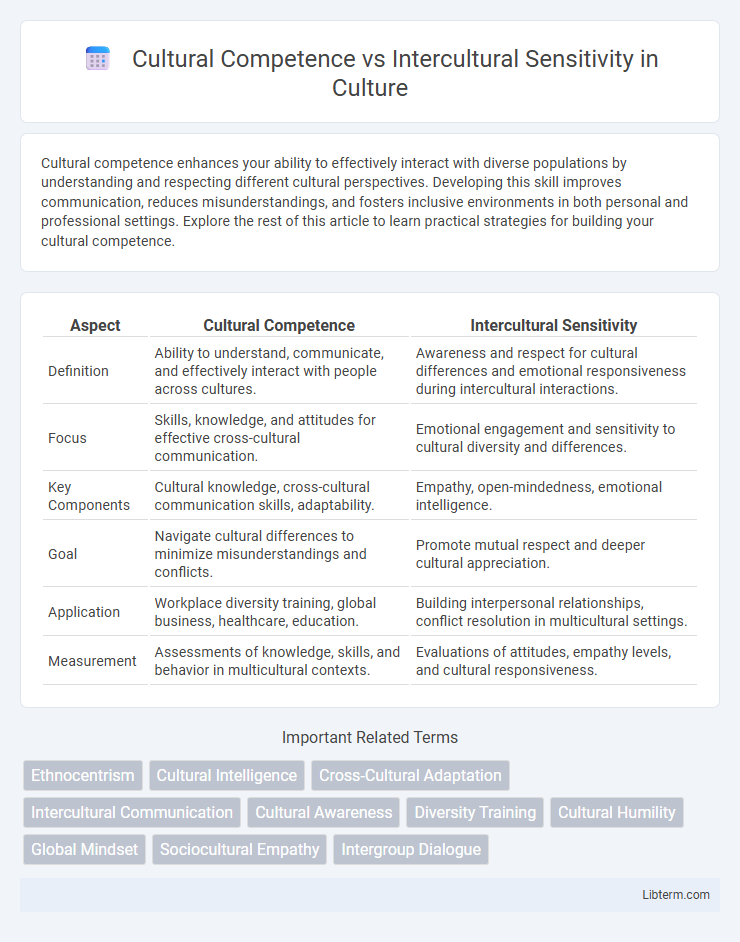
| Aspect | Cultural Competence | Intercultural Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to understand, communicate, and effectively interact with people across cultures. | Awareness and respect for cultural differences and emotional responsiveness during intercultural interactions. |
| Focus | Skills, knowledge, and attitudes for effective cross-cultural communication. | Emotional engagement and sensitivity to cultural diversity and differences. |
| Key Components | Cultural knowledge, cross-cultural communication skills, adaptability. | Empathy, open-mindedness, emotional intelligence. |
| Goal | Navigate cultural differences to minimize misunderstandings and conflicts. | Promote mutual respect and deeper cultural appreciation. |
| Application | Workplace diversity training, global business, healthcare, education. | Building interpersonal relationships, conflict resolution in multicultural settings. |
| Measurement | Assessments of knowledge, skills, and behavior in multicultural contexts. | Evaluations of attitudes, empathy levels, and cultural responsiveness. |
Understanding Cultural Competence: Definition and Scope
Cultural competence encompasses the ability to effectively interact, communicate, and work within diverse cultural contexts by integrating knowledge, attitudes, and skills. It involves awareness of cultural differences, respect for diversity, and the capacity to adapt behaviors to meet the needs of various cultural groups. The scope of cultural competence extends across personal, organizational, and societal levels, promoting inclusivity and minimizing cultural misunderstandings.
Defining Intercultural Sensitivity: Key Concepts
Intercultural sensitivity refers to an individual's ability to recognize, respect, and adapt to cultural differences in communication and behavior, promoting effective and respectful interactions across diverse cultural contexts. It involves emotional responsiveness and self-awareness that facilitate understanding and empathy towards cultural diversity. Key concepts include openness, tolerance for ambiguity, empathy, and the willingness to learn from cultural encounters, distinguishing it from broader cultural competence which encompasses skills, knowledge, and attitudes necessary for effective intercultural communication.
Core Differences Between Cultural Competence and Intercultural Sensitivity
Cultural competence refers to the ability to effectively interact with people from diverse cultural backgrounds by acquiring knowledge, skills, and attitudes that enable appropriate communication and behavior. Intercultural sensitivity emphasizes an individual's awareness and appreciation of cultural differences, fostering empathy and openness without necessarily requiring mastery of cultural norms. The core difference lies in cultural competence's action-oriented skillset for practical engagement versus intercultural sensitivity's attitudinal focus on recognizing and valuing cultural diversity.
Why Cultural Competence Matters in a Globalized World
Cultural competence entails acquiring specific knowledge, skills, and behaviors to effectively interact with diverse cultures, while intercultural sensitivity emphasizes emotional awareness and respect for cultural differences. In a globalized world, cultural competence matters because it enables individuals and organizations to navigate complex multicultural environments, fostering effective communication, collaboration, and conflict resolution. This competence directly impacts global business success, international relations, and social integration by promoting mutual understanding and reducing cultural misunderstandings.
The Importance of Intercultural Sensitivity in Cross-Cultural Interactions
Intercultural sensitivity enables individuals to recognize, respect, and adapt to cultural differences, fostering effective communication in diverse environments. Unlike cultural competence, which emphasizes knowledge and skills, intercultural sensitivity highlights emotional awareness and empathy crucial for meaningful cross-cultural interactions. Developing intercultural sensitivity reduces misunderstandings and enhances collaboration in globalized settings.
Building Blocks: Skills Required for Cultural Competence
Cultural competence involves developing specific skills such as effective communication, empathy, and adaptability to navigate diverse cultural contexts successfully. These skills enable individuals to understand cultural differences, reduce biases, and foster inclusive interactions. Building intercultural sensitivity requires continuous self-awareness and the ability to interpret cultural cues accurately, promoting deeper respect and collaboration across cultures.
Developing Intercultural Sensitivity: Essential Behaviors and Attitudes
Developing intercultural sensitivity requires embracing empathy, openness, and respect toward diverse cultural perspectives while actively seeking to understand and appreciate cultural differences. Essential behaviors include effective listening, open-minded communication, and adaptability in cross-cultural interactions, fostering trust and collaboration. Cultivating attitudes of humility and curiosity enhances the ability to navigate cultural complexities, promote inclusivity, and reduce ethnocentric bias.
Practical Strategies to Enhance Cultural Competence
Enhancing cultural competence requires active engagement in cross-cultural communication, including practicing empathy and open-mindedness to understand diverse perspectives effectively. Implementing tailored training programs emphasizing real-life scenarios and role-playing can build practical skills in adapting behaviors and attitudes for various cultural contexts. Continuous self-assessment and feedback mechanisms foster awareness of implicit biases, promoting ongoing growth in cultural competence within global or multicultural environments.
Methods for Fostering Intercultural Sensitivity in Individuals and Organizations
Effective methods for fostering intercultural sensitivity in individuals and organizations include immersive cultural training programs that emphasize experiential learning and self-reflection. Utilizing role-playing exercises and open dialogue sessions enhances empathy and reduces ethnocentric attitudes, promoting deeper cultural understanding. Incorporating continuous feedback mechanisms and cross-cultural mentoring supports sustainable development of intercultural skills and adaptive communication strategies.
Integrating Cultural Competence and Intercultural Sensitivity for Effective Communication
Integrating cultural competence and intercultural sensitivity enhances effective communication by fostering awareness, respect, and adaptability to diverse cultural norms. Cultural competence provides the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate cultural differences, while intercultural sensitivity emphasizes emotional engagement and openness to others' perspectives. Combining these elements enables individuals to build trust, reduce misunderstandings, and communicate more effectively in multicultural environments.
Cultural Competence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com