Explicit culture encompasses the tangible, visible aspects of a society, such as language, dress, cuisine, rituals, and art, which are easily observed and communicated. Understanding explicit culture helps You navigate social interactions and appreciate cultural diversity in everyday life. Explore the rest of this article to delve deeper into the components and significance of explicit culture.
Table of Comparison
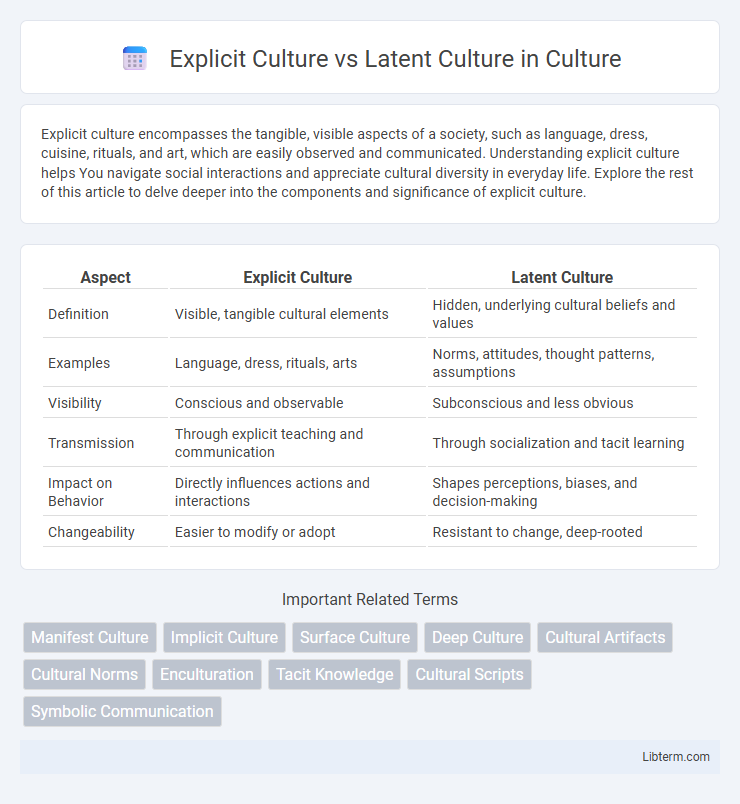
| Aspect | Explicit Culture | Latent Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Visible, tangible cultural elements | Hidden, underlying cultural beliefs and values |
| Examples | Language, dress, rituals, arts | Norms, attitudes, thought patterns, assumptions |
| Visibility | Conscious and observable | Subconscious and less obvious |
| Transmission | Through explicit teaching and communication | Through socialization and tacit learning |
| Impact on Behavior | Directly influences actions and interactions | Shapes perceptions, biases, and decision-making |
| Changeability | Easier to modify or adopt | Resistant to change, deep-rooted |
Understanding Explicit Culture: Key Definitions
Explicit culture encompasses the tangible, visible elements of a society such as language, dress, customs, and rituals that are easily observed and articulated. Understanding explicit culture involves recognizing these concrete manifestations as expressions of deeper societal values and norms. This clear external behavior provides a foundation for interpreting more complex cultural dynamics embedded within latent culture.
What is Latent Culture? Core Concepts
Latent culture refers to the underlying, often unconscious values, beliefs, and norms that shape social behavior within a group, contrasting with explicit culture, which includes visible symbols, rituals, and language. Core concepts of latent culture encompass deep-seated attitudes, implicit expectations, and ingrained emotional responses that influence how individuals interpret their environment and interact with others. Understanding latent culture is essential for effective cross-cultural communication, as it reveals the hidden drivers behind observable cultural expressions.
Explicit vs Latent Culture: Main Differences
Explicit culture consists of visible and tangible elements such as language, dress, rituals, and customs that are easily observed and shared among members of a group. Latent culture involves underlying values, beliefs, and thought patterns that are subconscious and influence behavior without being directly visible. The main difference lies in explicit culture's external expression versus latent culture's internal, often unspoken, processes shaping social norms.
Origins and Development of Cultural Norms
Explicit culture, comprising observable behaviors, rituals, and symbols, originates from conscious social agreements and formalized traditions that are taught and reinforced through institutions like education and religion. Latent culture, consisting of underlying values, beliefs, and assumptions, develops unconsciously over generations through shared experiences and socialization, shaping implicit expectations and worldviews. The interplay between explicit and latent culture drives the evolution of cultural norms, with explicit expressions often reflecting the deeper, latent structures within a society.
Examples of Explicit Culture in Daily Life
Explicit culture is evident in tangible and observable elements such as language, dress codes, food customs, and holiday celebrations. Examples include wearing traditional attire during festivals, using specific greeting phrases like "hello" or "good morning," and following dietary practices tied to cultural identity, such as eating sushi in Japan or having Thanksgiving dinner in the United States. These visible practices serve as clear markers of cultural identity, easily recognized and shared within and across communities.
Illustrations of Latent Culture in Society
Latent culture encompasses the unconscious, underlying values, beliefs, and norms that shape behavior and social interactions without overt expression. Examples in society include unspoken social hierarchies, implicit gender roles, and ingrained attitudes toward authority that influence decision-making and relationship dynamics. These subtle cultural dimensions often manifest through nonverbal communication, rituals, and informal social expectations that maintain societal cohesion and continuity.
Importance of Recognizing Latent Cultural Factors
Recognizing latent cultural factors is crucial for accurately interpreting behaviors and decisions that are not immediately observable in explicit culture, such as rituals, values, and assumptions deeply embedded in social practices. Latent culture shapes perceptions and motivations, influencing communication styles and conflict resolution methods within organizations and societies. Ignoring these underlying cultural elements can lead to misunderstandings and ineffective strategies in cross-cultural interactions and global business environments.
Impact of Explicit and Latent Culture in Organizations
Explicit culture in organizations, comprising visible elements like dress codes, rituals, and formal policies, directly shapes employee behavior and sets clear expectations, enhancing operational efficiency and alignment. Latent culture, which includes underlying beliefs, values, and assumptions, deeply influences decision-making processes, innovation, and adaptability by guiding subconscious behaviors and attitudes. The interplay of explicit and latent culture determines organizational climate, employee engagement, and overall performance, making both critical for sustainable competitive advantage.
Navigating Cultural Barriers: Practical Strategies
Navigating explicit culture, which includes visible behaviors and customs, requires direct communication and clear guidelines to avoid misunderstandings. Latent culture involves underlying values and beliefs, necessitating deeper cultural awareness and empathy to interpret unspoken norms effectively. Practical strategies include active listening, cultural competence training, and fostering open dialogue to bridge gaps between explicit and latent cultural expressions.
Fostering Cultural Awareness for Global Success
Explicit culture includes visible elements such as language, dress, customs, and rituals that are easily observed and taught, while latent culture involves underlying values, beliefs, and thought patterns that influence behavior unconsciously. Fostering cultural awareness requires understanding both explicit and latent cultural dimensions to navigate global interactions effectively and avoid miscommunication. Incorporating cultural training that emphasizes empathy and deep cultural insights enhances global business success and cross-cultural collaboration.
Explicit Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com